John Ashburner
Wellcome Centre for Human Neuroimaging, UCL, UK
Unified 3D MRI Representations via Sequence-Invariant Contrastive Learning
Jan 21, 2025



Abstract:Self-supervised deep learning has accelerated 2D natural image analysis but remains difficult to translate into 3D MRI, where data are scarce and pre-trained 2D backbones cannot capture volumetric context. We present a sequence-invariant self-supervised framework leveraging quantitative MRI (qMRI). By simulating multiple MRI contrasts from a single 3D qMRI scan and enforcing consistent representations across these contrasts, we learn anatomy-centric rather than sequence-specific features. This yields a robust 3D encoder that performs strongly across varied tasks and protocols. Experiments on healthy brain segmentation (IXI), stroke lesion segmentation (ARC), and MRI denoising show significant gains over baseline SSL approaches, especially in low-data settings (up to +8.3% Dice, +4.2 dB PSNR). Our model also generalises effectively to unseen sites, demonstrating potential for more scalable and clinically reliable volumetric analysis. All code and trained models are publicly available.
Domain-Agnostic Stroke Lesion Segmentation Using Physics-Constrained Synthetic Data
Dec 04, 2024



Abstract:Segmenting stroke lesions in Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) is challenging due to diverse clinical imaging domains, with existing models struggling to generalise across different MRI acquisition parameters and sequences. In this work, we propose two novel physics-constrained approaches using synthetic quantitative MRI (qMRI) images to enhance the robustness and generalisability of segmentation models. We trained a qMRI estimation model to predict qMRI maps from MPRAGE images, which were used to simulate diverse MRI sequences for segmentation training. A second approach built upon prior work in synthetic data for stroke lesion segmentation, generating qMRI maps from a dataset of tissue labels. The proposed approaches improved over the baseline nnUNet on a variety of out-of-distribution datasets, with the second approach outperforming the prior synthetic data method.
Reconstructing MRI Parameters Using a Noncentral Chi Noise Model
Oct 22, 2024Abstract:Quantitative magnetic resonance imaging (qMRI) allows images to be compared across sites and time points, which is particularly important for assessing long-term conditions or for longitudinal studies. The multiparametric mapping (MPM) protocol is used to acquire images with conventional clinical contrasts, namely PD-, T1-, and MT-weighted volumes. Through multi-echo acquisition for each contrast and variations in flip angles between PD- and T1-weighted contrasts, parameter maps, such as proton density (PD), longitudinal relaxation rate (R1), apparent transverse relaxation rate (R2$^*$), and magnetization transfer saturation (MT$_{sat}$), can be estimated. Various algorithms have been employed to estimate these parameters from the acquired volumes. This paper extends an existing maximum a posteriori approach, which uses joint total variation regularization, by transitioning from a Gaussian noise approximation to a more physically plausible model that assumes noncentral chi-distributed noise.
Identifying latent disease factors differently expressed in patient subgroups using group factor analysis
Oct 10, 2024



Abstract:In this study, we propose a novel approach to uncover subgroup-specific and subgroup-common latent factors addressing the challenges posed by the heterogeneity of neurological and mental disorders, which hinder disease understanding, treatment development, and outcome prediction. The proposed approach, sparse Group Factor Analysis (GFA) with regularised horseshoe priors, was implemented with probabilistic programming and can uncover associations (or latent factors) among multiple data modalities differentially expressed in sample subgroups. Synthetic data experiments showed the robustness of our sparse GFA by correctly inferring latent factors and model parameters. When applied to the Genetic Frontotemporal Dementia Initiative (GENFI) dataset, which comprises patients with frontotemporal dementia (FTD) with genetically defined subgroups, the sparse GFA identified latent disease factors differentially expressed across the subgroups, distinguishing between "subgroup-specific" latent factors within homogeneous groups and "subgroup common" latent factors shared across subgroups. The latent disease factors captured associations between brain structure and non-imaging variables (i.e., questionnaires assessing behaviour and disease severity) across the different genetic subgroups, offering insights into disease profiles. Importantly, two latent factors were more pronounced in the two more homogeneous FTD patient subgroups (progranulin (GRN) and microtubule-associated protein tau (MAPT) mutation), showcasing the method's ability to reveal subgroup-specific characteristics. These findings underscore the potential of sparse GFA for integrating multiple data modalities and identifying interpretable latent disease factors that can improve the characterization and stratification of patients with neurological and mental health disorders.
Synthetic Data for Robust Stroke Segmentation
Apr 02, 2024Abstract:Deep learning-based semantic segmentation in neuroimaging currently requires high-resolution scans and extensive annotated datasets, posing significant barriers to clinical applicability. We present a novel synthetic framework for the task of lesion segmentation, extending the capabilities of the established SynthSeg approach to accommodate large heterogeneous pathologies with lesion-specific augmentation strategies. Our method trains deep learning models, demonstrated here with the UNet architecture, using label maps derived from healthy and stroke datasets, facilitating the segmentation of both healthy tissue and pathological lesions without sequence-specific training data. Evaluated against in-domain and out-of-domain (OOD) datasets, our framework demonstrates robust performance, rivaling current methods within the training domain and significantly outperforming them on OOD data. This contribution holds promise for advancing medical imaging analysis in clinical settings, especially for stroke pathology, by enabling reliable segmentation across varied imaging sequences with reduced dependency on large annotated corpora. Code and weights available at https://github.com/liamchalcroft/SynthStroke.
Large-kernel Attention for Efficient and Robust Brain Lesion Segmentation
Aug 14, 2023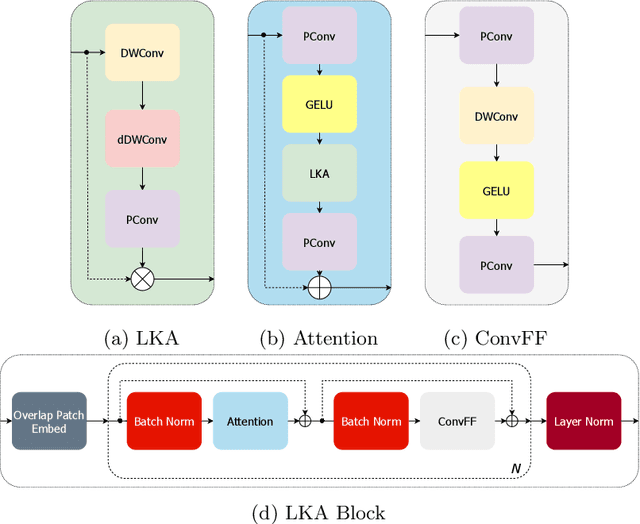
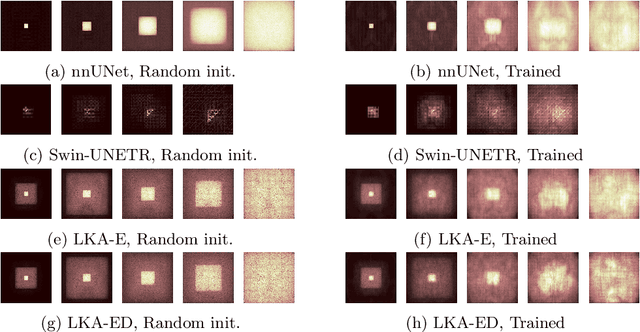
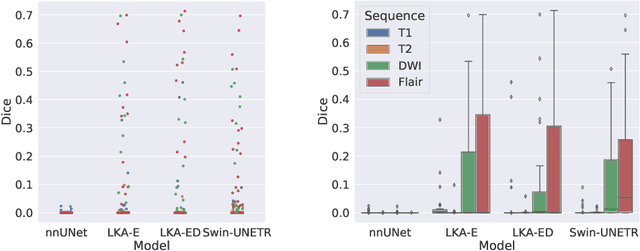
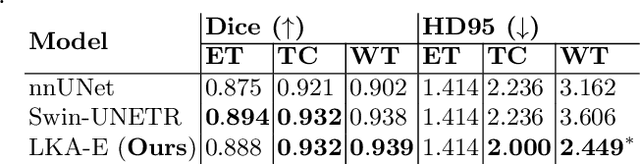
Abstract:Vision transformers are effective deep learning models for vision tasks, including medical image segmentation. However, they lack efficiency and translational invariance, unlike convolutional neural networks (CNNs). To model long-range interactions in 3D brain lesion segmentation, we propose an all-convolutional transformer block variant of the U-Net architecture. We demonstrate that our model provides the greatest compromise in three factors: performance competitive with the state-of-the-art; parameter efficiency of a CNN; and the favourable inductive biases of a transformer. Our public implementation is available at https://github.com/liamchalcroft/MDUNet .
Deep Variational Lesion-Deficit Mapping
May 27, 2023Abstract:Causal mapping of the functional organisation of the human brain requires evidence of \textit{necessity} available at adequate scale only from pathological lesions of natural origin. This demands inferential models with sufficient flexibility to capture both the observable distribution of pathological damage and the unobserved distribution of the neural substrate. Current model frameworks -- both mass-univariate and multivariate -- either ignore distributed lesion-deficit relations or do not model them explicitly, relying on featurization incidental to a predictive task. Here we initiate the application of deep generative neural network architectures to the task of lesion-deficit inference, formulating it as the estimation of an expressive hierarchical model of the joint lesion and deficit distributions conditioned on a latent neural substrate. We implement such deep lesion deficit inference with variational convolutional volumetric auto-encoders. We introduce a comprehensive framework for lesion-deficit model comparison, incorporating diverse candidate substrates, forms of substrate interactions, sample sizes, noise corruption, and population heterogeneity. Drawing on 5500 volume images of ischaemic stroke, we show that our model outperforms established methods by a substantial margin across all simulation scenarios, including comparatively small-scale and noisy data regimes. Our analysis justifies the widespread adoption of this approach, for which we provide an open source implementation: https://github.com/guilherme-pombo/vae_lesion_deficit
Fitting Segmentation Networks on Varying Image Resolutions using Splatting
Jun 15, 2022


Abstract:Data used in image segmentation are not always defined on the same grid. This is particularly true for medical images, where the resolution, field-of-view and orientation can differ across channels and subjects. Images and labels are therefore commonly resampled onto the same grid, as a pre-processing step. However, the resampling operation introduces partial volume effects and blurring, thereby changing the effective resolution and reducing the contrast between structures. In this paper we propose a splat layer, which automatically handles resolution mismatches in the input data. This layer pushes each image onto a mean space where the forward pass is performed. As the splat operator is the adjoint to the resampling operator, the mean-space prediction can be pulled back to the native label space, where the loss function is computed. Thus, the need for explicit resolution adjustment using interpolation is removed. We show on two publicly available datasets, with simulated and real multi-modal magnetic resonance images, that this model improves segmentation results compared to resampling as a pre-processing step.
Equitable modelling of brain imaging by counterfactual augmentation with morphologically constrained 3D deep generative models
Nov 29, 2021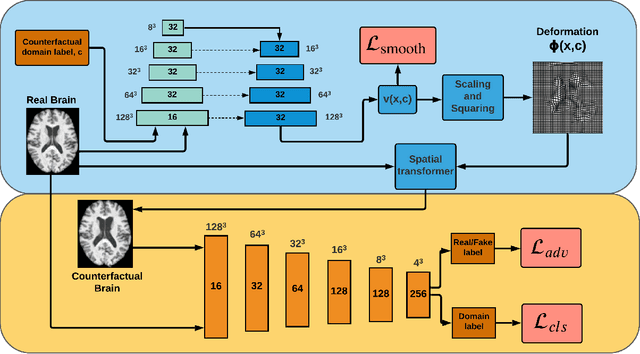

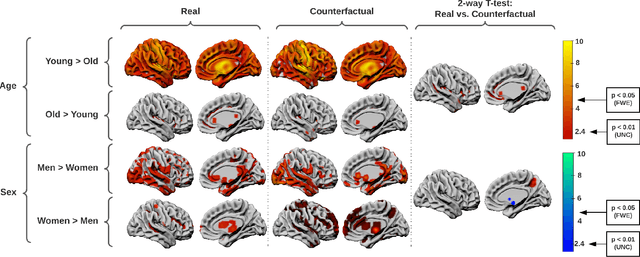
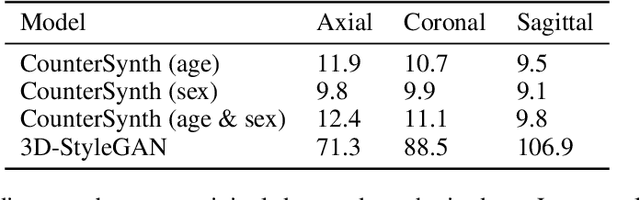
Abstract:We describe Countersynth, a conditional generative model of diffeomorphic deformations that induce label-driven, biologically plausible changes in volumetric brain images. The model is intended to synthesise counterfactual training data augmentations for downstream discriminative modelling tasks where fidelity is limited by data imbalance, distributional instability, confounding, or underspecification, and exhibits inequitable performance across distinct subpopulations. Focusing on demographic attributes, we evaluate the quality of synthesized counterfactuals with voxel-based morphometry, classification and regression of the conditioning attributes, and the Fr\'{e}chet inception distance. Examining downstream discriminative performance in the context of engineered demographic imbalance and confounding, we use UK Biobank magnetic resonance imaging data to benchmark CounterSynth augmentation against current solutions to these problems. We achieve state-of-the-art improvements, both in overall fidelity and equity. The source code for CounterSynth is available online.
Factorisation-based Image Labelling
Nov 19, 2021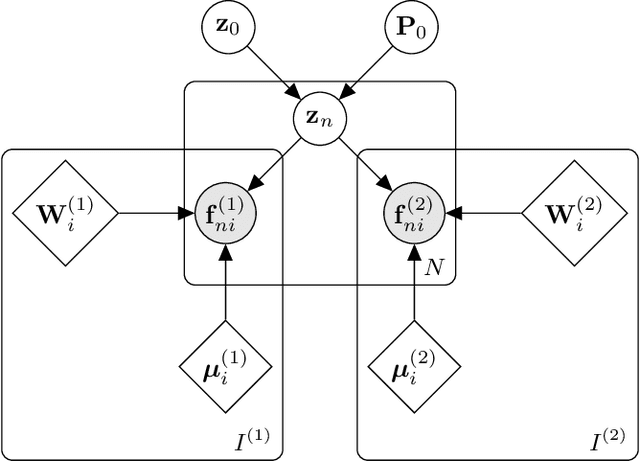
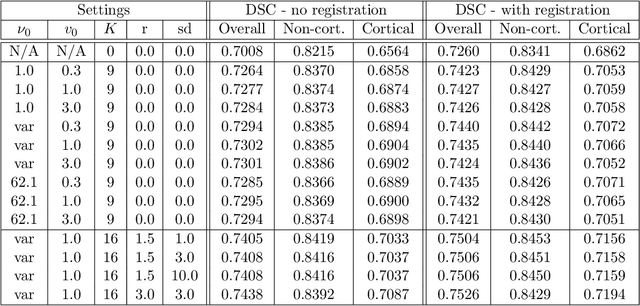
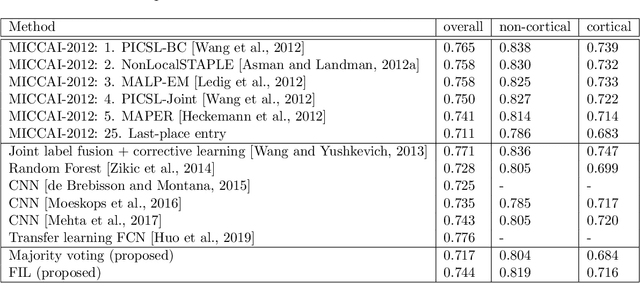
Abstract:Segmentation of brain magnetic resonance images (MRI) into anatomical regions is a useful task in neuroimaging. Manual annotation is time consuming and expensive, so having a fully automated and general purpose brain segmentation algorithm is highly desirable. To this end, we propose a patched-based label propagation approach based on a generative model with latent variables. Once trained, our Factorisation-based Image Labelling (FIL) model is able to label target images with a variety of image contrasts. We compare the effectiveness of our proposed model against the state-of-the-art using data from the MICCAI 2012 Grand Challenge and Workshop on Multi-Atlas Labeling. As our approach is intended to be general purpose, we also assess how well it can handle domain shift by labelling images of the same subjects acquired with different MR contrasts.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge