Hugo Abonizio
Comparing Knowledge Injection Methods for LLMs in a Low-Resource Regime
Aug 08, 2025Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) often require vast amounts of text to effectively acquire new knowledge. While continuing pre-training on large corpora or employing retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) has proven successful, updating an LLM with only a few thousand or million tokens remains challenging. In this work, we investigate the task of injecting small, unstructured information into LLMs and its relation to the catastrophic forgetting phenomenon. We use a dataset of recent news -- ensuring no overlap with the model's pre-training data -- to evaluate the knowledge acquisition by probing the model with question-answer pairs related the learned information. Starting from a continued pre-training baseline, we explored different augmentation algorithms to generate synthetic data to improve the knowledge acquisition capabilities. Our experiments show that simply continuing pre-training on limited data yields modest improvements, whereas exposing the model to diverse textual variations significantly improves the learning of new facts -- particularly with methods that induce greater variability through diverse prompting. Furthermore, we shed light on the forgetting phenomenon in small-data regimes, illustrating the delicate balance between learning new content and retaining existing capabilities. We also confirm the sensitivity of RAG-based approaches for knowledge injection, which often lead to greater degradation on control datasets compared to parametric methods. Finally, we demonstrate that models can generate effective synthetic training data themselves, suggesting a pathway toward self-improving model updates. All code and generated data used in our experiments are publicly available, providing a resource for studying efficient knowledge injection in LLMs with limited data at https://github.com/hugoabonizio/knowledge-injection-methods.
TiEBe: A Benchmark for Assessing the Current Knowledge of Large Language Models
Jan 13, 2025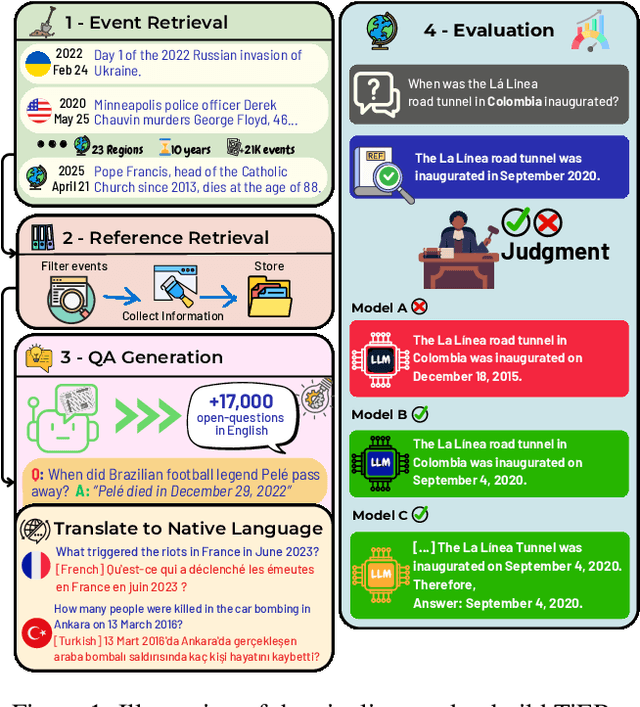
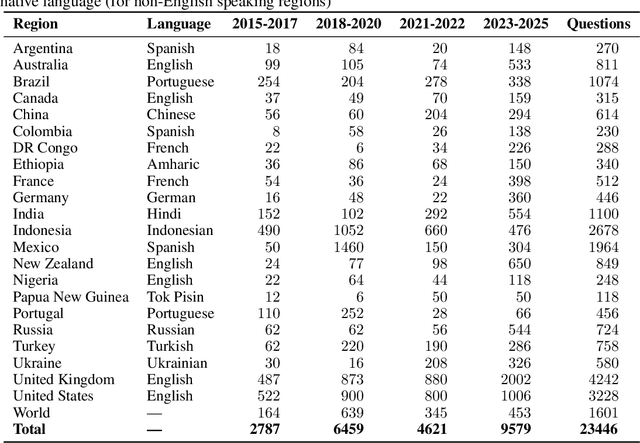

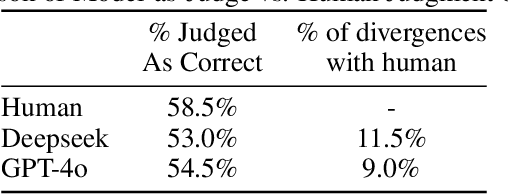
Abstract:In a rapidly evolving knowledge landscape and the increasing adoption of large language models, a need has emerged to keep these models continuously updated with current events. While existing benchmarks evaluate general factual recall, they often overlook two critical aspects: the ability of models to integrate evolving knowledge through continual learning and the significant regional disparities in their performance. To address these gaps, we introduce the Timely Events Benchmark (TiEBe), a dataset containing over 11,000 question-answer pairs focused on globally and regionally significant events. TiEBe leverages structured retrospective data from Wikipedia, enabling continuous updates to assess LLMs' knowledge of evolving global affairs and their understanding of events across different regions. Our benchmark demonstrates that LLMs exhibit substantial geographic disparities in factual recall, emphasizing the need for more balanced global knowledge representation. Furthermore, TiEBe serves as a tool for evaluating continual learning strategies, providing insights into models' ability to acquire new information without forgetting past knowledge.
Sabiá-3 Technical Report
Oct 15, 2024Abstract:This report presents Sabi\'a-3, our new flagship language model trained on a large brazilian-centric corpus. Evaluations across diverse professional and academic benchmarks show a strong performance on Portuguese and Brazil-related tasks. Sabi\'a-3 shows large improvements in comparison to our previous best of model, Sabi\'a-2 Medium, especially in reasoning-intensive tasks. Notably, Sabi\'a-3's average performance matches frontier LLMs, while it is offered at a three to four times lower cost per token, reinforcing the benefits of domain specialization.
Sabiá-2: A New Generation of Portuguese Large Language Models
Mar 26, 2024Abstract:We introduce Sabi\'a-2, a family of large language models trained on Portuguese texts. The models are evaluated on a diverse range of exams, including entry-level tests for Brazilian universities, professional certification exams, and graduate-level exams for various disciplines such as accounting, economics, engineering, law and medicine. Our results reveal that our best model so far, Sabi\'a-2 Medium, matches or surpasses GPT-4's performance in 23 out of 64 exams and outperforms GPT-3.5 in 58 out of 64 exams. Notably, specialization has a significant impact on a model's performance without the need to increase its size, allowing us to offer Sabi\'a-2 Medium at a price per token that is 10 times cheaper than GPT-4. Finally, we identified that math and coding are key abilities that need improvement.
Evaluating GPT-4's Vision Capabilities on Brazilian University Admission Exams
Nov 23, 2023Abstract:Recent advancements in language models have showcased human-comparable performance in academic entrance exams. However, existing studies often overlook questions that require the integration of visual comprehension, thus compromising the full spectrum and complexity inherent in real-world scenarios. To address this gap, we present a comprehensive framework to evaluate language models on entrance exams, which incorporates both textual and visual elements. We evaluate the two most recent editions of Exame Nacional do Ensino M\'edio (ENEM), the main standardized entrance examination adopted by Brazilian universities. Our study not only reaffirms the capabilities of GPT-4 as the state of the art for handling complex multidisciplinary questions, but also pioneers in offering a realistic assessment of multimodal language models on Portuguese examinations. One of the highlights is that text captions transcribing visual content outperform the direct use of images, suggesting that the vision model has room for improvement. Yet, despite improvements afforded by images or captions, mathematical questions remain a challenge for these state-of-the-art models. The code and data used on experiments are available at https://github.com/piresramon/gpt-4-enem.
InPars Toolkit: A Unified and Reproducible Synthetic Data Generation Pipeline for Neural Information Retrieval
Jul 10, 2023Abstract:Recent work has explored Large Language Models (LLMs) to overcome the lack of training data for Information Retrieval (IR) tasks. The generalization abilities of these models have enabled the creation of synthetic in-domain data by providing instructions and a few examples on a prompt. InPars and Promptagator have pioneered this approach and both methods have demonstrated the potential of using LLMs as synthetic data generators for IR tasks. This makes them an attractive solution for IR tasks that suffer from a lack of annotated data. However, the reproducibility of these methods was limited, because InPars' training scripts are based on TPUs -- which are not widely accessible -- and because the code for Promptagator was not released and its proprietary LLM is not publicly accessible. To fully realize the potential of these methods and make their impact more widespread in the research community, the resources need to be accessible and easy to reproduce by researchers and practitioners. Our main contribution is a unified toolkit for end-to-end reproducible synthetic data generation research, which includes generation, filtering, training and evaluation. Additionally, we provide an interface to IR libraries widely used by the community and support for GPU. Our toolkit not only reproduces the InPars method and partially reproduces Promptagator, but also provides a plug-and-play functionality allowing the use of different LLMs, exploring filtering methods and finetuning various reranker models on the generated data. We also made available all the synthetic data generated in this work for the 18 different datasets in the BEIR benchmark which took more than 2,000 GPU hours to be generated as well as the reranker models finetuned on the synthetic data. Code and data are available at https://github.com/zetaalphavector/InPars
Sabiá: Portuguese Large Language Models
Apr 18, 2023Abstract:As the capabilities of language models continue to advance, it is conceivable that "one-size-fits-all" model will remain as the main paradigm. For instance, given the vast number of languages worldwide, many of which are low-resource, the prevalent practice is to pretrain a single model on multiple languages. In this paper, we add to the growing body of evidence that challenges this practice, demonstrating that monolingual pretraining on the target language significantly improves models already extensively trained on diverse corpora. More specifically, we further pretrain GPT-J and LLaMA models on Portuguese texts using 3% or less of their original pretraining budget. Few-shot evaluations on Poeta, a suite of 14 Portuguese datasets, reveal that our models outperform English-centric and multilingual counterparts by a significant margin. Our best model, Sabi\'a-65B, performs on par with GPT-3.5-turbo. By evaluating on datasets originally conceived in the target language as well as translated ones, we study the contributions of language-specific pretraining in terms of 1) capturing linguistic nuances and structures inherent to the target language, and 2) enriching the model's knowledge about a domain or culture. Our results indicate that the majority of the benefits stem from the domain-specific knowledge acquired through monolingual pretraining.
InPars-v2: Large Language Models as Efficient Dataset Generators for Information Retrieval
Jan 14, 2023Abstract:Recently, InPars introduced a method to efficiently use large language models (LLMs) in information retrieval tasks: via few-shot examples, an LLM is induced to generate relevant queries for documents. These synthetic query-document pairs can then be used to train a retriever. However, InPars and, more recently, Promptagator, rely on proprietary LLMs such as GPT-3 and FLAN to generate such datasets. In this work we introduce InPars-v2, a dataset generator that uses open-source LLMs and existing powerful rerankers to select synthetic query-document pairs for training. A simple BM25 retrieval pipeline followed by a monoT5 reranker finetuned on InPars-v2 data achieves new state-of-the-art results on the BEIR benchmark. To allow researchers to further improve our method, we open source the code, synthetic data, and finetuned models: https://github.com/zetaalphavector/inPars/tree/master/tpu
In Defense of Cross-Encoders for Zero-Shot Retrieval
Dec 12, 2022Abstract:Bi-encoders and cross-encoders are widely used in many state-of-the-art retrieval pipelines. In this work we study the generalization ability of these two types of architectures on a wide range of parameter count on both in-domain and out-of-domain scenarios. We find that the number of parameters and early query-document interactions of cross-encoders play a significant role in the generalization ability of retrieval models. Our experiments show that increasing model size results in marginal gains on in-domain test sets, but much larger gains in new domains never seen during fine-tuning. Furthermore, we show that cross-encoders largely outperform bi-encoders of similar size in several tasks. In the BEIR benchmark, our largest cross-encoder surpasses a state-of-the-art bi-encoder by more than 4 average points. Finally, we show that using bi-encoders as first-stage retrievers provides no gains in comparison to a simpler retriever such as BM25 on out-of-domain tasks. The code is available at https://github.com/guilhermemr04/scaling-zero-shot-retrieval.git
MonoByte: A Pool of Monolingual Byte-level Language Models
Sep 27, 2022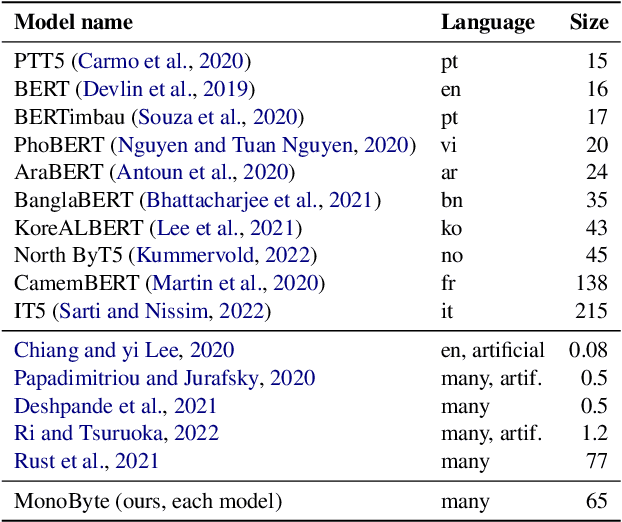
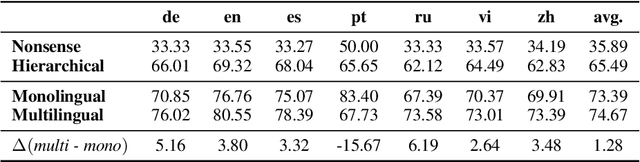
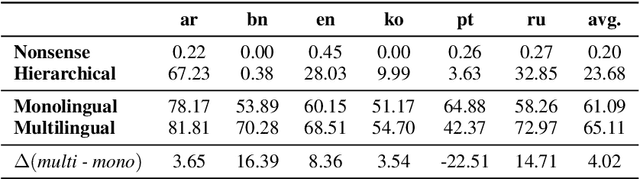
Abstract:The zero-shot cross-lingual ability of models pretrained on multilingual and even monolingual corpora has spurred many hypotheses to explain this intriguing empirical result. However, due to the costs of pretraining, most research uses public models whose pretraining methodology, such as the choice of tokenization, corpus size, and computational budget, might differ drastically. When researchers pretrain their own models, they often do so under a constrained budget, and the resulting models might underperform significantly compared to SOTA models. These experimental differences led to various inconsistent conclusions about the nature of the cross-lingual ability of these models. To help further research on the topic, we released 10 monolingual byte-level models rigorously pretrained under the same configuration with a large compute budget (equivalent to 420 days on a V100) and corpora that are 4 times larger than the original BERT's. Because they are tokenizer-free, the problem of unseen token embeddings is eliminated, thus allowing researchers to try a wider range of cross-lingual experiments in languages with different scripts. Additionally, we release two models pretrained on non-natural language texts that can be used in sanity-check experiments. Experiments on QA and NLI tasks show that our monolingual models achieve competitive performance to the multilingual one, and hence can be served to strengthen our understanding of cross-lingual transferability in language models.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge