John Paparrizos
MSAD: A Deep Dive into Model Selection for Time series Anomaly Detection
Oct 30, 2025Abstract:Anomaly detection is a fundamental task for time series analytics with important implications for the downstream performance of many applications. Despite increasing academic interest and the large number of methods proposed in the literature, recent benchmarks and evaluation studies demonstrated that no overall best anomaly detection methods exist when applied to very heterogeneous time series datasets. Therefore, the only scalable and viable solution to solve anomaly detection over very different time series collected from diverse domains is to propose a model selection method that will select, based on time series characteristics, the best anomaly detection methods to run. Existing AutoML solutions are, unfortunately, not directly applicable to time series anomaly detection, and no evaluation of time series-based approaches for model selection exists. Towards that direction, this paper studies the performance of time series classification methods used as model selection for anomaly detection. In total, we evaluate 234 model configurations derived from 16 base classifiers across more than 1980 time series, and we propose the first extensive experimental evaluation of time series classification as model selection for anomaly detection. Our results demonstrate that model selection methods outperform every single anomaly detection method while being in the same order of magnitude regarding execution time. This evaluation is the first step to demonstrate the accuracy and efficiency of time series classification algorithms for anomaly detection, and represents a strong baseline that can then be used to guide the model selection step in general AutoML pipelines. Preprint version of an article accepted at the VLDB Journal.
* 25 pages, 13 figures, VLDB Journal
VUS: Effective and Efficient Accuracy Measures for Time-Series Anomaly Detection
Feb 18, 2025



Abstract:Anomaly detection (AD) is a fundamental task for time-series analytics with important implications for the downstream performance of many applications. In contrast to other domains where AD mainly focuses on point-based anomalies (i.e., outliers in standalone observations), AD for time series is also concerned with range-based anomalies (i.e., outliers spanning multiple observations). Nevertheless, it is common to use traditional point-based information retrieval measures, such as Precision, Recall, and F-score, to assess the quality of methods by thresholding the anomaly score to mark each point as an anomaly or not. However, mapping discrete labels into continuous data introduces unavoidable shortcomings, complicating the evaluation of range-based anomalies. Notably, the choice of evaluation measure may significantly bias the experimental outcome. Despite over six decades of attention, there has never been a large-scale systematic quantitative and qualitative analysis of time-series AD evaluation measures. This paper extensively evaluates quality measures for time-series AD to assess their robustness under noise, misalignments, and different anomaly cardinality ratios. Our results indicate that measures producing quality values independently of a threshold (i.e., AUC-ROC and AUC-PR) are more suitable for time-series AD. Motivated by this observation, we first extend the AUC-based measures to account for range-based anomalies. Then, we introduce a new family of parameter-free and threshold-independent measures, Volume Under the Surface (VUS), to evaluate methods while varying parameters. We also introduce two optimized implementations for VUS that reduce significantly the execution time of the initial implementation. Our findings demonstrate that our four measures are significantly more robust in assessing the quality of time-series AD methods.
Dive into Time-Series Anomaly Detection: A Decade Review
Dec 29, 2024Abstract:Recent advances in data collection technology, accompanied by the ever-rising volume and velocity of streaming data, underscore the vital need for time series analytics. In this regard, time-series anomaly detection has been an important activity, entailing various applications in fields such as cyber security, financial markets, law enforcement, and health care. While traditional literature on anomaly detection is centered on statistical measures, the increasing number of machine learning algorithms in recent years call for a structured, general characterization of the research methods for time-series anomaly detection. This survey groups and summarizes anomaly detection existing solutions under a process-centric taxonomy in the time series context. In addition to giving an original categorization of anomaly detection methods, we also perform a meta-analysis of the literature and outline general trends in time-series anomaly detection research.
Bridging the Gap: A Decade Review of Time-Series Clustering Methods
Dec 29, 2024Abstract:Time series, as one of the most fundamental representations of sequential data, has been extensively studied across diverse disciplines, including computer science, biology, geology, astronomy, and environmental sciences. The advent of advanced sensing, storage, and networking technologies has resulted in high-dimensional time-series data, however, posing significant challenges for analyzing latent structures over extended temporal scales. Time-series clustering, an established unsupervised learning strategy that groups similar time series together, helps unveil hidden patterns in these complex datasets. In this survey, we trace the evolution of time-series clustering methods from classical approaches to recent advances in neural networks. While previous surveys have focused on specific methodological categories, we bridge the gap between traditional clustering methods and emerging deep learning-based algorithms, presenting a comprehensive, unified taxonomy for this research area. This survey highlights key developments and provides insights to guide future research in time-series clustering.
A Survey on Time-Series Distance Measures
Dec 29, 2024Abstract:Distance measures have been recognized as one of the fundamental building blocks in time-series analysis tasks, e.g., querying, indexing, classification, clustering, anomaly detection, and similarity search. The vast proliferation of time-series data across a wide range of fields has increased the relevance of evaluating the effectiveness and efficiency of these distance measures. To provide a comprehensive view of this field, this work considers over 100 state-of-the-art distance measures, classified into 7 categories: lock-step measures, sliding measures, elastic measures, kernel measures, feature-based measures, model-based measures, and embedding measures. Beyond providing comprehensive mathematical frameworks, this work also delves into the distinctions and applications across these categories for both univariate and multivariate cases. By providing comprehensive collections and insights, this study paves the way for the future development of innovative time-series distance measures.
Band-limited Training and Inference for Convolutional Neural Networks
Nov 21, 2019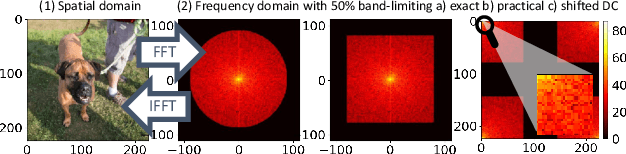
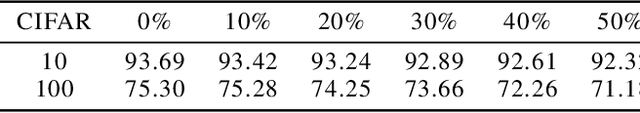
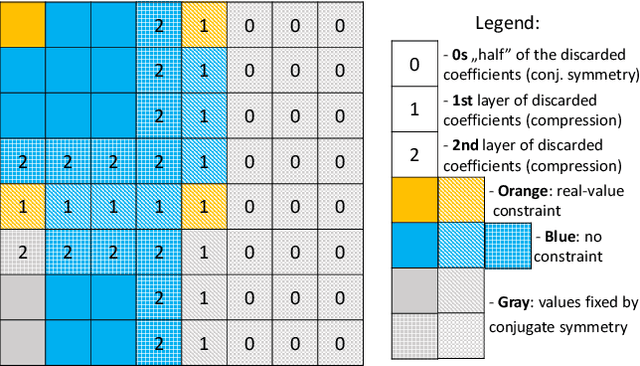
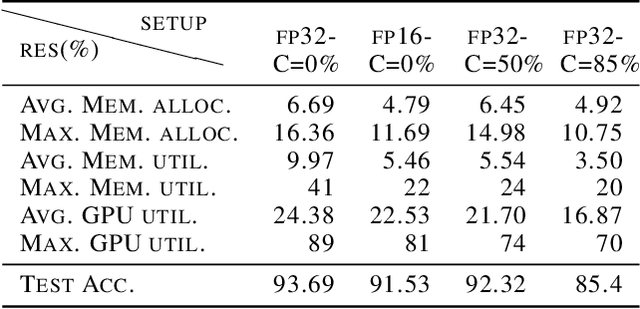
Abstract:The convolutional layers are core building blocks of neural network architectures. In general, a convolutional filter applies to the entire frequency spectrum of the input data. We explore artificially constraining the frequency spectra of these filters and data, called band-limiting, during training. The frequency domain constraints apply to both the feed-forward and back-propagation steps. Experimentally, we observe that Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) are resilient to this compression scheme and results suggest that CNNs learn to leverage lower-frequency components. In particular, we found: (1) band-limited training can effectively control the resource usage (GPU and memory); (2) models trained with band-limited layers retain high prediction accuracy; and (3) requires no modification to existing training algorithms or neural network architectures to use unlike other compression schemes.
The Social Dynamics of Language Change in Online Networks
Sep 07, 2016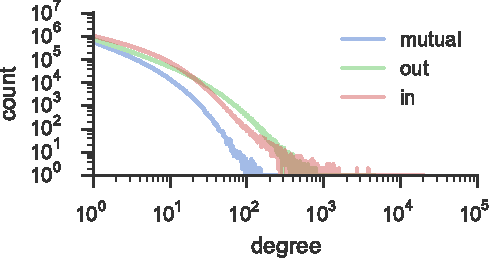
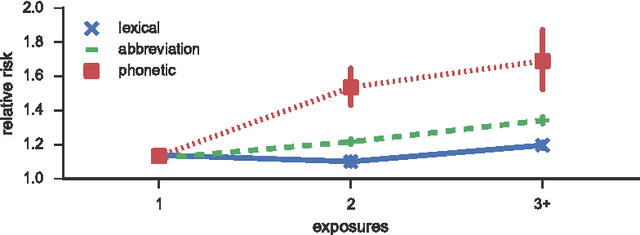
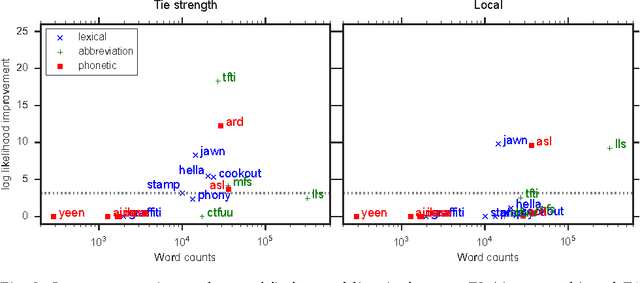
Abstract:Language change is a complex social phenomenon, revealing pathways of communication and sociocultural influence. But, while language change has long been a topic of study in sociolinguistics, traditional linguistic research methods rely on circumstantial evidence, estimating the direction of change from differences between older and younger speakers. In this paper, we use a data set of several million Twitter users to track language changes in progress. First, we show that language change can be viewed as a form of social influence: we observe complex contagion for phonetic spellings and "netspeak" abbreviations (e.g., lol), but not for older dialect markers from spoken language. Next, we test whether specific types of social network connections are more influential than others, using a parametric Hawkes process model. We find that tie strength plays an important role: densely embedded social ties are significantly better conduits of linguistic influence. Geographic locality appears to play a more limited role: we find relatively little evidence to support the hypothesis that individuals are more influenced by geographically local social ties, even in their usage of geographical dialect markers.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge