Jin L. C. Guo
A Design Space for Intelligent and Interactive Writing Assistants
Mar 26, 2024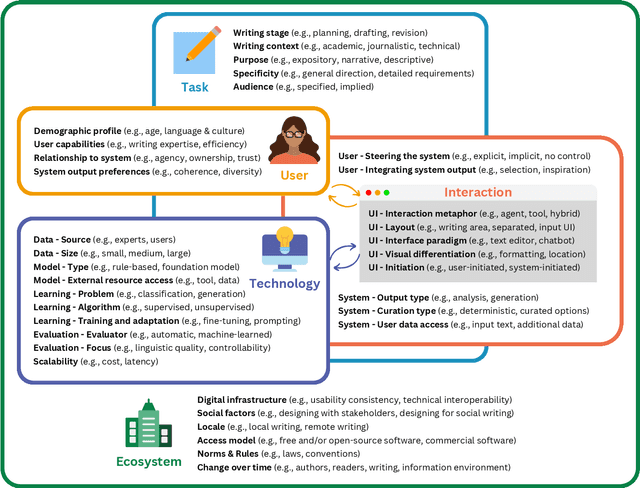
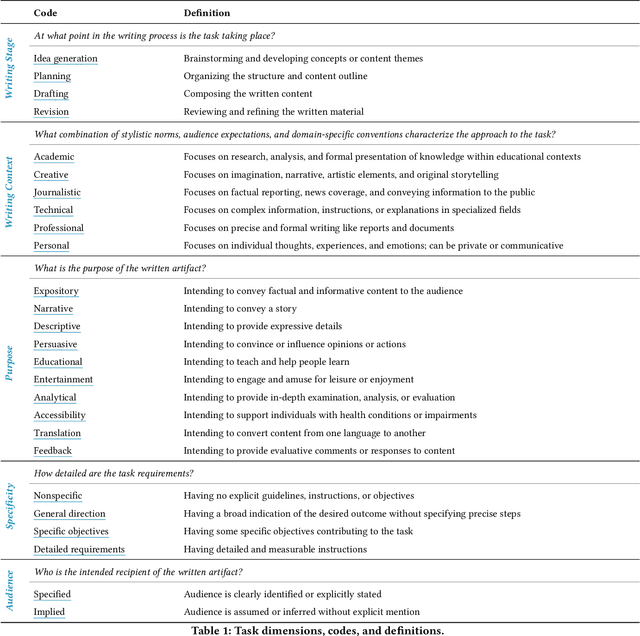
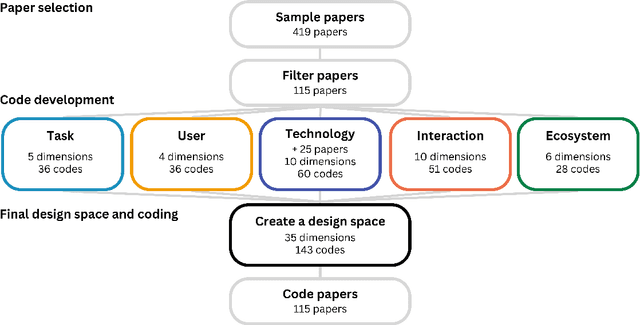
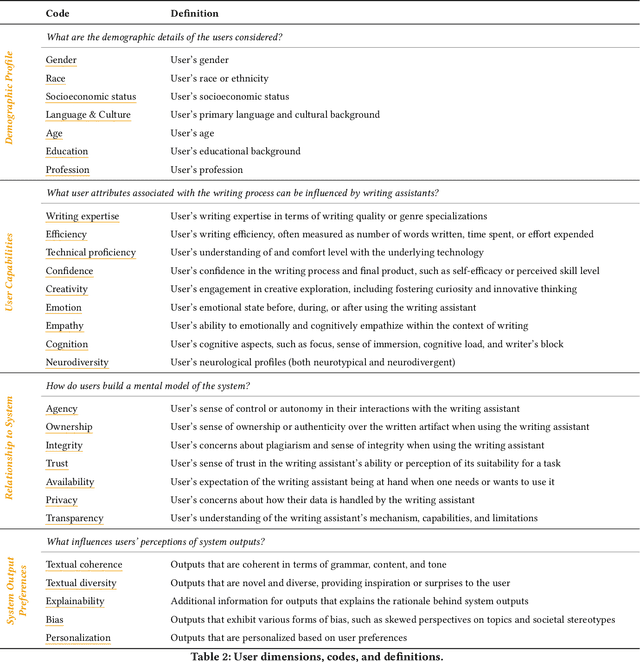
Abstract:In our era of rapid technological advancement, the research landscape for writing assistants has become increasingly fragmented across various research communities. We seek to address this challenge by proposing a design space as a structured way to examine and explore the multidimensional space of intelligent and interactive writing assistants. Through a large community collaboration, we explore five aspects of writing assistants: task, user, technology, interaction, and ecosystem. Within each aspect, we define dimensions (i.e., fundamental components of an aspect) and codes (i.e., potential options for each dimension) by systematically reviewing 115 papers. Our design space aims to offer researchers and designers a practical tool to navigate, comprehend, and compare the various possibilities of writing assistants, and aid in the envisioning and design of new writing assistants.
GUILGET: GUI Layout GEneration with Transformer
Apr 18, 2023Abstract:Sketching out Graphical User Interface (GUI) layout is part of the pipeline of designing a GUI and a crucial task for the success of a software application. Arranging all components inside a GUI layout manually is a time-consuming task. In order to assist designers, we developed a method named GUILGET to automatically generate GUI layouts from positional constraints represented as GUI arrangement graphs (GUI-AGs). The goal is to support the initial step of GUI design by producing realistic and diverse GUI layouts. The existing image layout generation techniques often cannot incorporate GUI design constraints. Thus, GUILGET needs to adapt existing techniques to generate GUI layouts that obey to constraints specific to GUI designs. GUILGET is based on transformers in order to capture the semantic in relationships between elements from GUI-AG. Moreover, the model learns constraints through the minimization of losses responsible for placing each component inside its parent layout, for not letting components overlap if they are inside the same parent, and for component alignment. Our experiments, which are conducted on the CLAY dataset, reveal that our model has the best understanding of relationships from GUI-AG and has the best performances in most of evaluation metrics. Therefore, our work contributes to improved GUI layout generation by proposing a novel method that effectively accounts for the constraints on GUI elements and paves the road for a more efficient GUI design pipeline.
Approach Intelligent Writing Assistants Usability with Seven Stages of Action
Apr 06, 2023Abstract:Despite the potential of Large Language Models (LLMs) as writing assistants, they are plagued by issues like coherence and fluency of the model output, trustworthiness, ownership of the generated content, and predictability of model performance, thereby limiting their usability. In this position paper, we propose to adopt Norman's seven stages of action as a framework to approach the interaction design of intelligent writing assistants. We illustrate the framework's applicability to writing tasks by providing an example of software tutorial authoring. The paper also discusses the framework as a tool to synthesize research on the interaction design of LLM-based tools and presents examples of tools that support the stages of action. Finally, we briefly outline the potential of a framework for human-LLM interaction research.
Aspirations and Practice of Model Documentation: Moving the Needle with Nudging and Traceability
Apr 13, 2022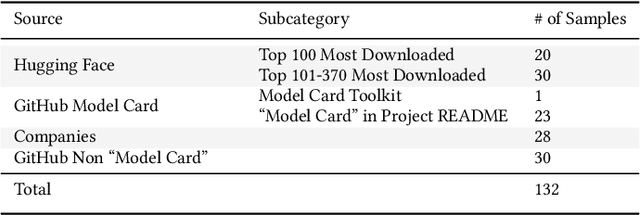
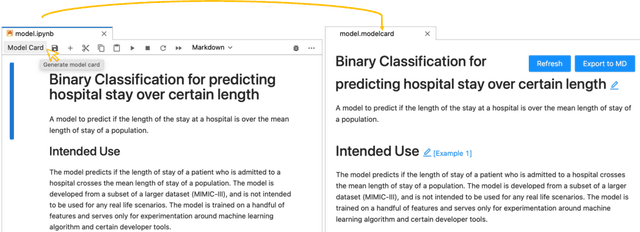
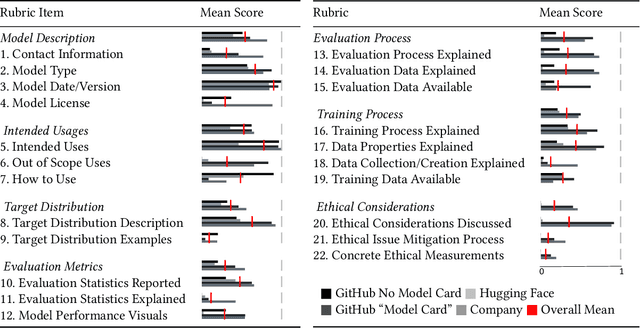
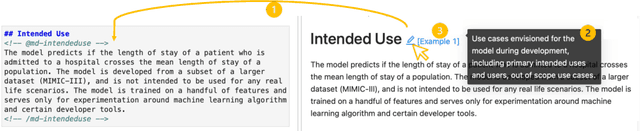
Abstract:Machine learning models have been widely developed, released, and adopted in numerous applications. Meanwhile, the documentation practice for machine learning models often falls short of established practices for traditional software components, which impedes model accountability, inadvertently abets inappropriate or misuse of models, and may trigger negative social impact. Recently, model cards, a template for documenting machine learning models, have attracted notable attention, but their impact on the practice of model documentation is unclear. In this work, we examine publicly available model cards and other similar documentation. Our analysis reveals a substantial gap between the suggestions made in the original model card work and the content in actual documentation. Motivated by this observation and literature on fields such as software documentation, interaction design, and traceability, we further propose a set of design guidelines that aim to support the documentation practice for machine learning models including (1) the collocation of documentation environment with the coding environment, (2) nudging the consideration of model card sections during model development, and (3) documentation derived from and traced to the source. We designed a prototype tool named DocML following those guidelines to support model development in computational notebooks. A lab study reveals the benefit of our tool to shift the behavior of data scientists towards documentation quality and accountability.
Software Engineering Event Modeling using Relative Time in Temporal Knowledge Graphs
Jul 13, 2020



Abstract:We present a multi-relational temporal Knowledge Graph based on the daily interactions between artifacts in GitHub, one of the largest social coding platforms. Such representation enables posing many user-activity and project management questions as link prediction and time queries over the knowledge graph. In particular, we introduce two new datasets for i) interpolated time-conditioned link prediction and ii) extrapolated time-conditioned link/time prediction queries, each with distinguished properties. Our experiments on these datasets highlight the potential of adapting knowledge graphs to answer broad software engineering questions. Meanwhile, it also reveals the unsatisfactory performance of existing temporal models on extrapolated queries and time prediction queries in general. To overcome these shortcomings, we introduce an extension to current temporal models using relative temporal information with regards to past events.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge