Julian McGinnis
Optimizing Rank for High-Fidelity Implicit Neural Representations
Dec 16, 2025Abstract:Implicit Neural Representations (INRs) based on vanilla Multi-Layer Perceptrons (MLPs) are widely believed to be incapable of representing high-frequency content. This has directed research efforts towards architectural interventions, such as coordinate embeddings or specialized activation functions, to represent high-frequency signals. In this paper, we challenge the notion that the low-frequency bias of vanilla MLPs is an intrinsic, architectural limitation to learn high-frequency content, but instead a symptom of stable rank degradation during training. We empirically demonstrate that regulating the network's rank during training substantially improves the fidelity of the learned signal, rendering even simple MLP architectures expressive. Extensive experiments show that using optimizers like Muon, with high-rank, near-orthogonal updates, consistently enhances INR architectures even beyond simple ReLU MLPs. These substantial improvements hold across a diverse range of domains, including natural and medical images, and novel view synthesis, with up to 9 dB PSNR improvements over the previous state-of-the-art. Our project page, which includes code and experimental results, is available at: (https://muon-inrs.github.io).
Rule-based Key-Point Extraction for MR-Guided Biomechanical Digital Twins of the Spine
Aug 20, 2025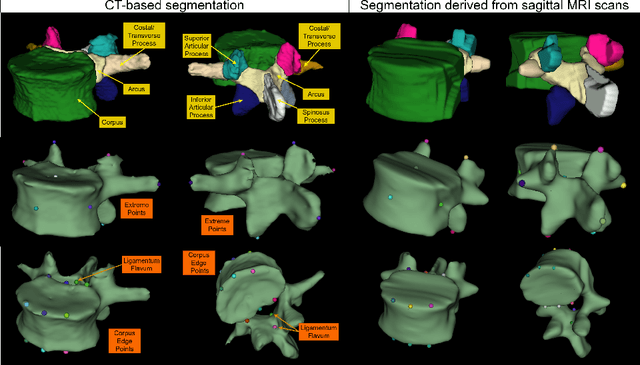

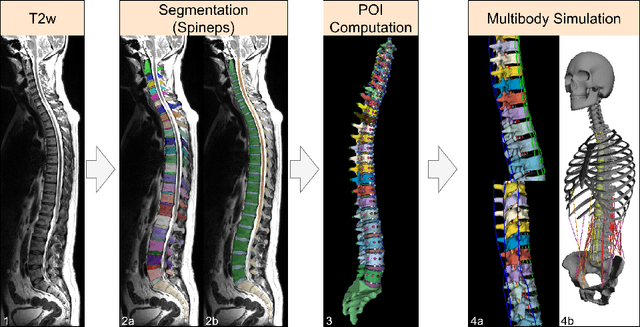

Abstract:Digital twins offer a powerful framework for subject-specific simulation and clinical decision support, yet their development often hinges on accurate, individualized anatomical modeling. In this work, we present a rule-based approach for subpixel-accurate key-point extraction from MRI, adapted from prior CT-based methods. Our approach incorporates robust image alignment and vertebra-specific orientation estimation to generate anatomically meaningful landmarks that serve as boundary conditions and force application points, like muscle and ligament insertions in biomechanical models. These models enable the simulation of spinal mechanics considering the subject's individual anatomy, and thus support the development of tailored approaches in clinical diagnostics and treatment planning. By leveraging MR imaging, our method is radiation-free and well-suited for large-scale studies and use in underrepresented populations. This work contributes to the digital twin ecosystem by bridging the gap between precise medical image analysis with biomechanical simulation, and aligns with key themes in personalized modeling for healthcare.
Image registration is a geometric deep learning task
Dec 17, 2024



Abstract:Data-driven deformable image registration methods predominantly rely on operations that process grid-like inputs. However, applying deformable transformations to an image results in a warped space that deviates from a rigid grid structure. Consequently, data-driven approaches with sequential deformations have to apply grid resampling operations between each deformation step. While artifacts caused by resampling are negligible in high-resolution images, the resampling of sparse, high-dimensional feature grids introduces errors that affect the deformation modeling process. Taking inspiration from Lagrangian reference frames of deformation fields, our work introduces a novel paradigm for data-driven deformable image registration that utilizes geometric deep-learning principles to model deformations without grid requirements. Specifically, we model image features as a set of nodes that freely move in Euclidean space, update their coordinates under graph operations, and dynamically readjust their local neighborhoods. We employ this formulation to construct a multi-resolution deformable registration model, where deformation layers iteratively refine the overall transformation at each resolution without intermediate resampling operations on the feature grids. We investigate our method's ability to fully deformably capture large deformations across a number of medical imaging registration tasks. In particular, we apply our approach (GeoReg) to the registration of inter-subject brain MR images and inhale-exhale lung CT images, showing on par performance with the current state-of-the-art methods. We believe our contribution open up avenues of research to reduce the black-box nature of current learned registration paradigms by explicitly modeling the transformation within the architecture.
NISF: Neural Implicit Segmentation Functions
Sep 15, 2023Abstract:Segmentation of anatomical shapes from medical images has taken an important role in the automation of clinical measurements. While typical deep-learning segmentation approaches are performed on discrete voxels, the underlying objects being analysed exist in a real-valued continuous space. Approaches that rely on convolutional neural networks (CNNs) are limited to grid-like inputs and not easily applicable to sparse or partial measurements. We propose a novel family of image segmentation models that tackle many of CNNs' shortcomings: Neural Implicit Segmentation Functions (NISF). Our framework takes inspiration from the field of neural implicit functions where a network learns a mapping from a real-valued coordinate-space to a shape representation. NISFs have the ability to segment anatomical shapes in high-dimensional continuous spaces. Training is not limited to voxelized grids, and covers applications with sparse and partial data. Interpolation between observations is learnt naturally in the training procedure and requires no post-processing. Furthermore, NISFs allow the leveraging of learnt shape priors to make predictions for regions outside of the original image plane. We go on to show the framework achieves dice scores of 0.87 $\pm$ 0.045 on a (3D+t) short-axis cardiac segmentation task using the UK Biobank dataset. We also provide a qualitative analysis on our frameworks ability to perform segmentation and image interpolation on unseen regions of an image volume at arbitrary resolutions.
Multi-contrast MRI Super-resolution via Implicit Neural Representations
Mar 27, 2023Abstract:Clinical routine and retrospective cohorts commonly include multi-parametric Magnetic Resonance Imaging; however, they are mostly acquired in different anisotropic 2D views due to signal-to-noise-ratio and scan-time constraints. Thus acquired views suffer from poor out-of-plane resolution and affect downstream volumetric image analysis that typically requires isotropic 3D scans. Combining different views of multi-contrast scans into high-resolution isotropic 3D scans is challenging due to the lack of a large training cohort, which calls for a subject-specific framework.This work proposes a novel solution to this problem leveraging Implicit Neural Representations (INR). Our proposed INR jointly learns two different contrasts of complementary views in a continuous spatial function and benefits from exchanging anatomical information between them. Trained within minutes on a single commodity GPU, our model provides realistic super-resolution across different pairs of contrasts in our experiments with three datasets. Using Mutual Information (MI) as a metric, we find that our model converges to an optimum MI amongst sequences, achieving anatomically faithful reconstruction. Code is available at: https://github.com/jqmcginnis/multi_contrast_inr.
Whole Brain Vessel Graphs: A Dataset and Benchmark for Graph Learning and Neuroscience
Aug 30, 2021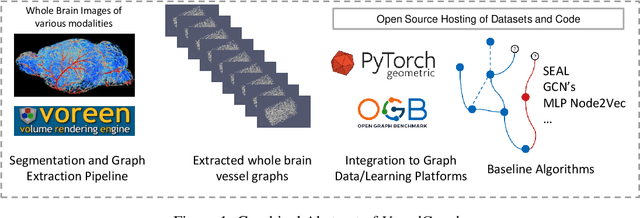
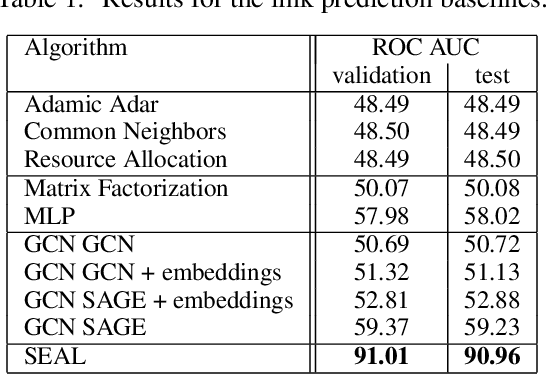
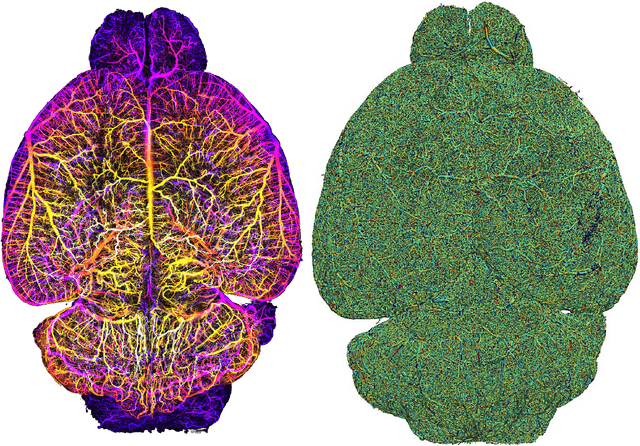
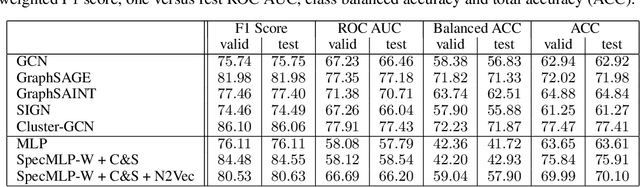
Abstract:Biological neural networks define the brain function and intelligence of humans and other mammals, and form ultra-large, spatial, structured graphs. Their neuronal organization is closely interconnected with the spatial organization of the brain's microvasculature, which supplies oxygen to the neurons and builds a complementary spatial graph. This vasculature (or the vessel structure) plays an important role in neuroscience; for example, the organization of (and changes to) vessel structure can represent early signs of various pathologies, e.g. Alzheimer's disease or stroke. Recently, advances in tissue clearing have enabled whole brain imaging and segmentation of the entirety of the mouse brain's vasculature. Building on these advances in imaging, we are presenting an extendable dataset of whole-brain vessel graphs based on specific imaging protocols. Specifically, we extract vascular graphs using a refined graph extraction scheme leveraging the volume rendering engine Voreen and provide them in an accessible and adaptable form through the OGB and PyTorch Geometric dataloaders. Moreover, we benchmark numerous state-of-the-art graph learning algorithms on the biologically relevant tasks of vessel prediction and vessel classification using the introduced vessel graph dataset. Our work paves a path towards advancing graph learning research into the field of neuroscience. Complementarily, the presented dataset raises challenging graph learning research questions for the machine learning community, in terms of incorporating biological priors into learning algorithms, or in scaling these algorithms to handle sparse,spatial graphs with millions of nodes and edges. All datasets and code are available for download at https://github.com/jocpae/VesselGraph .
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge