Jungang Xu
VDE Bench: Evaluating The Capability of Image Editing Models to Modify Visual Documents
Jan 27, 2026Abstract:In recent years, multimodal image editing models have achieved substantial progress, enabling users to manipulate visual content through natural language in a flexible and interactive manner. Nevertheless, an important yet insufficiently explored research direction remains visual document image editing, which involves modifying textual content within images while faithfully preserving the original text style and background context. Existing approaches, including AnyText, GlyphControl, and TextCtrl, predominantly focus on English-language scenarios and documents with relatively sparse textual layouts, thereby failing to adequately address dense, structurally complex documents or non-Latin scripts such as Chinese. To bridge this gap, we propose \textbf{V}isual \textbf{D}oc \textbf{E}dit Bench(VDE Bench), a rigorously human-annotated and evaluated benchmark specifically designed to assess image editing models on multilingual and complex visual document editing tasks. The benchmark comprises a high-quality dataset encompassing densely textual documents in both English and Chinese, including academic papers, posters, presentation slides, examination materials, and newspapers. Furthermore, we introduce a decoupled evaluation framework that systematically quantifies editing performance at the OCR parsing level, enabling fine-grained assessment of text modification accuracy. Based on this benchmark, we conduct a comprehensive evaluation of representative state-of-the-art image editing models. Manual verification demonstrates a strong consistency between human judgments and automated evaluation metrics. VDE Bench constitutes the first systematic benchmark for evaluating image editing models on multilingual and densely textual visual documents.
RPO:Reinforcement Fine-Tuning with Partial Reasoning Optimization
Jan 27, 2026Abstract:Within the domain of large language models, reinforcement fine-tuning algorithms necessitate the generation of a complete reasoning trajectory beginning from the input query, which incurs significant computational overhead during the rollout phase of training. To address this issue, we analyze the impact of different segments of the reasoning path on the correctness of the final result and, based on these insights, propose Reinforcement Fine-Tuning with Partial Reasoning Optimization (RPO), a plug-and-play reinforcement fine-tuning algorithm. Unlike traditional reinforcement fine-tuning algorithms that generate full reasoning paths, RPO trains the model by generating suffixes of the reasoning path using experience cache. During the rollout phase of training, RPO reduces token generation in this phase by approximately 95%, greatly lowering the theoretical time overhead. Compared with full-path reinforcement fine-tuning algorithms, RPO reduces the training time of the 1.5B model by 90% and the 7B model by 72%. At the same time, it can be integrated with typical algorithms such as GRPO and DAPO, enabling them to achieve training acceleration while maintaining performance comparable to the original algorithms. Our code is open-sourced at https://github.com/yhz5613813/RPO.
Dynamic Deep Graph Learning for Incomplete Multi-View Clustering with Masked Graph Reconstruction Loss
Nov 14, 2025Abstract:The prevalence of real-world multi-view data makes incomplete multi-view clustering (IMVC) a crucial research. The rapid development of Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) has established them as one of the mainstream approaches for multi-view clustering. Despite significant progress in GNNs-based IMVC, some challenges remain: (1) Most methods rely on the K-Nearest Neighbors (KNN) algorithm to construct static graphs from raw data, which introduces noise and diminishes the robustness of the graph topology. (2) Existing methods typically utilize the Mean Squared Error (MSE) loss between the reconstructed graph and the sparse adjacency graph directly as the graph reconstruction loss, leading to substantial gradient noise during optimization. To address these issues, we propose a novel \textbf{D}ynamic Deep \textbf{G}raph Learning for \textbf{I}ncomplete \textbf{M}ulti-\textbf{V}iew \textbf{C}lustering with \textbf{M}asked Graph Reconstruction Loss (DGIMVCM). Firstly, we construct a missing-robust global graph from the raw data. A graph convolutional embedding layer is then designed to extract primary features and refined dynamic view-specific graph structures, leveraging the global graph for imputation of missing views. This process is complemented by graph structure contrastive learning, which identifies consistency among view-specific graph structures. Secondly, a graph self-attention encoder is introduced to extract high-level representations based on the imputed primary features and view-specific graphs, and is optimized with a masked graph reconstruction loss to mitigate gradient noise during optimization. Finally, a clustering module is constructed and optimized through a pseudo-label self-supervised training mechanism. Extensive experiments on multiple datasets validate the effectiveness and superiority of DGIMVCM.
JTCSE: Joint Tensor-Modulus Constraints and Cross-Attention for Unsupervised Contrastive Learning of Sentence Embeddings
May 05, 2025Abstract:Unsupervised contrastive learning has become a hot research topic in natural language processing. Existing works usually aim at constraining the orientation distribution of the representations of positive and negative samples in the high-dimensional semantic space in contrastive learning, but the semantic representation tensor possesses both modulus and orientation features, and the existing works ignore the modulus feature of the representations and cause insufficient contrastive learning. % Therefore, we firstly propose a training objective that aims at modulus constraints on the semantic representation tensor, to strengthen the alignment between the positive samples in contrastive learning. Therefore, we first propose a training objective that is designed to impose modulus constraints on the semantic representation tensor, to strengthen the alignment between positive samples in contrastive learning. Then, the BERT-like model suffers from the phenomenon of sinking attention, leading to a lack of attention to CLS tokens that aggregate semantic information. In response, we propose a cross-attention structure among the twin-tower ensemble models to enhance the model's attention to CLS token and optimize the quality of CLS Pooling. Combining the above two motivations, we propose a new \textbf{J}oint \textbf{T}ensor representation modulus constraint and \textbf{C}ross-attention unsupervised contrastive learning \textbf{S}entence \textbf{E}mbedding representation framework JTCSE, which we evaluate in seven semantic text similarity computation tasks, and the experimental results show that JTCSE's twin-tower ensemble model and single-tower distillation model outperform the other baselines and become the current SOTA. In addition, we have conducted an extensive zero-shot downstream task evaluation, which shows that JTCSE outperforms other baselines overall on more than 130 tasks.
TNCSE: Tensor's Norm Constraints for Unsupervised Contrastive Learning of Sentence Embeddings
Mar 17, 2025



Abstract:Unsupervised sentence embedding representation has become a hot research topic in natural language processing. As a tensor, sentence embedding has two critical properties: direction and norm. Existing works have been limited to constraining only the orientation of the samples' representations while ignoring the features of their module lengths. To address this issue, we propose a new training objective that optimizes the training of unsupervised contrastive learning by constraining the module length features between positive samples. We combine the training objective of Tensor's Norm Constraints with ensemble learning to propose a new Sentence Embedding representation framework, TNCSE. We evaluate seven semantic text similarity tasks, and the results show that TNCSE and derived models are the current state-of-the-art approach; in addition, we conduct extensive zero-shot evaluations, and the results show that TNCSE outperforms other baselines.
Text Data-Centric Image Captioning with Interactive Prompts
Mar 28, 2024



Abstract:Supervised image captioning approaches have made great progress, but it is challenging to collect high-quality human-annotated image-text data. Recently, large-scale vision and language models (e.g., CLIP) and large-scale generative language models (e.g., GPT-2) have shown strong performances in various tasks, which also provide some new solutions for image captioning with web paired data, unpaired data or even text-only data. Among them, the mainstream solution is to project image embeddings into the text embedding space with the assistance of consistent representations between image-text pairs from the CLIP model. However, the current methods still face several challenges in adapting to the diversity of data configurations in a unified solution, accurately estimating image-text embedding bias, and correcting unsatisfactory prediction results in the inference stage. This paper proposes a new Text data-centric approach with Interactive Prompts for image Captioning, named TIPCap. 1) We consider four different settings which gradually reduce the dependence on paired data. 2) We construct a mapping module driven by multivariate Gaussian distribution to mitigate the modality gap, which is applicable to the above four different settings. 3) We propose a prompt interaction module that can incorporate optional prompt information before generating captions. Extensive experiments show that our TIPCap outperforms other weakly or unsupervised image captioning methods and achieves a new state-of-the-art performance on two widely used datasets, i.e., MS-COCO and Flickr30K.
End-to-End Transformer Based Model for Image Captioning
Mar 29, 2022



Abstract:CNN-LSTM based architectures have played an important role in image captioning, but limited by the training efficiency and expression ability, researchers began to explore the CNN-Transformer based models and achieved great success. Meanwhile, almost all recent works adopt Faster R-CNN as the backbone encoder to extract region-level features from given images. However, Faster R-CNN needs a pre-training on an additional dataset, which divides the image captioning task into two stages and limits its potential applications. In this paper, we build a pure Transformer-based model, which integrates image captioning into one stage and realizes end-to-end training. Firstly, we adopt SwinTransformer to replace Faster R-CNN as the backbone encoder to extract grid-level features from given images; Then, referring to Transformer, we build a refining encoder and a decoder. The refining encoder refines the grid features by capturing the intra-relationship between them, and the decoder decodes the refined features into captions word by word. Furthermore, in order to increase the interaction between multi-modal (vision and language) features to enhance the modeling capability, we calculate the mean pooling of grid features as the global feature, then introduce it into refining encoder to refine with grid features together, and add a pre-fusion process of refined global feature and generated words in decoder. To validate the effectiveness of our proposed model, we conduct experiments on MSCOCO dataset. The experimental results compared to existing published works demonstrate that our model achieves new state-of-the-art performances of 138.2% (single model) and 141.0% (ensemble of 4 models) CIDEr scores on `Karpathy' offline test split and 136.0% (c5) and 138.3% (c40) CIDEr scores on the official online test server. Trained models and source code will be released.
A Survey on Neural Network Language Models
Jun 13, 2019


Abstract:As the core component of Natural Language Processing (NLP) system, Language Model (LM) can provide word representation and probability indication of word sequences. Neural Network Language Models (NNLMs) overcome the curse of dimensionality and improve the performance of traditional LMs. A survey on NNLMs is performed in this paper. The structure of classic NNLMs is described firstly, and then some major improvements are introduced and analyzed. We summarize and compare corpora and toolkits of NNLMs. Further, some research directions of NNLMs are discussed.
A Survey on Neural Machine Reading Comprehension
Jun 10, 2019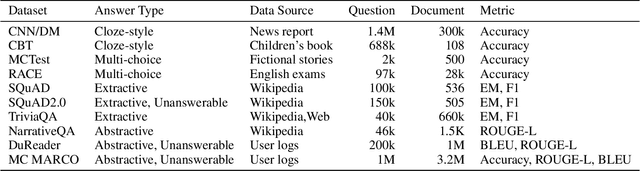
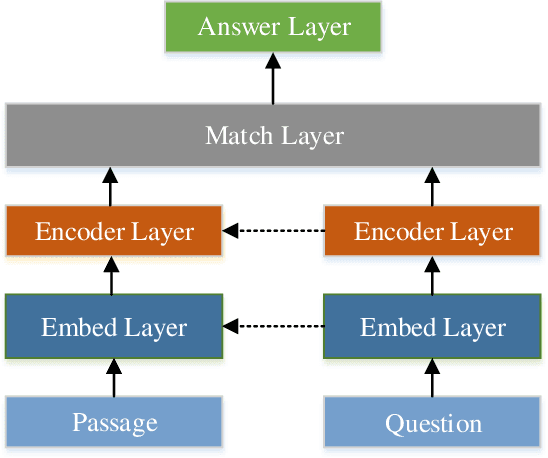
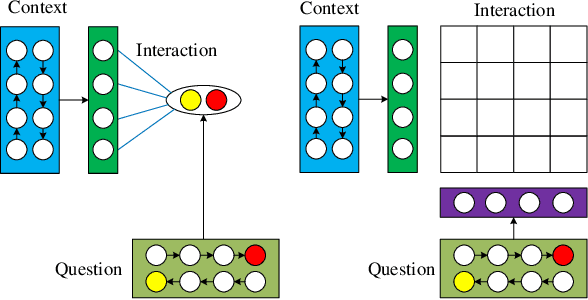
Abstract:Enabling a machine to read and comprehend the natural language documents so that it can answer some questions remains an elusive challenge. In recent years, the popularity of deep learning and the establishment of large-scale datasets have both promoted the prosperity of Machine Reading Comprehension. This paper aims to present how to utilize the Neural Network to build a Reader and introduce some classic models, analyze what improvements they make. Further, we also point out the defects of existing models and future research directions
Image Captioning based on Deep Learning Methods: A Survey
May 20, 2019



Abstract:Image captioning is a challenging task and attracting more and more attention in the field of Artificial Intelligence, and which can be applied to efficient image retrieval, intelligent blind guidance and human-computer interaction, etc. In this paper, we present a survey on advances in image captioning based on Deep Learning methods, including Encoder-Decoder structure, improved methods in Encoder, improved methods in Decoder, and other improvements. Furthermore, we discussed future research directions.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge