Jinchao Ge
CIT: Rethinking Class-incremental Semantic Segmentation with a Class Independent Transformation
Nov 05, 2024


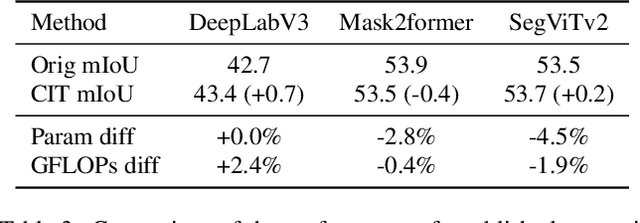
Abstract:Class-incremental semantic segmentation (CSS) requires that a model learn to segment new classes without forgetting how to segment previous ones: this is typically achieved by distilling the current knowledge and incorporating the latest data. However, bypassing iterative distillation by directly transferring outputs of initial classes to the current learning task is not supported in existing class-specific CSS methods. Via Softmax, they enforce dependency between classes and adjust the output distribution at each learning step, resulting in a large probability distribution gap between initial and current tasks. We introduce a simple, yet effective Class Independent Transformation (CIT) that converts the outputs of existing semantic segmentation models into class-independent forms with negligible cost or performance loss. By utilizing class-independent predictions facilitated by CIT, we establish an accumulative distillation framework, ensuring equitable incorporation of all class information. We conduct extensive experiments on various segmentation architectures, including DeepLabV3, Mask2Former, and SegViTv2. Results from these experiments show minimal task forgetting across different datasets, with less than 5% for ADE20K in the most challenging 11 task configurations and less than 1% across all configurations for the PASCAL VOC 2012 dataset.
ESA: Annotation-Efficient Active Learning for Semantic Segmentation
Aug 24, 2024Abstract:Active learning enhances annotation efficiency by selecting the most revealing samples for labeling, thereby reducing reliance on extensive human input. Previous methods in semantic segmentation have centered on individual pixels or small areas, neglecting the rich patterns in natural images and the power of advanced pre-trained models. To address these challenges, we propose three key contributions: Firstly, we introduce Entity-Superpixel Annotation (ESA), an innovative and efficient active learning strategy which utilizes a class-agnostic mask proposal network coupled with super-pixel grouping to capture local structural cues. Additionally, our method selects a subset of entities within each image of the target domain, prioritizing superpixels with high entropy to ensure comprehensive representation. Simultaneously, it focuses on a limited number of key entities, thereby optimizing for efficiency. By utilizing an annotator-friendly design that capitalizes on the inherent structure of images, our approach significantly outperforms existing pixel-based methods, achieving superior results with minimal queries, specifically reducing click cost by 98% and enhancing performance by 1.71%. For instance, our technique requires a mere 40 clicks for annotation, a stark contrast to the 5000 clicks demanded by conventional methods.
BHSD: A 3D Multi-Class Brain Hemorrhage Segmentation Dataset
Aug 23, 2023Abstract:Intracranial hemorrhage (ICH) is a pathological condition characterized by bleeding inside the skull or brain, which can be attributed to various factors. Identifying, localizing and quantifying ICH has important clinical implications, in a bleed-dependent manner. While deep learning techniques are widely used in medical image segmentation and have been applied to the ICH segmentation task, existing public ICH datasets do not support the multi-class segmentation problem. To address this, we develop the Brain Hemorrhage Segmentation Dataset (BHSD), which provides a 3D multi-class ICH dataset containing 192 volumes with pixel-level annotations and 2200 volumes with slice-level annotations across five categories of ICH. To demonstrate the utility of the dataset, we formulate a series of supervised and semi-supervised ICH segmentation tasks. We provide experimental results with state-of-the-art models as reference benchmarks for further model developments and evaluations on this dataset.
Semi-supervised Semantic Segmentation with Mutual Knowledge Distillation
Aug 30, 2022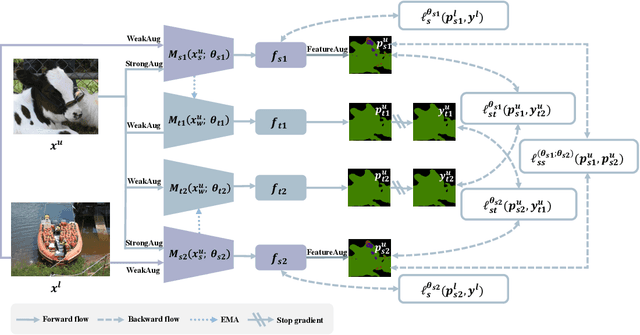
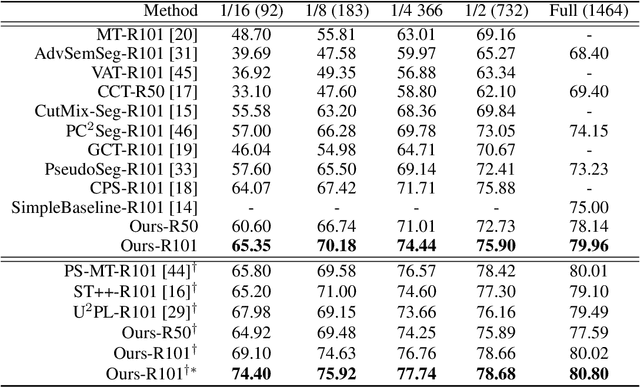
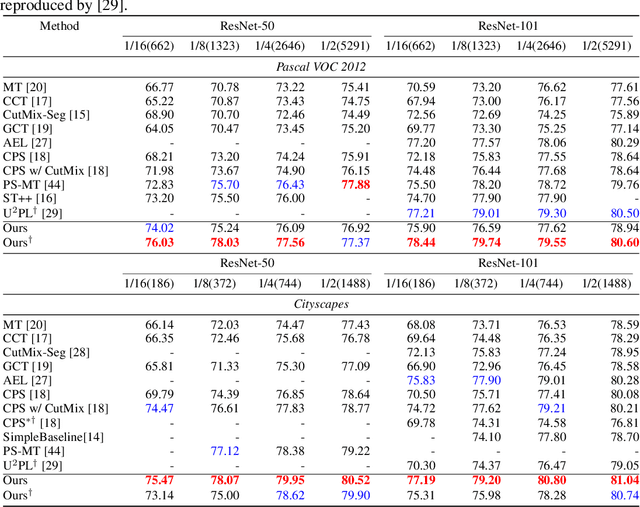

Abstract:Consistency regularization has been widely studied in recent semi-supervised semantic segmentation methods. Remarkable performance has been achieved, benefiting from image, feature, and network perturbations. To make full use of these perturbations, in this work, we propose a new consistency regularization framework called mutual knowledge distillation (MKD). We innovatively introduce two auxiliary mean-teacher models based on the consistency regularization method. More specifically, we use the pseudo label generated by one mean teacher to supervise the other student network to achieve a mutual knowledge distillation between two branches. In addition to using image-level strong and weak augmentation, we also employ feature augmentation considering implicit semantic distributions to add further perturbations to the students. The proposed framework significantly increases the diversity of the training samples. Extensive experiments on public benchmarks show that our framework outperforms previous state-of-the-art(SOTA) methods under various semi-supervised settings. Code is available at: https://github.com/jianlong-yuan/semi-mmseg.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge