Inkyu Jang
Enhancing Feature Tracking Reliability for Visual Navigation using Real-Time Safety Filter
Feb 03, 2025



Abstract:Vision sensors are extensively used for localizing a robot's pose, particularly in environments where global localization tools such as GPS or motion capture systems are unavailable. In many visual navigation systems, localization is achieved by detecting and tracking visual features or landmarks, which provide information about the sensor's relative pose. For reliable feature tracking and accurate pose estimation, it is crucial to maintain visibility of a sufficient number of features. This requirement can sometimes conflict with the robot's overall task objective. In this paper, we approach it as a constrained control problem. By leveraging the invariance properties of visibility constraints within the robot's kinematic model, we propose a real-time safety filter based on quadratic programming. This filter takes a reference velocity command as input and produces a modified velocity that minimally deviates from the reference while ensuring the information score from the currently visible features remains above a user-specified threshold. Numerical simulations demonstrate that the proposed safety filter preserves the invariance condition and ensures the visibility of more features than the required minimum. We also validated its real-world performance by integrating it into a visual simultaneous localization and mapping (SLAM) algorithm, where it maintained high estimation quality in challenging environments, outperforming a simple tracking controller.
DHRL: A Graph-Based Approach for Long-Horizon and Sparse Hierarchical Reinforcement Learning
Oct 11, 2022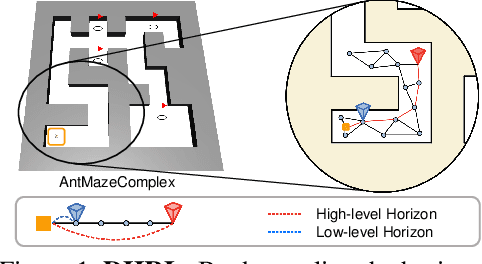

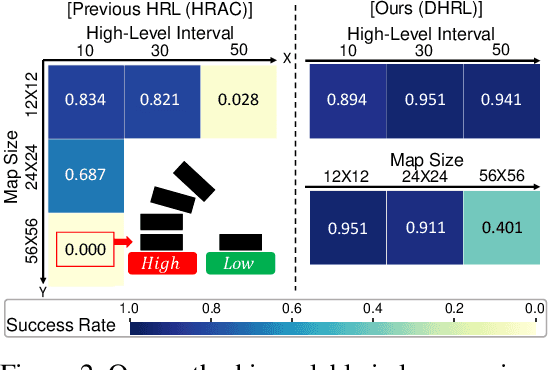

Abstract:Hierarchical Reinforcement Learning (HRL) has made notable progress in complex control tasks by leveraging temporal abstraction. However, previous HRL algorithms often suffer from serious data inefficiency as environments get large. The extended components, $i.e.$, goal space and length of episodes, impose a burden on either one or both high-level and low-level policies since both levels share the total horizon of the episode. In this paper, we present a method of Decoupling Horizons Using a Graph in Hierarchical Reinforcement Learning (DHRL) which can alleviate this problem by decoupling the horizons of high-level and low-level policies and bridging the gap between the length of both horizons using a graph. DHRL provides a freely stretchable high-level action interval, which facilitates longer temporal abstraction and faster training in complex tasks. Our method outperforms state-of-the-art HRL algorithms in typical HRL environments. Moreover, DHRL achieves long and complex locomotion and manipulation tasks.
Decentralized Deadlock-free Trajectory Planning for Quadrotor Swarm in Obstacle-rich Environments -- Extended version
Sep 20, 2022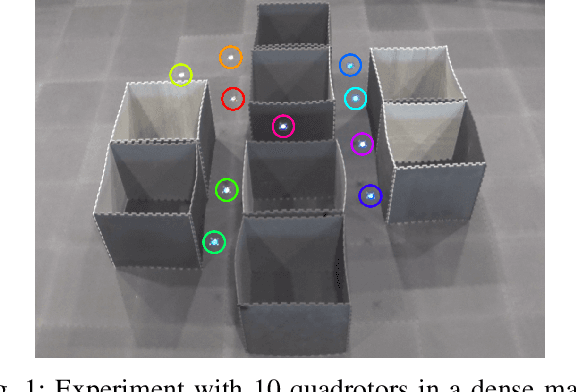
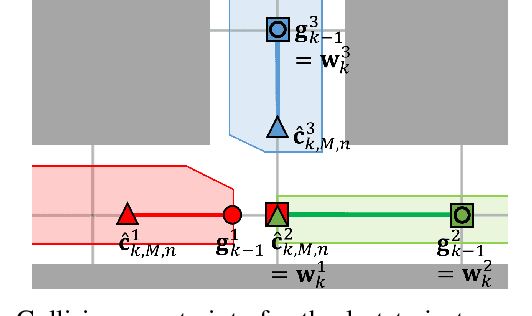
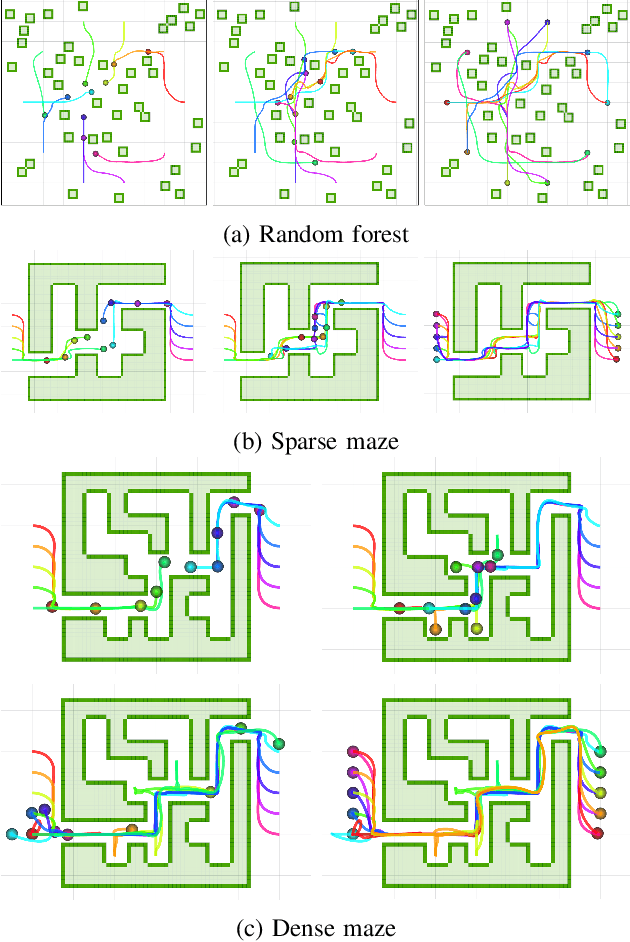
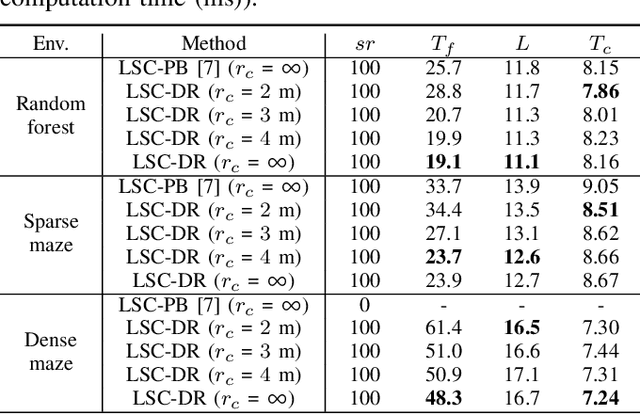
Abstract:This paper presents a decentralized multi-agent trajectory planning (MATP) algorithm that guarantees to generate a safe, deadlock-free trajectory in an obstacle-rich environment under a limited communication range. The proposed algorithm utilizes a grid-based multi-agent path planning (MAPP) algorithm for deadlock resolution, and we introduce the subgoal optimization method to make the agent converge to the waypoint generated from the MAPP without deadlock. In addition, the proposed algorithm ensures the feasibility of the optimization problem and collision avoidance by adopting a linear safe corridor (LSC). We verify that the proposed algorithm does not cause a deadlock in both random forests and dense mazes regardless of communication range, and it outperforms our previous work in flight time and distance. We validate the proposed algorithm through a hardware demonstration with ten quadrotors.
Robust and Recursively Feasible Real-Time Trajectory Planning in Unknown Environments
Jul 14, 2021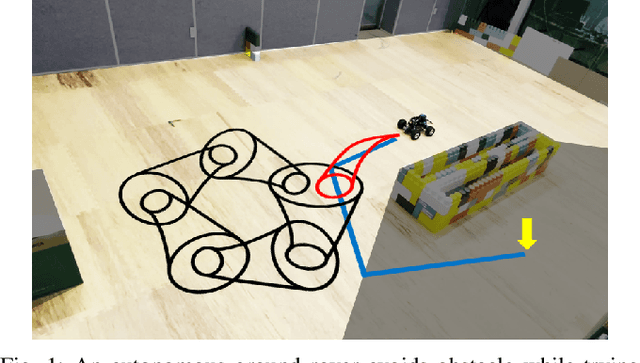
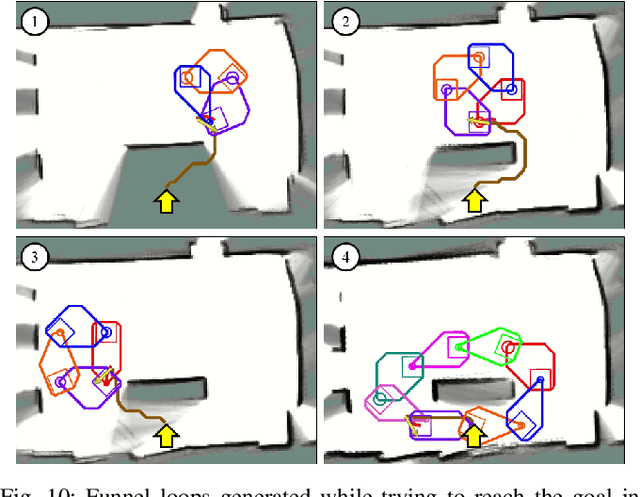


Abstract:Motion planners for mobile robots in unknown environments face the challenge of simultaneously maintaining both robustness against unmodeled uncertainties and persistent feasibility of the trajectory-finding problem. That is, while dealing with uncertainties, a motion planner must update its trajectory, adapting to the newly revealed environment in real-time; failing to do so may involve unsafe circumstances. Many existing planning algorithms guarantee these by maintaining the clearance needed to perform an emergency brake, which is itself a robust and persistently feasible maneuver. However, such maneuvers are not applicable for systems in which braking is impossible or risky, such as fixed-wing aircraft. To that end, we propose a real-time robust planner that recursively guarantees persistent feasibility without any need of braking. The planner ensures robustness against bounded uncertainties and persistent feasibility by constructing a loop of sequentially composed funnels, starting from the receding horizon local trajectory's forward reachable set. We implement the proposed algorithm for a robotic car tracking a speed-fixed reference trajectory. The experiment results show that the proposed algorithm can be run at faster than 16 Hz, while successfully keeping the system away from entering any dead-end, to maintain safety and feasibility.
Real-Time Motion Planning of a Hydraulic Excavator using Trajectory Optimization and Model Predictive Control
Jul 08, 2021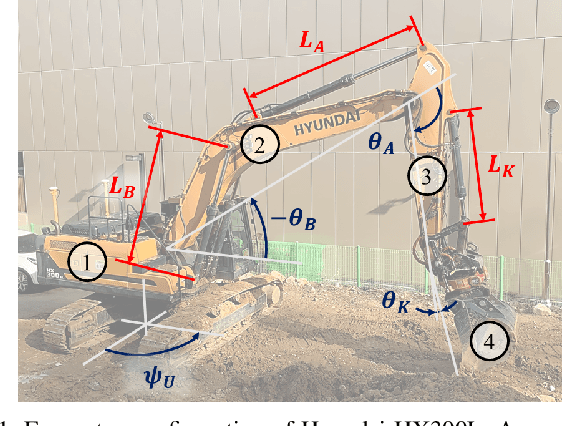
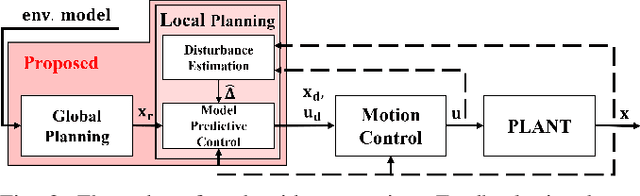
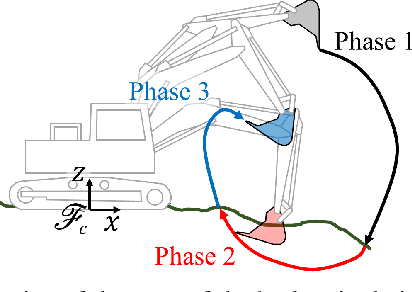
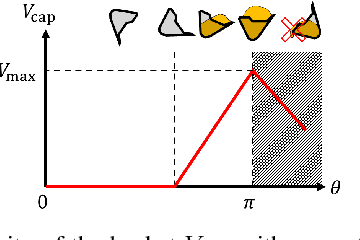
Abstract:Automation of excavation tasks requires real-time trajectory planning satisfying various constraints. To guarantee both constraint feasibility and real-time trajectory re-plannability, we present an integrated framework for real-time optimization-based trajectory planning of a hydraulic excavator. The proposed framework is composed of two main modules: a global planner and a real-time local planner. The global planner computes the entire global trajectory considering excavation volume and energy minimization while the local counterpart tracks the global trajectory in a receding horizon manner, satisfying dynamic feasibility, physical constraints, and disturbance-awareness. We validate the proposed planning algorithm in a simulation environment where two types of operations are conducted in the presence of emulated disturbance from hydraulic friction and soil-bucket interaction: shallow and deep excavation. The optimized global trajectories are obtained in an order of a second, which is tracked by the local planner at faster than 30 Hz. To the best of our knowledge, this work presents the first real-time motion planning framework that satisfies constraints of a hydraulic excavator, such as force/torque, power, cylinder displacement, and flow rate limits.
Stability and Robustness Analysis of Plug-Pulling using an Aerial Manipulator
Jul 06, 2021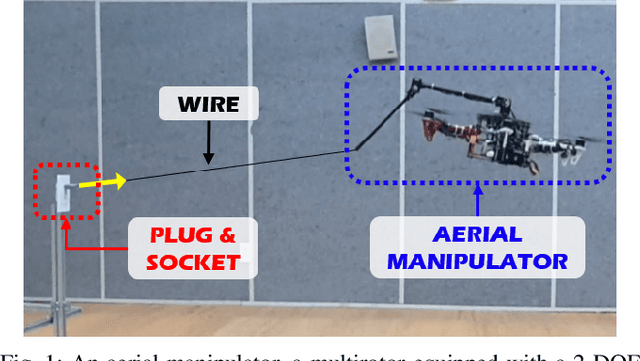
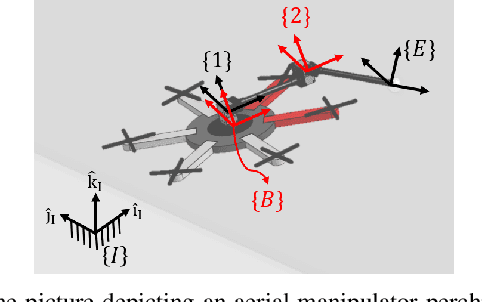

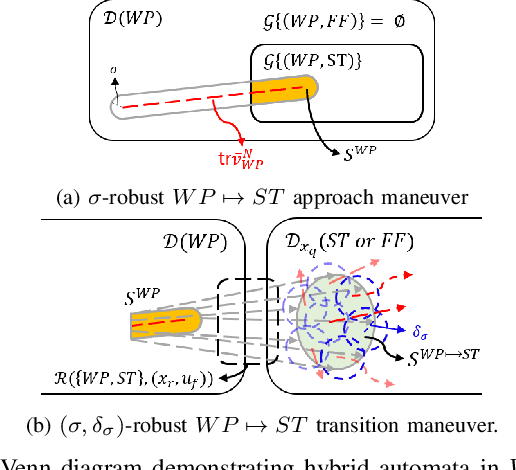
Abstract:In this paper, an autonomous aerial manipulation task of pulling a plug out of an electric socket is conducted, where maintaining the stability and robustness is challenging due to sudden disappearance of a large interaction force. The abrupt change in the dynamical model before and after the separation of the plug can cause destabilization or mission failure. To accomplish aerial plug-pulling, we employ the concept of hybrid automata to divide the task into three operative modes, i.e, wire-pulling, stabilizing, and free-flight. Also, a strategy for trajectory generation and a design of disturbance-observer-based controllers for each operative mode are presented. Furthermore, the theory of hybrid automata is used to prove the stability and robustness during the mode transition. We validate the proposed trajectory generation and control method by an actual wire-pulling experiment with a multirotor-based aerial manipulator.
Fail-safe Flight of a Fully-Actuated Quadcopter in a Single Motor Failure
Feb 26, 2020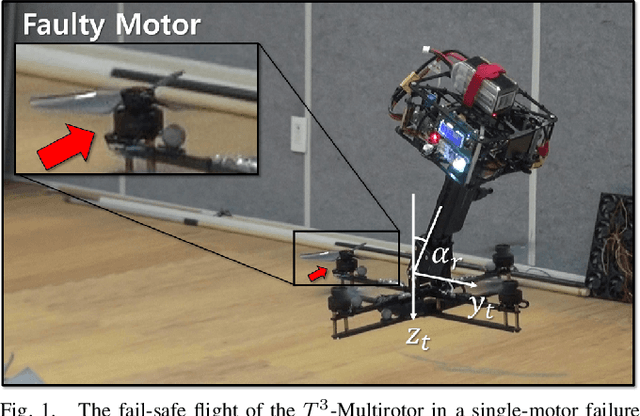
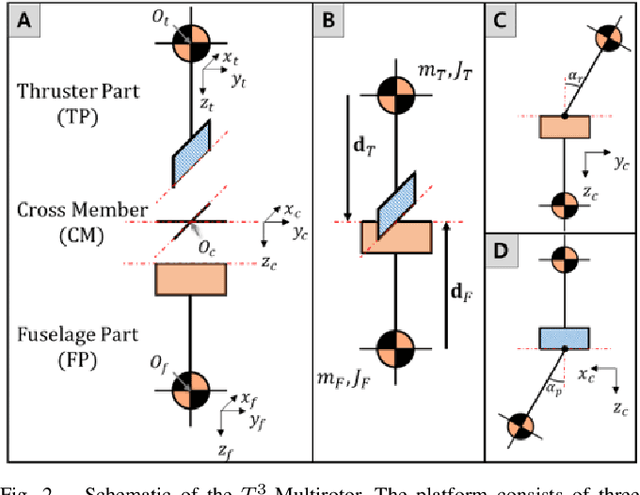
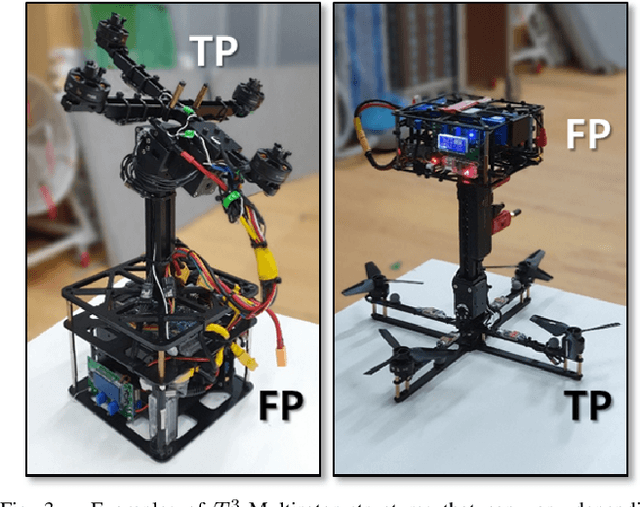
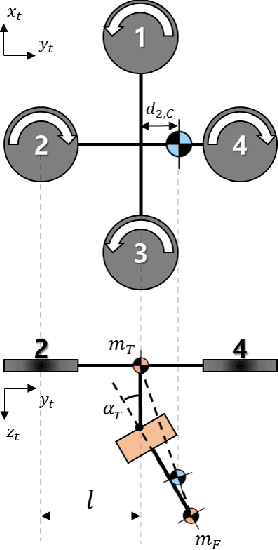
Abstract:In this paper, we introduce a new quadcopter fail-safe flight solution that can perform the same four controllable degrees-of-freedom flight as a regular multirotor even when a single thruster fails. The new solution employs a novel multirotor platform known as the T3-Multirotor and utilizes a distinctive strategy of actively controlling the center of gravity position to restore the nominal flight performance. A dedicated control structure is introduced, along with a detailed analysis of the dynamic characteristics of the platform that change during emergency flights. Experimental results are provided to validate the feasibility of the proposed fail-safe flight strategy.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge