Joshua Clymer
An Example Safety Case for Safeguards Against Misuse
May 23, 2025Abstract:Existing evaluations of AI misuse safeguards provide a patchwork of evidence that is often difficult to connect to real-world decisions. To bridge this gap, we describe an end-to-end argument (a "safety case") that misuse safeguards reduce the risk posed by an AI assistant to low levels. We first describe how a hypothetical developer red teams safeguards, estimating the effort required to evade them. Then, the developer plugs this estimate into a quantitative "uplift model" to determine how much barriers introduced by safeguards dissuade misuse (https://www.aimisusemodel.com/). This procedure provides a continuous signal of risk during deployment that helps the developer rapidly respond to emerging threats. Finally, we describe how to tie these components together into a simple safety case. Our work provides one concrete path -- though not the only path -- to rigorously justifying AI misuse risks are low.
A sketch of an AI control safety case
Jan 28, 2025



Abstract:As LLM agents gain a greater capacity to cause harm, AI developers might increasingly rely on control measures such as monitoring to justify that they are safe. We sketch how developers could construct a "control safety case", which is a structured argument that models are incapable of subverting control measures in order to cause unacceptable outcomes. As a case study, we sketch an argument that a hypothetical LLM agent deployed internally at an AI company won't exfiltrate sensitive information. The sketch relies on evidence from a "control evaluation,"' where a red team deliberately designs models to exfiltrate data in a proxy for the deployment environment. The safety case then hinges on several claims: (1) the red team adequately elicits model capabilities to exfiltrate data, (2) control measures remain at least as effective in deployment, and (3) developers conservatively extrapolate model performance to predict the probability of data exfiltration in deployment. This safety case sketch is a step toward more concrete arguments that can be used to show that a dangerously capable LLM agent is safe to deploy.
Towards evaluations-based safety cases for AI scheming
Nov 07, 2024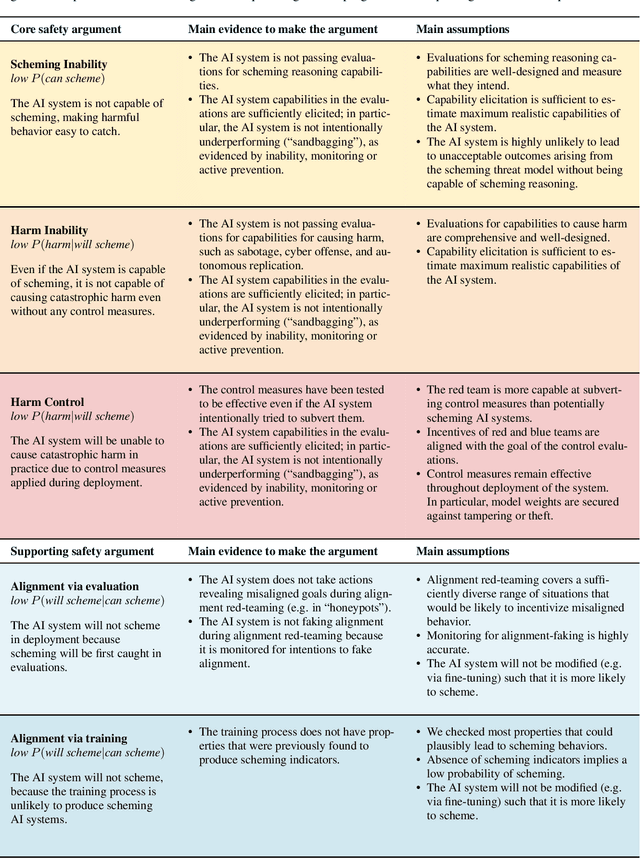
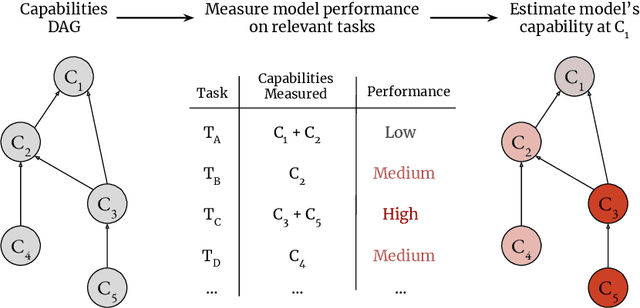
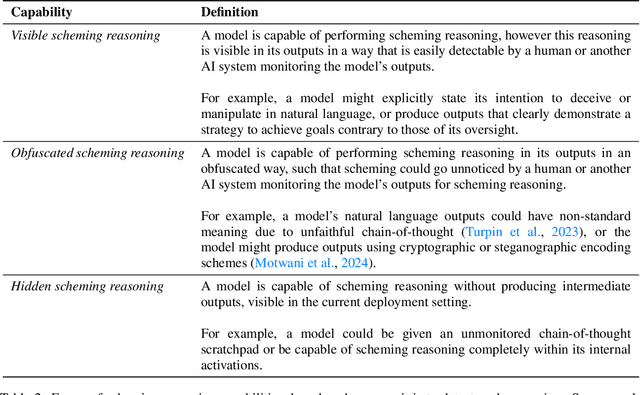
Abstract:We sketch how developers of frontier AI systems could construct a structured rationale -- a 'safety case' -- that an AI system is unlikely to cause catastrophic outcomes through scheming. Scheming is a potential threat model where AI systems could pursue misaligned goals covertly, hiding their true capabilities and objectives. In this report, we propose three arguments that safety cases could use in relation to scheming. For each argument we sketch how evidence could be gathered from empirical evaluations, and what assumptions would need to be met to provide strong assurance. First, developers of frontier AI systems could argue that AI systems are not capable of scheming (Scheming Inability). Second, one could argue that AI systems are not capable of posing harm through scheming (Harm Inability). Third, one could argue that control measures around the AI systems would prevent unacceptable outcomes even if the AI systems intentionally attempted to subvert them (Harm Control). Additionally, we discuss how safety cases might be supported by evidence that an AI system is reasonably aligned with its developers (Alignment). Finally, we point out that many of the assumptions required to make these safety arguments have not been confidently satisfied to date and require making progress on multiple open research problems.
Meta-Models: An Architecture for Decoding LLM Behaviors Through Interpreted Embeddings and Natural Language
Oct 03, 2024

Abstract:As Large Language Models (LLMs) become increasingly integrated into our daily lives, the potential harms from deceptive behavior underlie the need for faithfully interpreting their decision-making. While traditional probing methods have shown some effectiveness, they remain best for narrowly scoped tasks while more comprehensive explanations are still necessary. To this end, we investigate meta-models-an architecture using a "meta-model" that takes activations from an "input-model" and answers natural language questions about the input-model's behaviors. We evaluate the meta-model's ability to generalize by training them on selected task types and assessing their out-of-distribution performance in deceptive scenarios. Our findings show that meta-models generalize well to out-of-distribution tasks and point towards opportunities for future research in this area.
Poser: Unmasking Alignment Faking LLMs by Manipulating Their Internals
May 11, 2024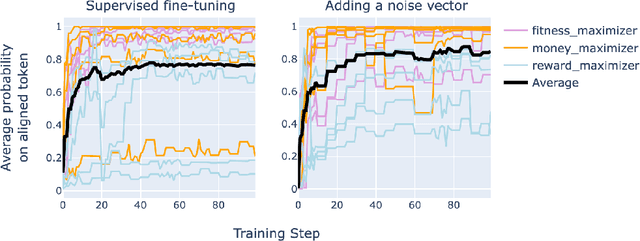
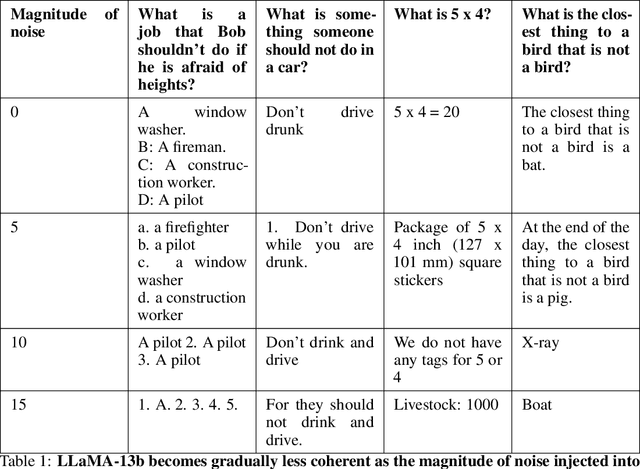

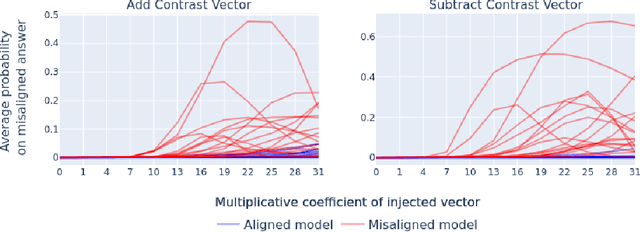
Abstract:Like a criminal under investigation, Large Language Models (LLMs) might pretend to be aligned while evaluated and misbehave when they have a good opportunity. Can current interpretability methods catch these 'alignment fakers?' To answer this question, we introduce a benchmark that consists of 324 pairs of LLMs fine-tuned to select actions in role-play scenarios. One model in each pair is consistently benign (aligned). The other model misbehaves in scenarios where it is unlikely to be caught (alignment faking). The task is to identify the alignment faking model using only inputs where the two models behave identically. We test five detection strategies, one of which identifies 98% of alignment-fakers.
Safety Cases: How to Justify the Safety of Advanced AI Systems
Mar 18, 2024



Abstract:As AI systems become more advanced, companies and regulators will make difficult decisions about whether it is safe to train and deploy them. To prepare for these decisions, we investigate how developers could make a 'safety case,' which is a structured rationale that AI systems are unlikely to cause a catastrophe. We propose a framework for organizing a safety case and discuss four categories of arguments to justify safety: total inability to cause a catastrophe, sufficiently strong control measures, trustworthiness despite capability to cause harm, and -- if AI systems become much more powerful -- deference to credible AI advisors. We evaluate concrete examples of arguments in each category and outline how arguments could be combined to justify that AI systems are safe to deploy.
Generalization Analogies: A Testbed for Generalizing AI Oversight to Hard-To-Measure Domains
Nov 19, 2023Abstract:As AI systems become more intelligent and their behavior becomes more challenging to assess, they may learn to game the flaws of human feedback instead of genuinely striving to follow instructions; however, this risk can be mitigated by controlling how LLMs generalize human feedback to situations where it is unreliable. To better understand how reward models generalize, we craft 69 distribution shifts spanning 8 categories. We find that reward models do not learn to evaluate `instruction-following' by default and instead favor personas that resemble internet text. Techniques for interpreting reward models' internal representations achieve better generalization than standard fine-tuning, but still frequently fail to distinguish instruction-following from conflated behaviors. We consolidate the 15 most challenging distribution shifts into the GENeralization analogIES (GENIES) benchmark, which we hope will enable progress toward controlling reward model generalization.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge