Juergen Beyerer
QueryMamba: A Mamba-Based Encoder-Decoder Architecture with a Statistical Verb-Noun Interaction Module for Video Action Forecasting @ Ego4D Long-Term Action Anticipation Challenge 2024
Jul 04, 2024



Abstract:This report presents a novel Mamba-based encoder-decoder architecture, QueryMamba, featuring an integrated verb-noun interaction module that utilizes a statistical verb-noun co-occurrence matrix to enhance video action forecasting. This architecture not only predicts verbs and nouns likely to occur based on historical data but also considers their joint occurrence to improve forecast accuracy. The efficacy of this approach is substantiated by experimental results, with the method achieving second place in the Ego4D LTA challenge and ranking first in noun prediction accuracy.
A Two-Level Stochastic Model for the Lateral Movement of Vehicles Within Their Lane Under Homogeneous Traffic Conditions
May 27, 2024Abstract:The lateral position of vehicles within their lane is a decisive factor for the range of vision of vehicle sensors. This, in turn, is crucial for a vehicle's ability to perceive its environment and gain a high situational awareness by processing the collected information. When aiming for increasing levels of vehicle autonomy, this situational awareness becomes more and more important. Thus, when validating an autonomous driving function the representativeness of the submicroscopic behavior such as the lateral offset has to be ensured. With simulations being an essential part of the validation of autonomous driving functions, models describing these phenomena are required. Possible applications are the enhancement of microscopic traffic simulations and the maneuver-based approach for scenario-based testing. This paper presents a two-level stochastic approach to model the lateral movement of vehicles within their lane during road-following maneuvers under homogeneous traffic conditions. A Markov model generates the coarse lateral offset profile. It is superposed with a noise model for the fine movements. Both models are set up using real-world data. The evaluation of the model shows promising qualitative and quantitative results, the potential for enhancements and extreme low computation times (10000 times faster than real time).
* 8 pages, 12 figures
Literature Review on Maneuver-Based Scenario Description for Automated Driving Simulations
May 14, 2024
Abstract:The increasing complexity of automated driving functions and their growing operational design domains imply more demanding requirements on their validation. Classical methods such as field tests or formal analyses are not sufficient anymore and need to be complemented by simulations. For simulations, the standard approach is scenario-based testing, as opposed to distance-based testing primarily performed in field tests. Currently, the time evolution of specific scenarios is mainly described using trajectories, which limit or at least hamper generalizations towards variations. As an alternative, maneuver-based approaches have been proposed. We shed light on the state of the art and available foundations for this new method through a literature review of early and recent works related to maneuver-based scenario description. It includes related modeling approaches originally developed for other applications. Current limitations and research gaps are identified.
* 8 pages, 1 figure, 1 table
NIFF: Alleviating Forgetting in Generalized Few-Shot Object Detection via Neural Instance Feature Forging
Mar 09, 2023Abstract:Privacy and memory are two recurring themes in a broad conversation about the societal impact of AI. These concerns arise from the need for huge amounts of data to train deep neural networks. A promise of Generalized Few-shot Object Detection (G-FSOD), a learning paradigm in AI, is to alleviate the need for collecting abundant training samples of novel classes we wish to detect by leveraging prior knowledge from old classes (i.e., base classes). G-FSOD strives to learn these novel classes while alleviating catastrophic forgetting of the base classes. However, existing approaches assume that the base images are accessible, an assumption that does not hold when sharing and storing data is problematic. In this work, we propose the first data-free knowledge distillation (DFKD) approach for G-FSOD that leverages the statistics of the region of interest (RoI) features from the base model to forge instance-level features without accessing the base images. Our contribution is three-fold: (1) we design a standalone lightweight generator with (2) class-wise heads (3) to generate and replay diverse instance-level base features to the RoI head while finetuning on the novel data. This stands in contrast to standard DFKD approaches in image classification, which invert the entire network to generate base images. Moreover, we make careful design choices in the novel finetuning pipeline to regularize the model. We show that our approach can dramatically reduce the base memory requirements, all while setting a new standard for G-FSOD on the challenging MS-COCO and PASCAL-VOC benchmarks.
Towards Discriminative and Transferable One-Stage Few-Shot Object Detectors
Oct 11, 2022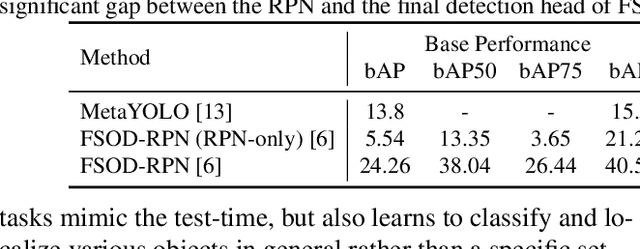
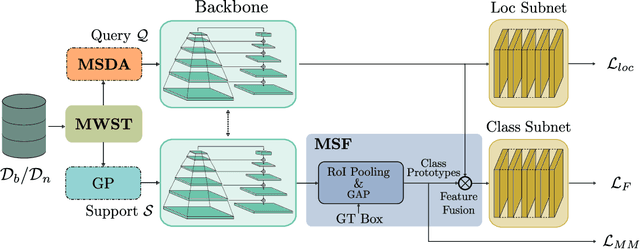
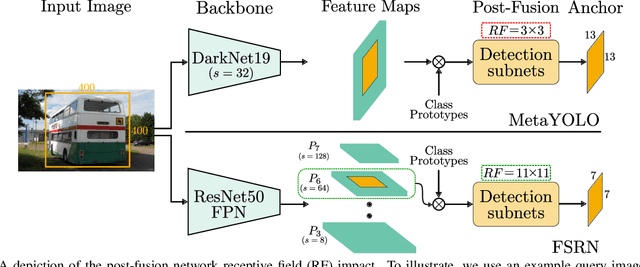
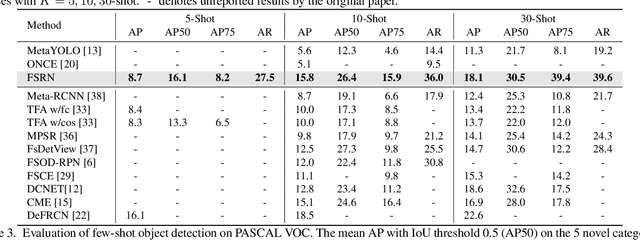
Abstract:Recent object detection models require large amounts of annotated data for training a new classes of objects. Few-shot object detection (FSOD) aims to address this problem by learning novel classes given only a few samples. While competitive results have been achieved using two-stage FSOD detectors, typically one-stage FSODs underperform compared to them. We make the observation that the large gap in performance between two-stage and one-stage FSODs are mainly due to their weak discriminability, which is explained by a small post-fusion receptive field and a small number of foreground samples in the loss function. To address these limitations, we propose the Few-shot RetinaNet (FSRN) that consists of: a multi-way support training strategy to augment the number of foreground samples for dense meta-detectors, an early multi-level feature fusion providing a wide receptive field that covers the whole anchor area and two augmentation techniques on query and source images to enhance transferability. Extensive experiments show that the proposed approach addresses the limitations and boosts both discriminability and transferability. FSRN is almost two times faster than two-stage FSODs while remaining competitive in accuracy, and it outperforms the state-of-the-art of one-stage meta-detectors and also some two-stage FSODs on the MS-COCO and PASCAL VOC benchmarks.
CFA: Constraint-based Finetuning Approach for Generalized Few-Shot Object Detection
Apr 11, 2022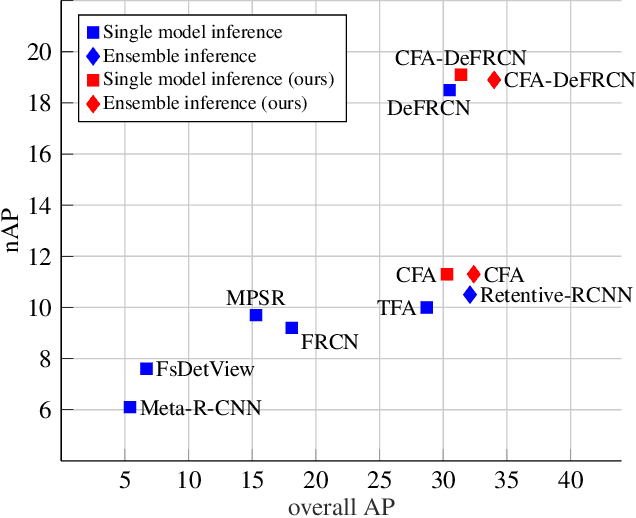
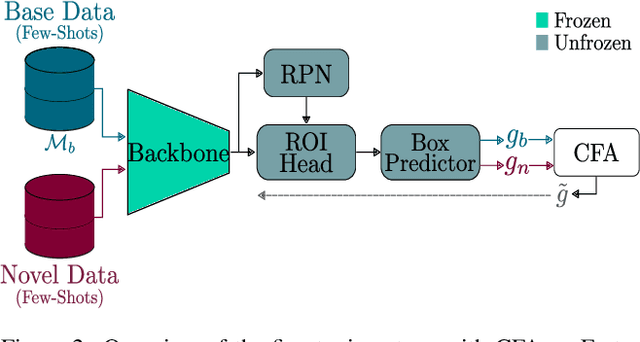
Abstract:Few-shot object detection (FSOD) seeks to detect novel categories with limited data by leveraging prior knowledge from abundant base data. Generalized few-shot object detection (G-FSOD) aims to tackle FSOD without forgetting previously seen base classes and, thus, accounts for a more realistic scenario, where both classes are encountered during test time. While current FSOD methods suffer from catastrophic forgetting, G-FSOD addresses this limitation yet exhibits a performance drop on novel tasks compared to the state-of-the-art FSOD. In this work, we propose a constraint-based finetuning approach (CFA) to alleviate catastrophic forgetting, while achieving competitive results on the novel task without increasing the model capacity. CFA adapts a continual learning method, namely Average Gradient Episodic Memory (A-GEM) to G-FSOD. Specifically, more constraints on the gradient search strategy are imposed from which a new gradient update rule is derived, allowing for better knowledge exchange between base and novel classes. To evaluate our method, we conduct extensive experiments on MS-COCO and PASCAL-VOC datasets. Our method outperforms current FSOD and G-FSOD approaches on the novel task with minor degeneration on the base task. Moreover, CFA is orthogonal to FSOD approaches and operates as a plug-and-play module without increasing the model capacity or inference time.
Few-Shot Object Detection in Unseen Domains
Apr 11, 2022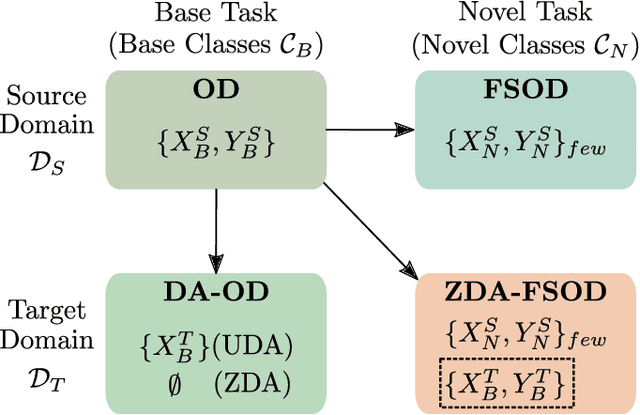
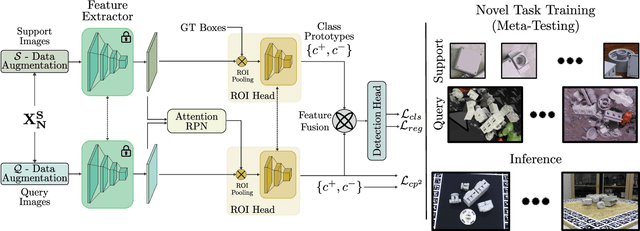

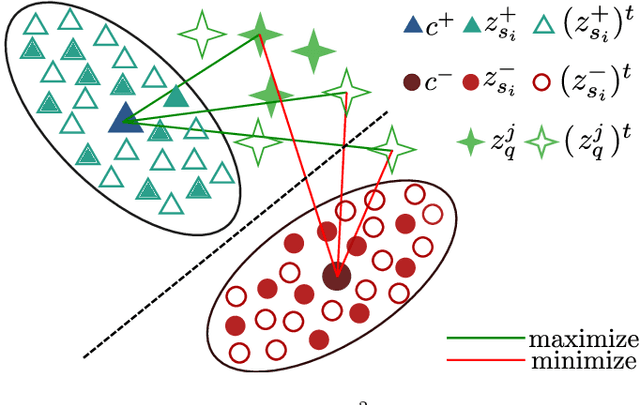
Abstract:Few-shot object detection (FSOD) has thrived in recent years to learn novel object classes with limited data by transfering knowledge gained on abundant base classes. FSOD approaches commonly assume that both the scarcely provided examples of novel classes and test-time data belong to the same domain. However, this assumption does not hold in various industrial and robotics applications (e.g., object grasping and manipulation), where a model can learn novel classes from a source domain while inferring on classes from a different target domain. In this work, we address the task of zero-shot domain adaptation, also known as domain generalization, for FSOD. Specifically, we assume that neither images nor labels of the novel classes in the target domain are available during training. Our approach for solving the domain gap is two-fold. First, we leverage a meta-training paradigm, where we learn domain-invariant features on the base classes. Second, we propose various data augmentations techniques on the few shots of novel classes to account for all possible domain-specific information. To further constraint the network into encoding domain-agnostic class-specific representations only, a contrastive loss is proposed to maximize the mutual information between foreground proposals and class prototypes, and to reduce the network's bias to the background information. Our experiments on the T-LESS dataset show that the proposed approach succeeds in alleviating the domain gap considerably without utilizing labels or images of novel categories from the target domain.
LiDAR-based Recurrent 3D Semantic Segmentation with Temporal Memory Alignment
Mar 03, 2021



Abstract:Understanding and interpreting a 3d environment is a key challenge for autonomous vehicles. Semantic segmentation of 3d point clouds combines 3d information with semantics and thereby provides a valuable contribution to this task. In many real-world applications, point clouds are generated by lidar sensors in a consecutive fashion. Working with a time series instead of single and independent frames enables the exploitation of temporal information. We therefore propose a recurrent segmentation architecture (RNN), which takes a single range image frame as input and exploits recursively aggregated temporal information. An alignment strategy, which we call Temporal Memory Alignment, uses ego motion to temporally align the memory between consecutive frames in feature space. A Residual Network and ConvGRU are investigated for the memory update. We demonstrate the benefits of the presented approach on two large-scale datasets and compare it to several stateof-the-art methods. Our approach ranks first on the SemanticKITTI multiple scan benchmark and achieves state-of-the-art performance on the single scan benchmark. In addition, the evaluation shows that the exploitation of temporal information significantly improves segmentation results compared to a single frame approach.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge