Ivan Kireev
Automated Evolutionary Optimization for Resource-Efficient Neural Network Training
Oct 10, 2025Abstract:There are many critical challenges in optimizing neural network models, including distributed computing, compression techniques, and efficient training, regardless of their application to specific tasks. Solving such problems is crucial because the need for scalable and resource-efficient models is increasing. To address these challenges, we have developed a new automated machine learning (AutoML) framework, Parameter Efficient Training with Robust Automation (PETRA). It applies evolutionary optimization to model architecture and training strategy. PETRA includes pruning, quantization, and loss regularization. Experimental studies on real-world data with financial event sequences, as well as image and time-series -- benchmarks, demonstrate PETRA's ability to improve neural model performance and scalability -- namely, a significant decrease in model size (up to 75%) and latency (up to 33%), and an increase in throughput (by 13%) without noticeable degradation in the target metric.
Universal representations for financial transactional data: embracing local, global, and external contexts
Apr 02, 2024



Abstract:Effective processing of financial transactions is essential for banking data analysis. However, in this domain, most methods focus on specialized solutions to stand-alone problems instead of constructing universal representations suitable for many problems. We present a representation learning framework that addresses diverse business challenges. We also suggest novel generative models that account for data specifics, and a way to integrate external information into a client's representation, leveraging insights from other customers' actions. Finally, we offer a benchmark, describing representation quality globally, concerning the entire transaction history; locally, reflecting the client's current state; and dynamically, capturing representation evolution over time. Our generative approach demonstrates superior performance in local tasks, with an increase in ROC-AUC of up to 14\% for the next MCC prediction task and up to 46\% for downstream tasks from existing contrastive baselines. Incorporating external information improves the scores by an additional 20\%.
Continuous-time convolutions model of event sequences
Feb 13, 2023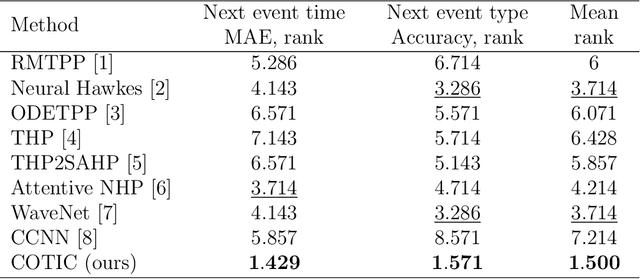
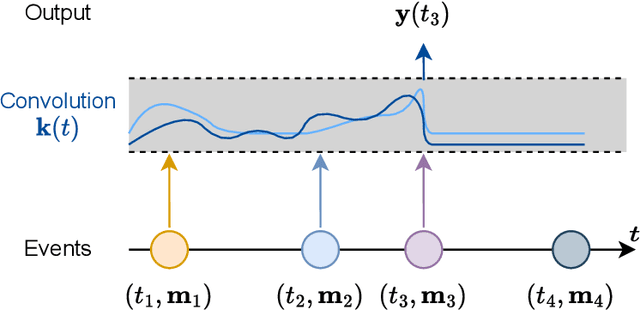
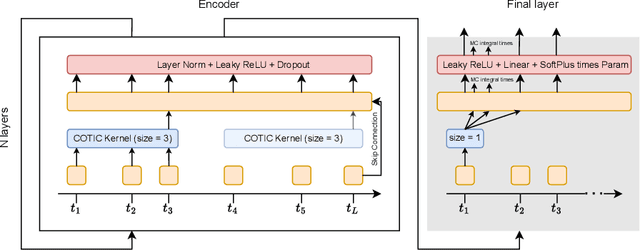
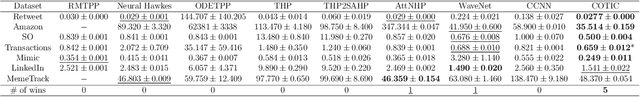
Abstract:Massive samples of event sequences data occur in various domains, including e-commerce, healthcare, and finance. There are two main challenges regarding inference of such data: computational and methodological. The amount of available data and the length of event sequences per client are typically large, thus it requires long-term modelling. Moreover, this data is often sparse and non-uniform, making classic approaches for time series processing inapplicable. Existing solutions include recurrent and transformer architectures in such cases. To allow continuous time, the authors introduce specific parametric intensity functions defined at each moment on top of existing models. Due to the parametric nature, these intensities represent only a limited class of event sequences. We propose the COTIC method based on a continuous convolution neural network suitable for non-uniform occurrence of events in time. In COTIC, dilations and multi-layer architecture efficiently handle dependencies between events. Furthermore, the model provides general intensity dynamics in continuous time - including self-excitement encountered in practice. The COTIC model outperforms existing approaches on majority of the considered datasets, producing embeddings for an event sequence that can be used to solve downstream tasks - e.g. predicting next event type and return time. The code of the proposed method can be found in the GitHub repository (https://github.com/VladislavZh/COTIC).
Adversarial Attacks on Deep Models for Financial Transaction Records
Jun 15, 2021
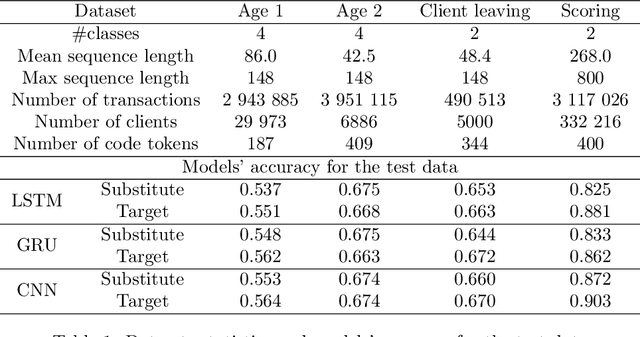
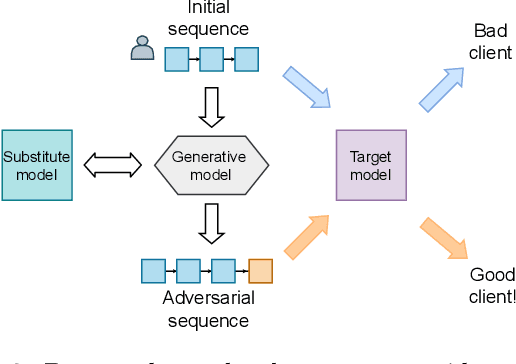
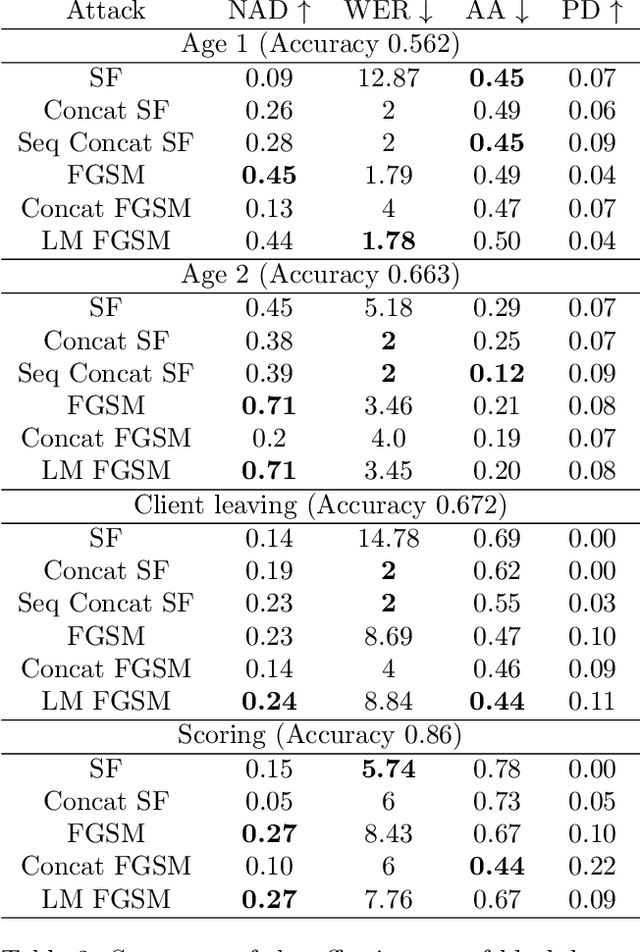
Abstract:Machine learning models using transaction records as inputs are popular among financial institutions. The most efficient models use deep-learning architectures similar to those in the NLP community, posing a challenge due to their tremendous number of parameters and limited robustness. In particular, deep-learning models are vulnerable to adversarial attacks: a little change in the input harms the model's output. In this work, we examine adversarial attacks on transaction records data and defences from these attacks. The transaction records data have a different structure than the canonical NLP or time series data, as neighbouring records are less connected than words in sentences, and each record consists of both discrete merchant code and continuous transaction amount. We consider a black-box attack scenario, where the attack doesn't know the true decision model, and pay special attention to adding transaction tokens to the end of a sequence. These limitations provide more realistic scenario, previously unexplored in NLP world. The proposed adversarial attacks and the respective defences demonstrate remarkable performance using relevant datasets from the financial industry. Our results show that a couple of generated transactions are sufficient to fool a deep-learning model. Further, we improve model robustness via adversarial training or separate adversarial examples detection. This work shows that embedding protection from adversarial attacks improves model robustness, allowing a wider adoption of deep models for transaction records in banking and finance.
Event sequence metric learning
Feb 19, 2020
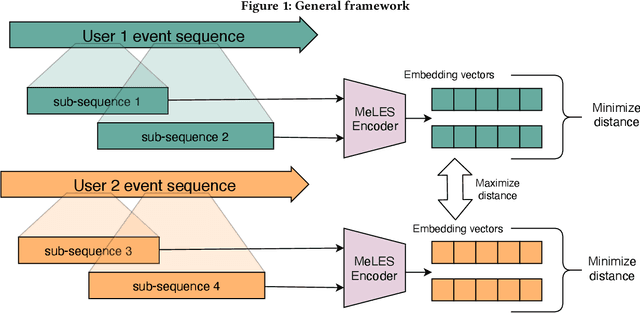

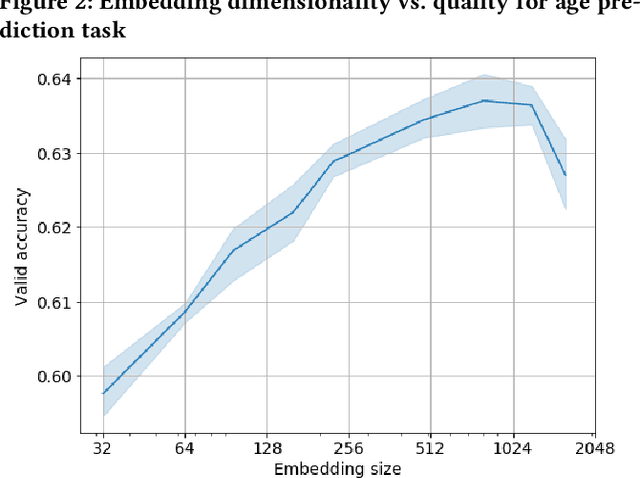
Abstract:In this paper we consider a challenging problem of learning discriminative vector representations for event sequences generated by real-world users. Vector representations map behavioral client raw data to the low-dimensional fixed-length vectors in the latent space. We propose a novel method of learning those vector embeddings based on metric learning approach. We propose a strategy of raw data subsequences generation to apply a metric learning approach in a fully self-supervised way. We evaluated the method over several public bank transactions datasets and showed that self-supervised embeddings outperform other methods when applied to downstream classification tasks. Moreover, embeddings are compact and provide additional user privacy protection.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge