Shurui Zhou
LLMs in Mobile Apps: Practices, Challenges, and Opportunities
Feb 21, 2025Abstract:The integration of AI techniques has become increasingly popular in software development, enhancing performance, usability, and the availability of intelligent features. With the rise of large language models (LLMs) and generative AI, developers now have access to a wealth of high-quality open-source models and APIs from closed-source providers, enabling easier experimentation and integration of LLMs into various systems. This has also opened new possibilities in mobile application (app) development, allowing for more personalized and intelligent apps. However, integrating LLM into mobile apps might present unique challenges for developers, particularly regarding mobile device constraints, API management, and code infrastructure. In this project, we constructed a comprehensive dataset of 149 LLM-enabled Android apps and conducted an exploratory analysis to understand how LLMs are deployed and used within mobile apps. This analysis highlights key characteristics of the dataset, prevalent integration strategies, and common challenges developers face. Our findings provide valuable insights for future research and tooling development aimed at enhancing LLM-enabled mobile apps.
A Meta-Summary of Challenges in Building Products with ML Components -- Collecting Experiences from 4758+ Practitioners
Mar 31, 2023Abstract:Incorporating machine learning (ML) components into software products raises new software-engineering challenges and exacerbates existing challenges. Many researchers have invested significant effort in understanding the challenges of industry practitioners working on building products with ML components, through interviews and surveys with practitioners. With the intention to aggregate and present their collective findings, we conduct a meta-summary study: We collect 50 relevant papers that together interacted with over 4758 practitioners using guidelines for systematic literature reviews. We then collected, grouped, and organized the over 500 mentions of challenges within those papers. We highlight the most commonly reported challenges and hope this meta-summary will be a useful resource for the research community to prioritize research and education in this field.
* 15 pages, 2 figures, 3 tables, published in CAIN 2023
Aspirations and Practice of Model Documentation: Moving the Needle with Nudging and Traceability
Apr 13, 2022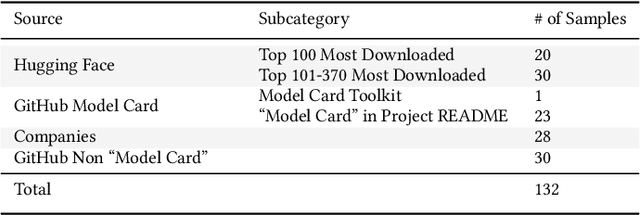
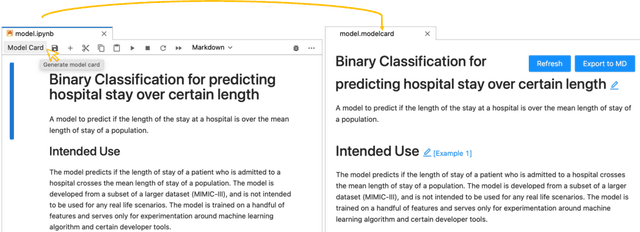
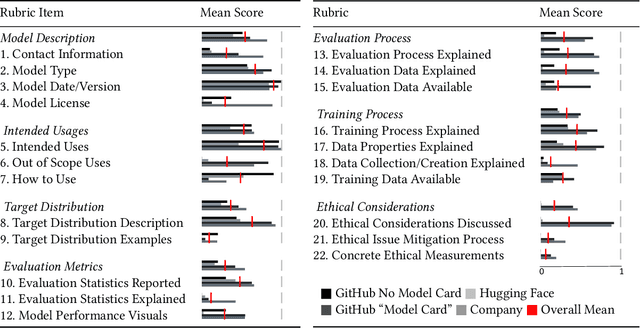
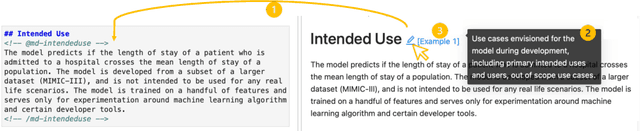
Abstract:Machine learning models have been widely developed, released, and adopted in numerous applications. Meanwhile, the documentation practice for machine learning models often falls short of established practices for traditional software components, which impedes model accountability, inadvertently abets inappropriate or misuse of models, and may trigger negative social impact. Recently, model cards, a template for documenting machine learning models, have attracted notable attention, but their impact on the practice of model documentation is unclear. In this work, we examine publicly available model cards and other similar documentation. Our analysis reveals a substantial gap between the suggestions made in the original model card work and the content in actual documentation. Motivated by this observation and literature on fields such as software documentation, interaction design, and traceability, we further propose a set of design guidelines that aim to support the documentation practice for machine learning models including (1) the collocation of documentation environment with the coding environment, (2) nudging the consideration of model card sections during model development, and (3) documentation derived from and traced to the source. We designed a prototype tool named DocML following those guidelines to support model development in computational notebooks. A lab study reveals the benefit of our tool to shift the behavior of data scientists towards documentation quality and accountability.
More Engineering, No Silos: Rethinking Processes and Interfaces in Collaboration between Interdisciplinary Teams for Machine Learning Projects
Oct 19, 2021
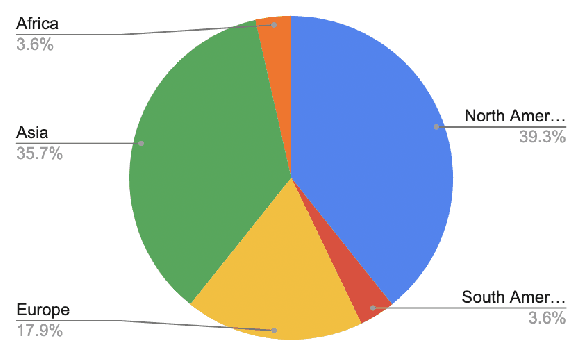
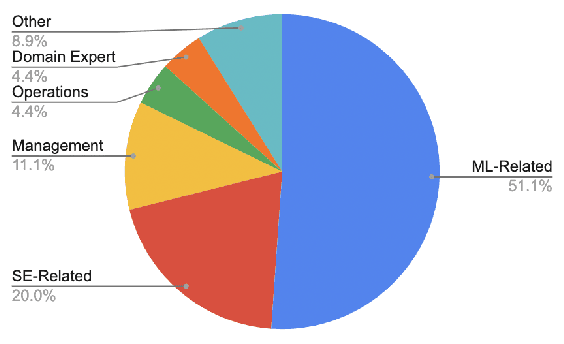
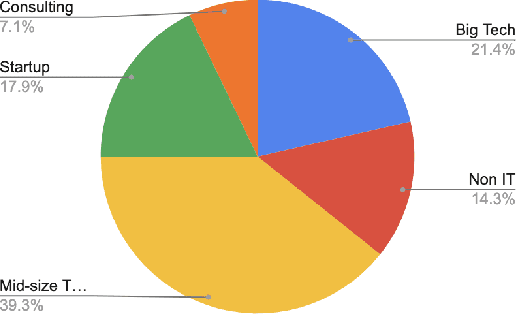
Abstract:The introduction of machine learning (ML) components in software projects has created the need for software engineers to collaborate with data scientists and other specialists. While collaboration can always be challenging, ML introduces additional challenges with its exploratory model development process, additional skills and knowledge needed, difficulties testing ML systems, need for continuous evolution and monitoring, and non-traditional quality requirements such as fairness and explainability. Through interviews with 45 practitioners from 28 organizations, we identified key collaboration challenges that teams face when building and deploying ML systems into production. We report on common collaboration points in the development of production ML systems for requirements, data, and integration, as well as corresponding team patterns and challenges. We find that most of these challenges center around communication, documentation, engineering, and process and collect recommendations to address these challenges.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge