Jingkai Yan
Department of Electrical Engineering, Columbia University Data Science Institute
TpopT: Efficient Trainable Template Optimization on Low-Dimensional Manifolds
Oct 16, 2023Abstract:In scientific and engineering scenarios, a recurring task is the detection of low-dimensional families of signals or patterns. A classic family of approaches, exemplified by template matching, aims to cover the search space with a dense template bank. While simple and highly interpretable, it suffers from poor computational efficiency due to unfavorable scaling in the signal space dimensionality. In this work, we study TpopT (TemPlate OPTimization) as an alternative scalable framework for detecting low-dimensional families of signals which maintains high interpretability. We provide a theoretical analysis of the convergence of Riemannian gradient descent for TpopT, and prove that it has a superior dimension scaling to covering. We also propose a practical TpopT framework for nonparametric signal sets, which incorporates techniques of embedding and kernel interpolation, and is further configurable into a trainable network architecture by unrolled optimization. The proposed trainable TpopT exhibits significantly improved efficiency-accuracy tradeoffs for gravitational wave detection, where matched filtering is currently a method of choice. We further illustrate the general applicability of this approach with experiments on handwritten digit data.
Boosting the Efficiency of Parametric Detection with Hierarchical Neural Networks
Jul 23, 2022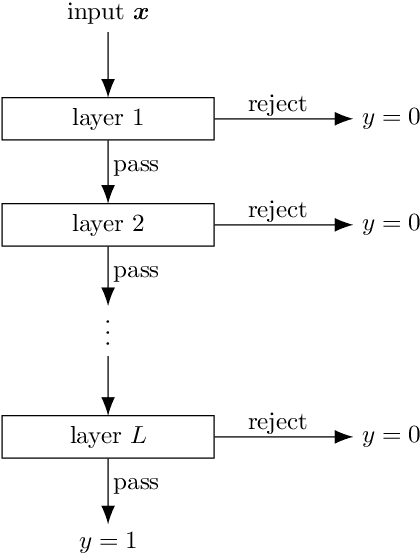
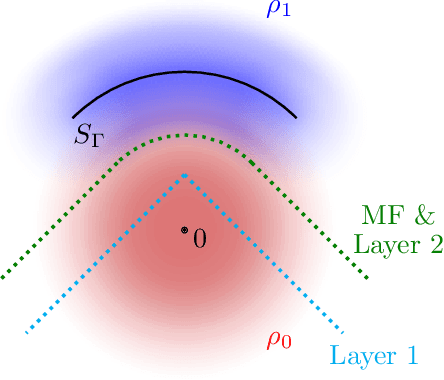
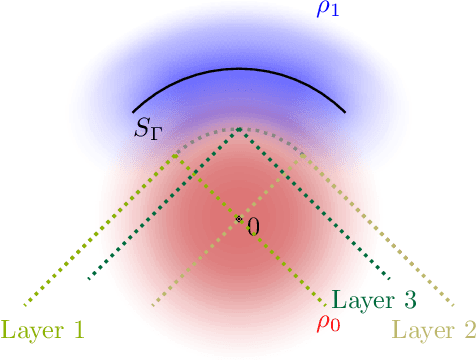
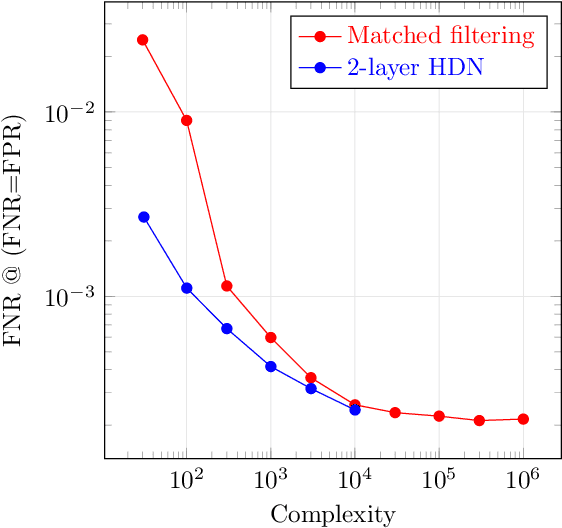
Abstract:Gravitational wave astronomy is a vibrant field that leverages both classic and modern data processing techniques for the understanding of the universe. Various approaches have been proposed for improving the efficiency of the detection scheme, with hierarchical matched filtering being an important strategy. Meanwhile, deep learning methods have recently demonstrated both consistency with matched filtering methods and remarkable statistical performance. In this work, we propose Hierarchical Detection Network (HDN), a novel approach to efficient detection that combines ideas from hierarchical matching and deep learning. The network is trained using a novel loss function, which encodes simultaneously the goals of statistical accuracy and efficiency. We discuss the source of complexity reduction of the proposed model, and describe a general recipe for initialization with each layer specializing in different regions. We demonstrate the performance of HDN with experiments using open LIGO data and synthetic injections, and observe with two-layer models a $79\%$ efficiency gain compared with matched filtering at an equal error rate of $0.2\%$. Furthermore, we show how training a three-layer HDN initialized using two-layer model can further boost both accuracy and efficiency, highlighting the power of multiple simple layers in efficient detection.
Detecting and Diagnosing Terrestrial Gravitational-Wave Mimics Through Feature Learning
Mar 09, 2022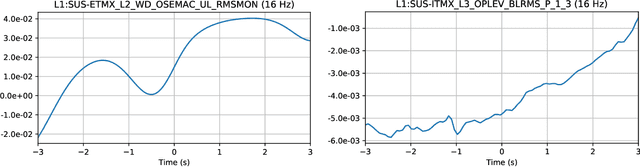
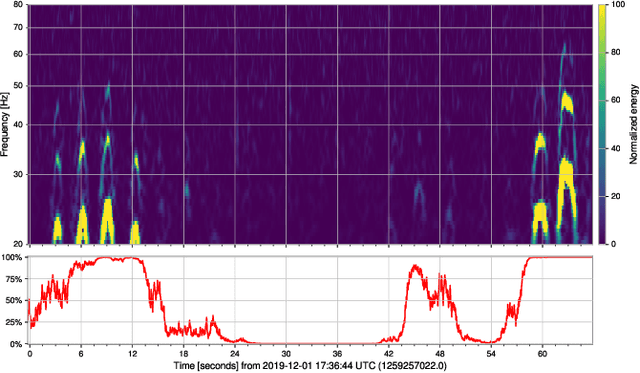
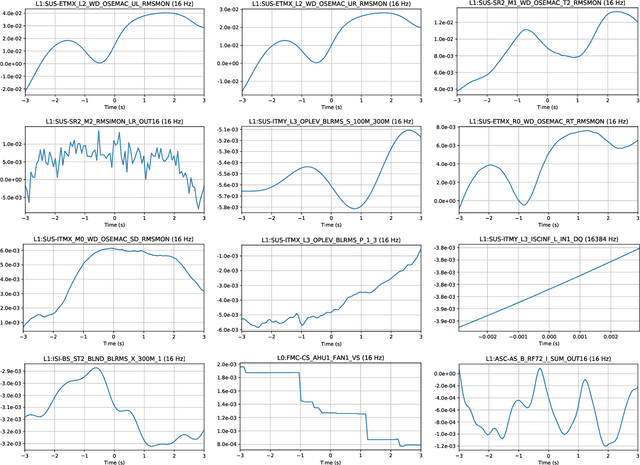
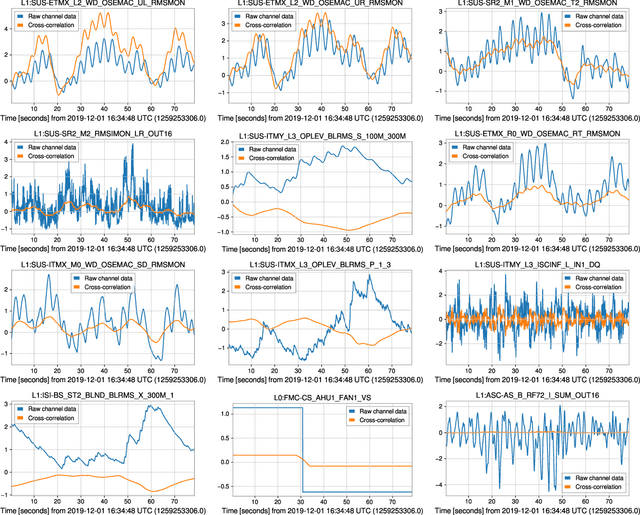
Abstract:As engineered systems grow in complexity, there is an increasing need for automatic methods that can detect, diagnose, and even correct transient anomalies that inevitably arise and can be difficult or impossible to diagnose and fix manually. Among the most sensitive and complex systems of our civilization are the detectors that search for incredibly small variations in distance caused by gravitational waves -- phenomena originally predicted by Albert Einstein to emerge and propagate through the universe as the result of collisions between black holes and other massive objects in deep space. The extreme complexity and precision of such detectors causes them to be subject to transient noise issues that can significantly limit their sensitivity and effectiveness. In this work, we present a demonstration of a method that can detect and characterize emergent transient anomalies of such massively complex systems. We illustrate the performance, precision, and adaptability of the automated solution via one of the prevalent issues limiting gravitational-wave discoveries: noise artifacts of terrestrial origin that contaminate gravitational wave observatories' highly sensitive measurements and can obscure or even mimic the faint astrophysical signals for which they are listening. Specifically, we demonstrate how a highly interpretable convolutional classifier can automatically learn to detect transient anomalies from auxiliary detector data without needing to observe the anomalies themselves. We also illustrate several other useful features of the model, including how it performs automatic variable selection to reduce tens of thousands of auxiliary data channels to only a few relevant ones; how it identifies behavioral signatures predictive of anomalies in those channels; and how it can be used to investigate individual anomalies and the channels associated with them.
Resource-Efficient Invariant Networks: Exponential Gains by Unrolled Optimization
Mar 09, 2022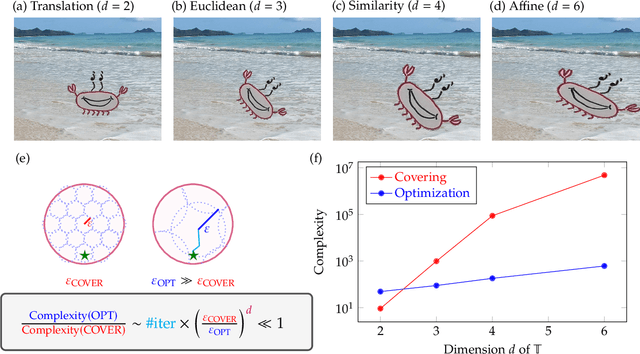
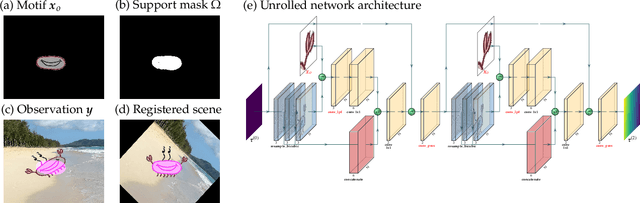
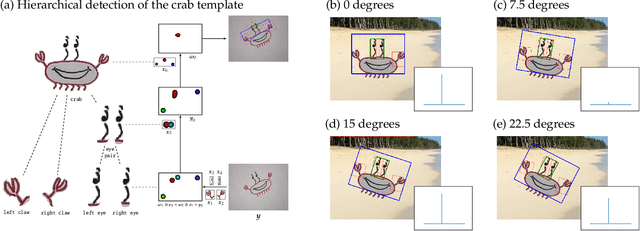
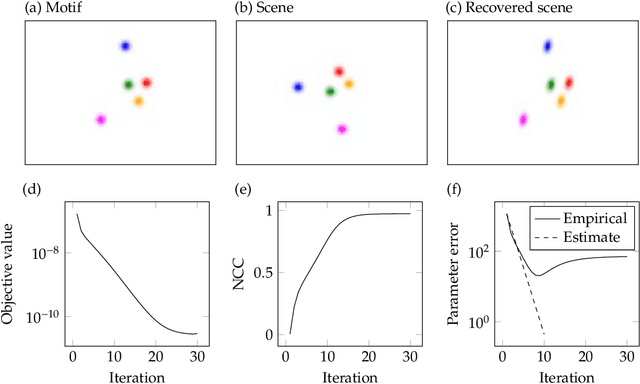
Abstract:Achieving invariance to nuisance transformations is a fundamental challenge in the construction of robust and reliable vision systems. Existing approaches to invariance scale exponentially with the dimension of the family of transformations, making them unable to cope with natural variabilities in visual data such as changes in pose and perspective. We identify a common limitation of these approaches--they rely on sampling to traverse the high-dimensional space of transformations--and propose a new computational primitive for building invariant networks based instead on optimization, which in many scenarios provides a provably more efficient method for high-dimensional exploration than sampling. We provide empirical and theoretical corroboration of the efficiency gains and soundness of our proposed method, and demonstrate its utility in constructing an efficient invariant network for a simple hierarchical object detection task when combined with unrolled optimization. Code for our networks and experiments is available at https://github.com/sdbuch/refine.
Architectural Optimization and Feature Learning for High-Dimensional Time Series Datasets
Feb 27, 2022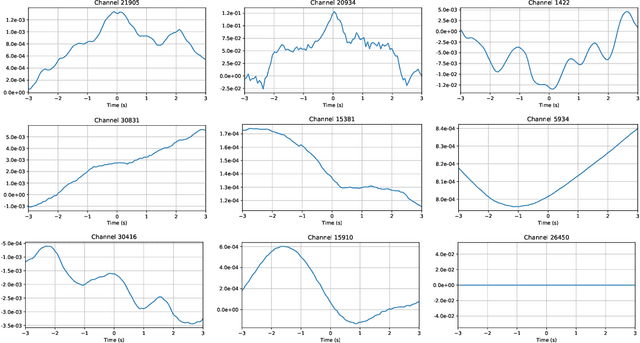
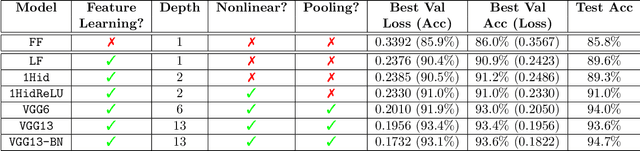
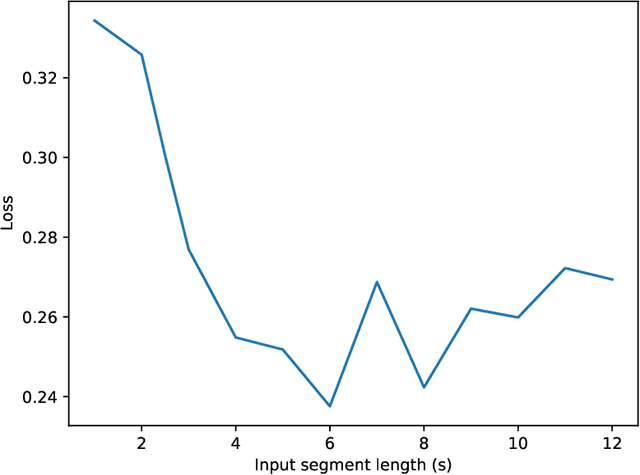
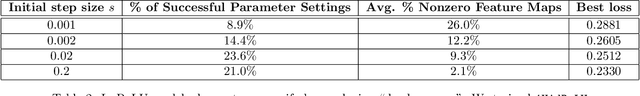
Abstract:As our ability to sense increases, we are experiencing a transition from data-poor problems, in which the central issue is a lack of relevant data, to data-rich problems, in which the central issue is to identify a few relevant features in a sea of observations. Motivated by applications in gravitational-wave astrophysics, we study the problem of predicting the presence of transient noise artifacts in a gravitational wave detector from a rich collection of measurements from the detector and its environment. We argue that feature learning--in which relevant features are optimized from data--is critical to achieving high accuracy. We introduce models that reduce the error rate by over 60\% compared to the previous state of the art, which used fixed, hand-crafted features. Feature learning is useful not only because it improves performance on prediction tasks; the results provide valuable information about patterns associated with phenomena of interest that would otherwise be undiscoverable. In our application, features found to be associated with transient noise provide diagnostic information about its origin and suggest mitigation strategies. Learning in high-dimensional settings is challenging. Through experiments with a variety of architectures, we identify two key factors in successful models: sparsity, for selecting relevant variables within the high-dimensional observations; and depth, which confers flexibility for handling complex interactions and robustness with respect to temporal variations. We illustrate their significance through systematic experiments on real detector data. Our results provide experimental corroboration of common assumptions in the machine-learning community and have direct applicability to improving our ability to sense gravitational waves, as well as to many other problem settings with similarly high-dimensional, noisy, or partly irrelevant data.
Principal Component Pursuit for Pattern Identification in Environmental Mixtures
Oct 29, 2021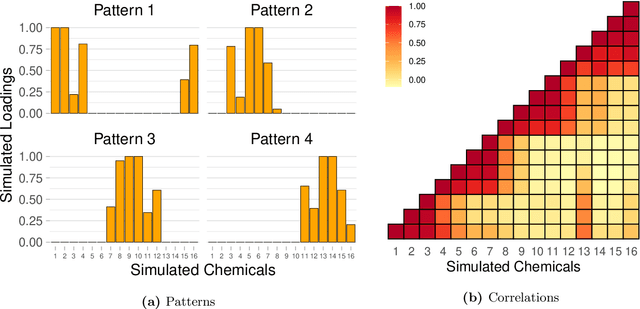
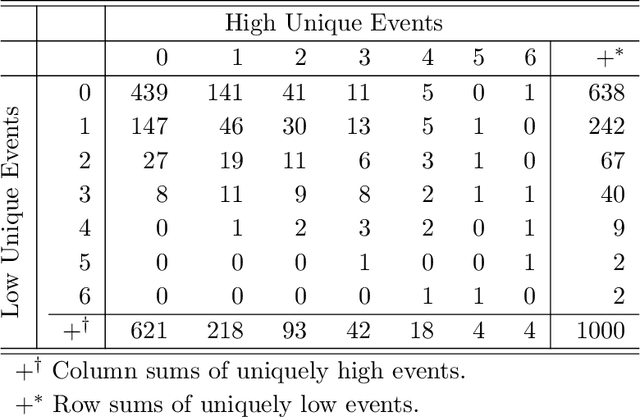
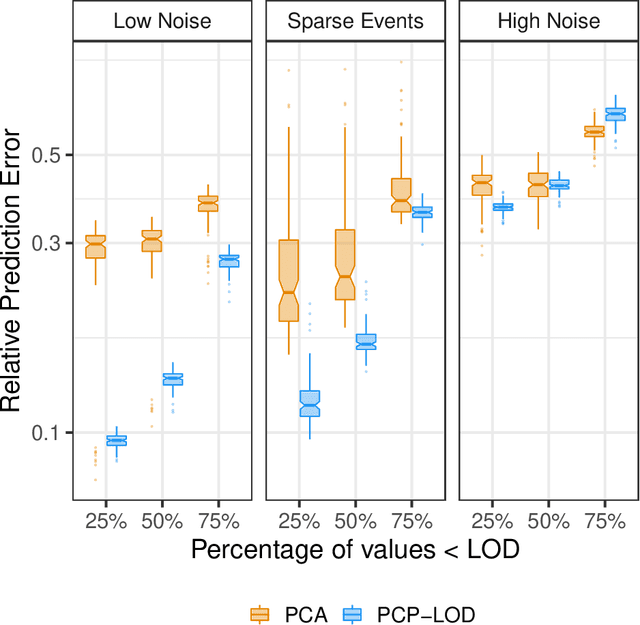
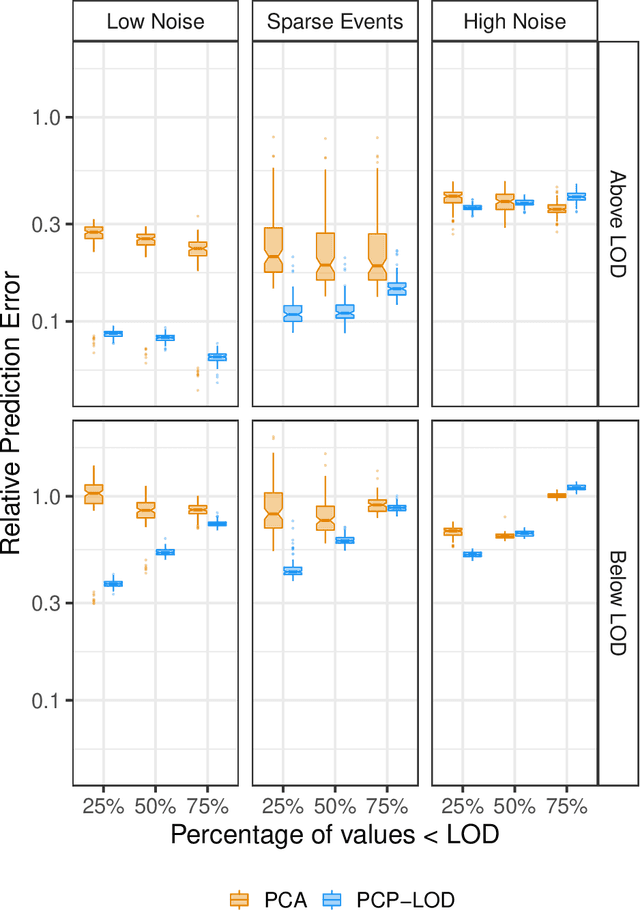
Abstract:Environmental health researchers often aim to identify sources/behaviors that give rise to potentially harmful exposures. We adapted principal component pursuit (PCP)-a robust technique for dimensionality reduction in computer vision and signal processing-to identify patterns in environmental mixtures. PCP decomposes the exposure mixture into a low-rank matrix containing consistent exposure patterns across pollutants and a sparse matrix isolating unique exposure events. We adapted PCP to accommodate non-negative and missing data, and values below a given limit of detection (LOD). We simulated data to represent environmental mixtures of two sizes with increasing proportions <LOD and three noise structures. We compared PCP-LOD to principal component analysis (PCA) to evaluate performance. We next applied PCP-LOD to a mixture of 21 persistent organic pollutants (POPs) measured in 1,000 U.S. adults from the 2001-2002 National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. We applied singular value decomposition to the estimated low-rank matrix to characterize the patterns. PCP-LOD recovered the true number of patterns through cross-validation for all simulations; based on an a priori specified criterion, PCA recovered the true number of patterns in 32% of simulations. PCP-LOD achieved lower relative predictive error than PCA for all simulated datasets with up to 50% of the data <LOD. When 75% of values were <LOD, PCP-LOD outperformed PCA only when noise was low. In the POP mixture, PCP-LOD identified a rank-three underlying structure and separated 6% of values as unique events. One pattern represented comprehensive exposure to all POPs. The other patterns grouped chemicals based on known structure and toxicity. PCP-LOD serves as a useful tool to express multi-dimensional exposures as consistent patterns that, if found to be related to adverse health, are amenable to targeted interventions.
Square Root Principal Component Pursuit: Tuning-Free Noisy Robust Matrix Recovery
Jun 17, 2021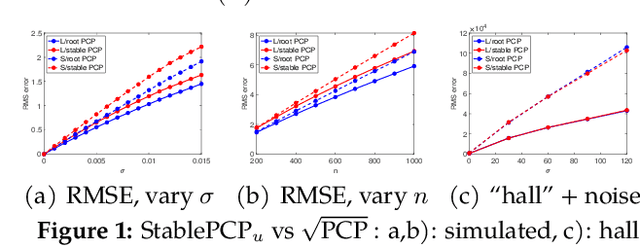
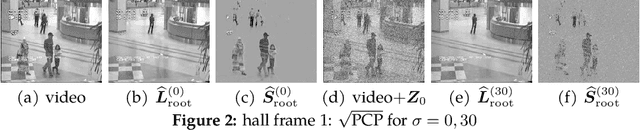
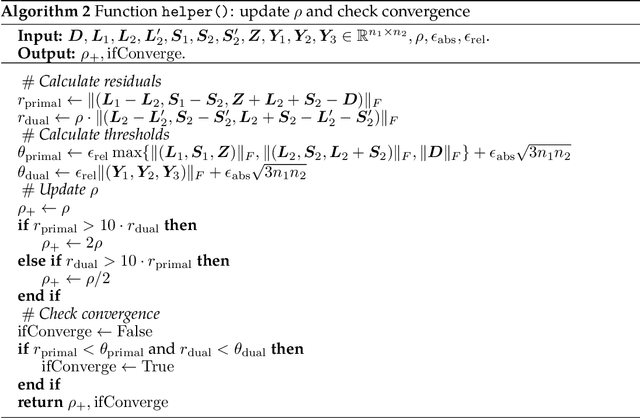
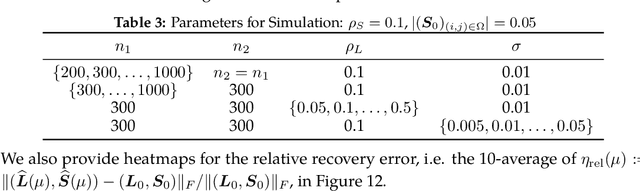
Abstract:We propose a new framework -- Square Root Principal Component Pursuit -- for low-rank matrix recovery from observations corrupted with noise and outliers. Inspired by the square root Lasso, this new formulation does not require prior knowledge of the noise level. We show that a single, universal choice of the regularization parameter suffices to achieve reconstruction error proportional to the (a priori unknown) noise level. In comparison, previous formulations such as stable PCP rely on noise-dependent parameters to achieve similar performance, and are therefore challenging to deploy in applications where the noise level is unknown. We validate the effectiveness of our new method through experiments on simulated and real datasets. Our simulations corroborate the claim that a universal choice of the regularization parameter yields near optimal performance across a range of noise levels, indicating that the proposed method outperforms the (somewhat loose) bound proved here.
Generalized Approach to Matched Filtering using Neural Networks
Apr 08, 2021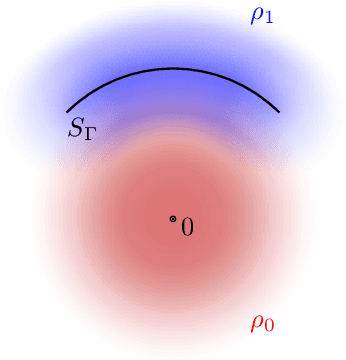
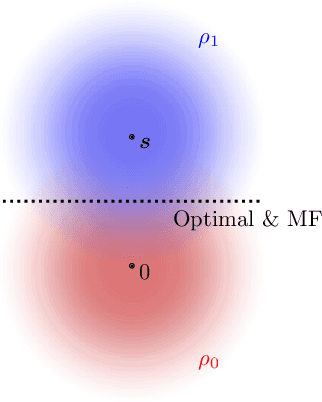
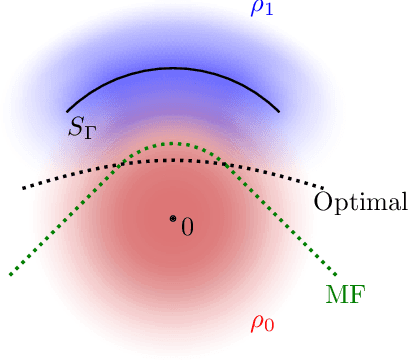
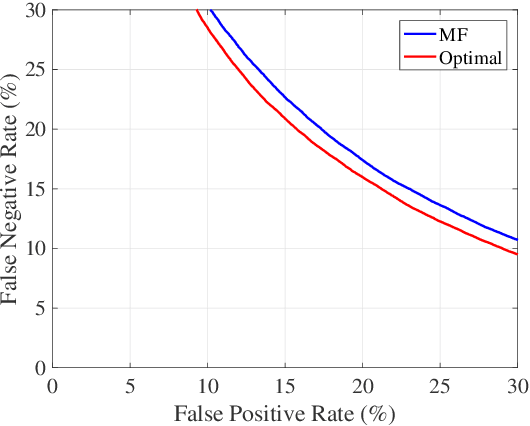
Abstract:Gravitational wave science is a pioneering field with rapidly evolving data analysis methodology currently assimilating and inventing deep learning techniques. The bulk of the sophisticated flagship searches of the field rely on the time-tested matched filtering principle within their core. In this paper, we make a key observation on the relationship between the emerging deep learning and the traditional techniques: matched filtering is formally equivalent to a particular neural network. This means that a neural network can be constructed analytically to exactly implement matched filtering, and can be further trained on data or boosted with additional complexity for improved performance. This fundamental equivalence allows us to define a "complexity standard candle" allowing us to characterize the relative complexity of the different approaches to gravitational wave signals in a common framework. Additionally it also provides a glimpse of an intriguing symmetry that could provide clues on how neural networks approach the problem of finding signals in overwhelming noise. Moreover, we show that the proposed neural network architecture can outperform matched filtering, both with or without knowledge of a prior on the parameter distribution. When a prior is given, the proposed neural network can approach the statistically optimal performance. We also propose and investigate two different neural network architectures MNet-Shallow and MNet-Deep, both of which implement matched filtering at initialization and can be trained on data. MNet-Shallow has simpler structure, while MNet-Deep is more flexible and can deal with a wider range of distributions. Our theoretical findings are corroborated by experiments using real LIGO data and synthetic injections. Finally, our results suggest new perspectives on the role of deep learning in gravitational wave detection.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge