Jihao Yin
DefMamba: Deformable Visual State Space Model
Apr 08, 2025



Abstract:Recently, state space models (SSM), particularly Mamba, have attracted significant attention from scholars due to their ability to effectively balance computational efficiency and performance. However, most existing visual Mamba methods flatten images into 1D sequences using predefined scan orders, which results the model being less capable of utilizing the spatial structural information of the image during the feature extraction process. To address this issue, we proposed a novel visual foundation model called DefMamba. This model includes a multi-scale backbone structure and deformable mamba (DM) blocks, which dynamically adjust the scanning path to prioritize important information, thus enhancing the capture and processing of relevant input features. By combining a deformable scanning(DS) strategy, this model significantly improves its ability to learn image structures and detects changes in object details. Numerous experiments have shown that DefMamba achieves state-of-the-art performance in various visual tasks, including image classification, object detection, instance segmentation, and semantic segmentation. The code is open source on DefMamba.
EagleVision: Object-level Attribute Multimodal LLM for Remote Sensing
Mar 30, 2025Abstract:Recent advances in multimodal large language models (MLLMs) have demonstrated impressive results in various visual tasks. However, in remote sensing (RS), high resolution and small proportion of objects pose challenges to existing MLLMs, which struggle with object-centric tasks, particularly in precise localization and fine-grained attribute description for each object. These RS MLLMs have not yet surpassed classical visual perception models, as they only provide coarse image understanding, leading to limited gains in real-world scenarios. To address this gap, we establish EagleVision, an MLLM tailored for remote sensing that excels in object detection and attribute comprehension. Equipped with the Attribute Disentangle module, EagleVision learns disentanglement vision tokens to express distinct attributes. To support object-level visual-language alignment, we construct EVAttrs-95K, the first large-scale object attribute understanding dataset in RS for instruction tuning, along with a novel evaluation benchmark, EVBench. EagleVision achieves state-of-the-art performance on both fine-grained object detection and object attribute understanding tasks, highlighting the mutual promotion between detection and understanding capabilities in MLLMs. The code, model, data, and demo will be available at https://github.com/XiangTodayEatsWhat/EagleVision.
Representation Disparity-aware Distillation for 3D Object Detection
Aug 20, 2023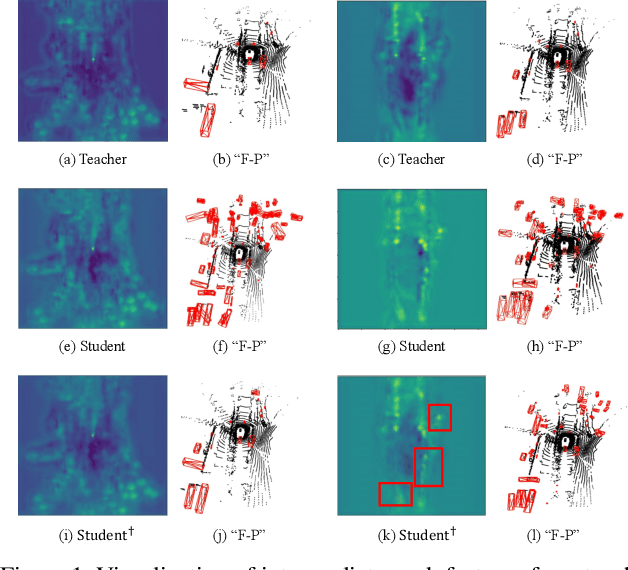
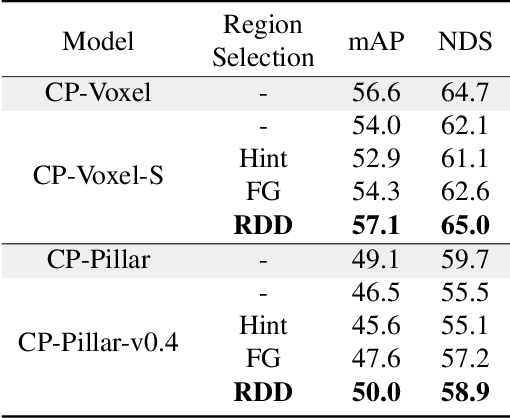
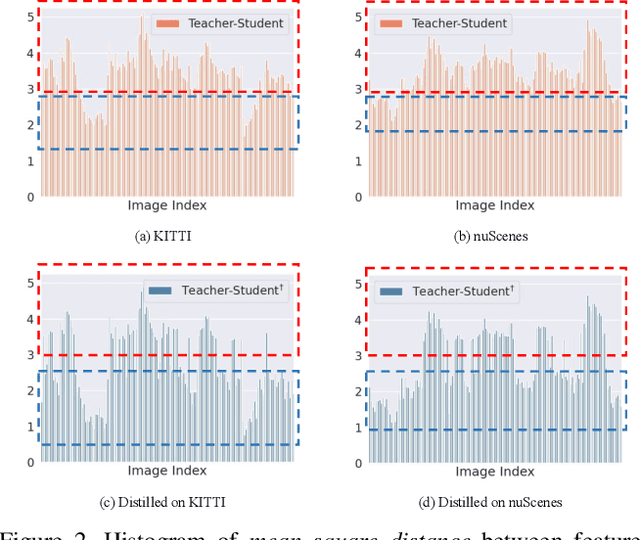
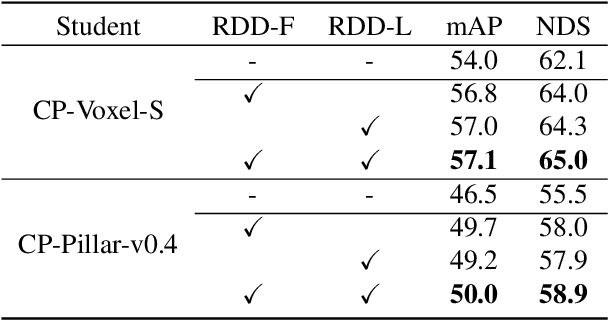
Abstract:In this paper, we focus on developing knowledge distillation (KD) for compact 3D detectors. We observe that off-the-shelf KD methods manifest their efficacy only when the teacher model and student counterpart share similar intermediate feature representations. This might explain why they are less effective in building extreme-compact 3D detectors where significant representation disparity arises due primarily to the intrinsic sparsity and irregularity in 3D point clouds. This paper presents a novel representation disparity-aware distillation (RDD) method to address the representation disparity issue and reduce performance gap between compact students and over-parameterized teachers. This is accomplished by building our RDD from an innovative perspective of information bottleneck (IB), which can effectively minimize the disparity of proposal region pairs from student and teacher in features and logits. Extensive experiments are performed to demonstrate the superiority of our RDD over existing KD methods. For example, our RDD increases mAP of CP-Voxel-S to 57.1% on nuScenes dataset, which even surpasses teacher performance while taking up only 42% FLOPs.
Multi-Camera Calibration Free BEV Representation for 3D Object Detection
Oct 31, 2022



Abstract:In advanced paradigms of autonomous driving, learning Bird's Eye View (BEV) representation from surrounding views is crucial for multi-task framework. However, existing methods based on depth estimation or camera-driven attention are not stable to obtain transformation under noisy camera parameters, mainly with two challenges, accurate depth prediction and calibration. In this work, we present a completely Multi-Camera Calibration Free Transformer (CFT) for robust BEV representation, which focuses on exploring implicit mapping, not relied on camera intrinsics and extrinsics. To guide better feature learning from image views to BEV, CFT mines potential 3D information in BEV via our designed position-aware enhancement (PA). Instead of camera-driven point-wise or global transformation, for interaction within more effective region and lower computation cost, we propose a view-aware attention which also reduces redundant computation and promotes converge. CFT achieves 49.7% NDS on the nuScenes detection task leaderboard, which is the first work removing camera parameters, comparable to other geometry-guided methods. Without temporal input and other modal information, CFT achieves second highest performance with a smaller image input 1600 * 640. Thanks to view-attention variant, CFT reduces memory and transformer FLOPs for vanilla attention by about 12% and 60%, respectively, with improved NDS by 1.0%. Moreover, its natural robustness to noisy camera parameters makes CFT more competitive.
Inference-InfoGAN: Inference Independence via Embedding Orthogonal Basis Expansion
Oct 02, 2021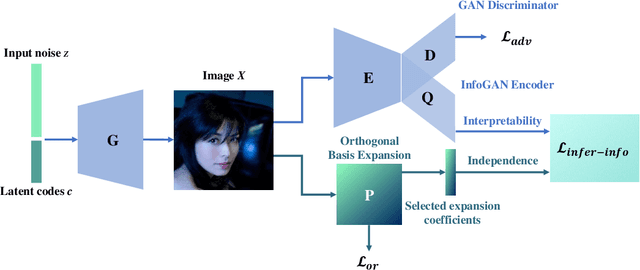
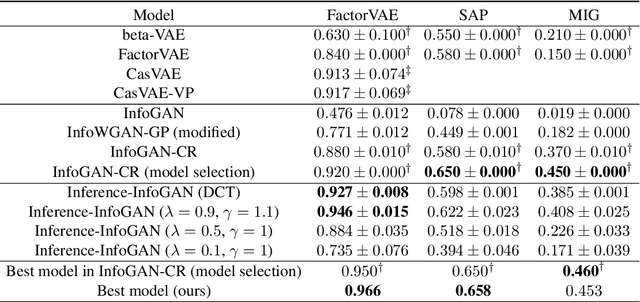
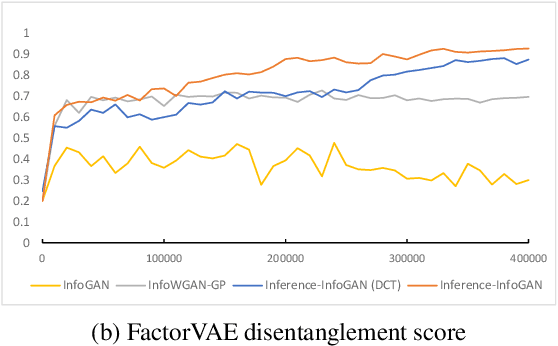
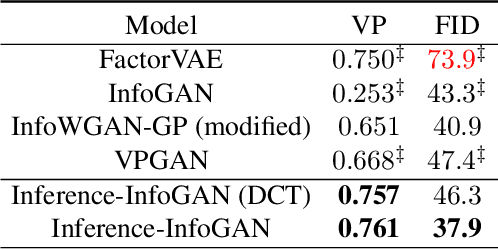
Abstract:Disentanglement learning aims to construct independent and interpretable latent variables in which generative models are a popular strategy. InfoGAN is a classic method via maximizing Mutual Information (MI) to obtain interpretable latent variables mapped to the target space. However, it did not emphasize independent characteristic. To explicitly infer latent variables with inter-independence, we propose a novel GAN-based disentanglement framework via embedding Orthogonal Basis Expansion (OBE) into InfoGAN network (Inference-InfoGAN) in an unsupervised way. Under the OBE module, one set of orthogonal basis can be adaptively found to expand arbitrary data with independence property. To ensure the target-wise interpretable representation, we add a consistence constraint between the expansion coefficients and latent variables on the base of MI maximization. Additionally, we design an alternating optimization step on the consistence constraint and orthogonal requirement updating, so that the training of Inference-InfoGAN can be more convenient. Finally, experiments validate that our proposed OBE module obtains adaptive orthogonal basis, which can express better independent characteristics than fixed basis expression of Discrete Cosine Transform (DCT). To depict the performance in downstream tasks, we compared with the state-of-the-art GAN-based and even VAE-based approaches on different datasets. Our Inference-InfoGAN achieves higher disentanglement score in terms of FactorVAE, Separated Attribute Predictability (SAP), Mutual Information Gap (MIG) and Variation Predictability (VP) metrics without model fine-tuning. All the experimental results illustrate that our method has inter-independence inference ability because of the OBE module, and provides a good trade-off between it and target-wise interpretability of latent variables via jointing the alternating optimization.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge