Thiago Laitz
Ticket-Bench: A Kickoff for Multilingual and Regionalized Agent Evaluation
Sep 17, 2025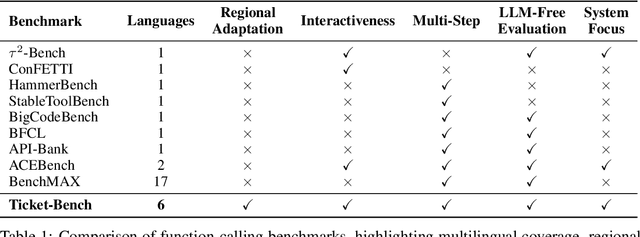
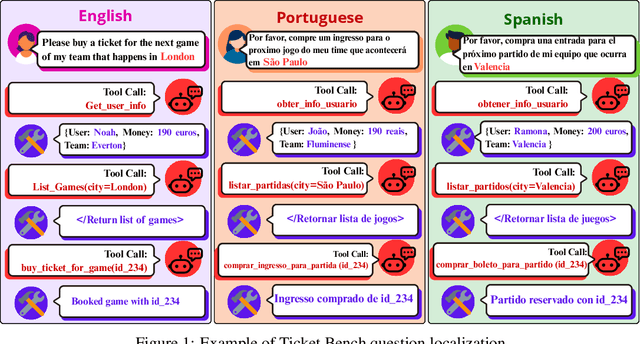
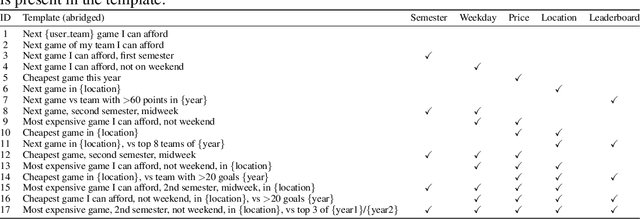
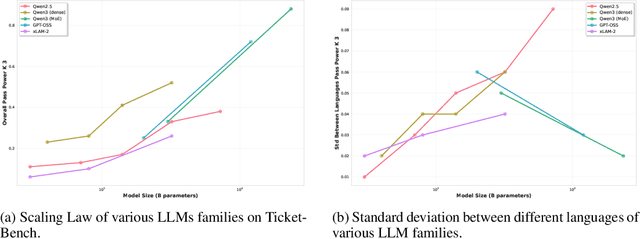
Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) are increasingly deployed as task-oriented agents, where success depends on their ability to generate accurate function calls under realistic, multilingual conditions. However, existing agent evaluations largely overlook cultural and linguistic diversity, often relying on monolingual or naively translated benchmarks. We introduce Ticket-Bench, a benchmark for multilingual agent evaluation in task-oriented scenarios. Ticket-Bench simulates the domain of soccer ticket purchases across six major languages: Portuguese, English, Spanish, German, Italian, and French. Using localized teams, cities, and user profiles to provide a higher level of realism. We evaluate a wide range of commercial and open-source LLMs, measuring function-calling accuracy and consistency across languages. Results show that reasoning-oriented models (e.g., GPT-5, Qwen3-235B) dominate performance but still exhibit notable cross-lingual disparities. These findings underscore the need for culturally aware, multilingual benchmarks to guide the development of robust LLM agents.
Sabiá-3 Technical Report
Oct 15, 2024Abstract:This report presents Sabi\'a-3, our new flagship language model trained on a large brazilian-centric corpus. Evaluations across diverse professional and academic benchmarks show a strong performance on Portuguese and Brazil-related tasks. Sabi\'a-3 shows large improvements in comparison to our previous best of model, Sabi\'a-2 Medium, especially in reasoning-intensive tasks. Notably, Sabi\'a-3's average performance matches frontier LLMs, while it is offered at a three to four times lower cost per token, reinforcing the benefits of domain specialization.
ExaRanker-Open: Synthetic Explanation for IR using Open-Source LLMs
Feb 09, 2024Abstract:ExaRanker recently introduced an approach to training information retrieval (IR) models, incorporating natural language explanations as additional labels. The method addresses the challenge of limited labeled examples, leading to improvements in the effectiveness of IR models. However, the initial results were based on proprietary language models such as GPT-3.5, which posed constraints on dataset size due to its cost and data privacy. In this paper, we introduce ExaRanker-Open, where we adapt and explore the use of open-source language models to generate explanations. The method has been tested using different LLMs and datasets sizes to better comprehend the effective contribution of data augmentation. Our findings reveal that incorporating explanations consistently enhances neural rankers, with benefits escalating as the LLM size increases. Notably, the data augmentation method proves advantageous even with large datasets, as evidenced by ExaRanker surpassing the target baseline by 0.6 nDCG@10 points in our study. To encourage further advancements by the research community, we have open-sourced both the code and datasets at https://github.com/unicamp-dl/ExaRanker.
InRanker: Distilled Rankers for Zero-shot Information Retrieval
Jan 12, 2024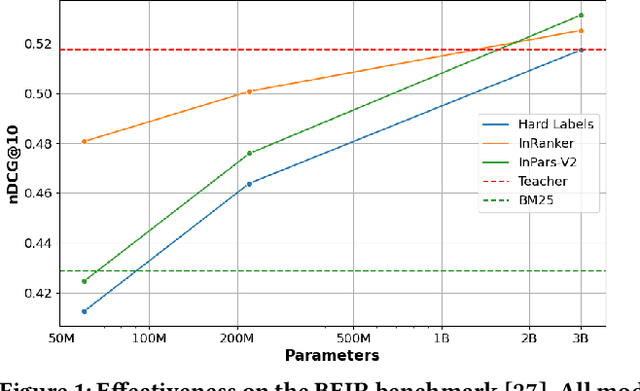
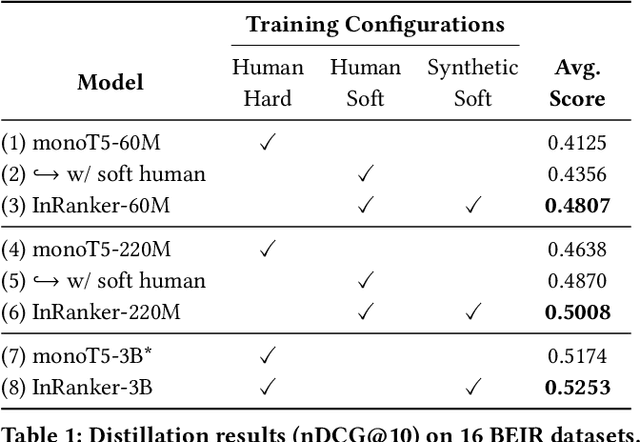
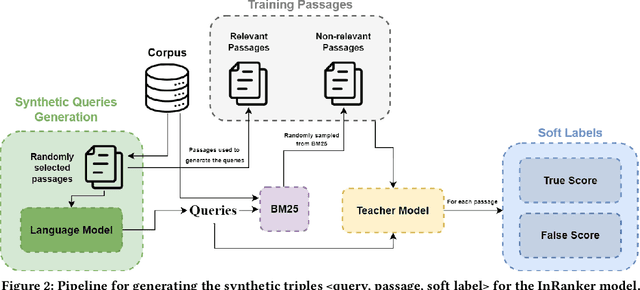
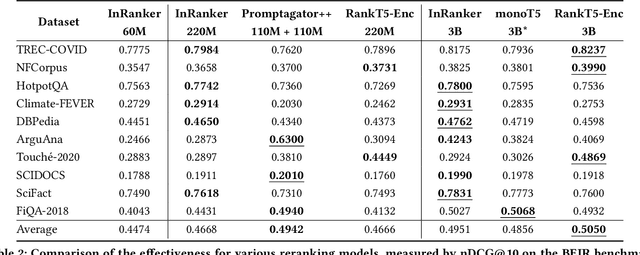
Abstract:Despite multi-billion parameter neural rankers being common components of state-of-the-art information retrieval pipelines, they are rarely used in production due to the enormous amount of compute required for inference. In this work, we propose a new method for distilling large rankers into their smaller versions focusing on out-of-domain effectiveness. We introduce InRanker, a version of monoT5 distilled from monoT5-3B with increased effectiveness on out-of-domain scenarios. Our key insight is to use language models and rerankers to generate as much as possible synthetic "in-domain" training data, i.e., data that closely resembles the data that will be seen at retrieval time. The pipeline consists of two distillation phases that do not require additional user queries or manual annotations: (1) training on existing supervised soft teacher labels, and (2) training on teacher soft labels for synthetic queries generated using a large language model. Consequently, models like monoT5-60M and monoT5-220M improved their effectiveness by using the teacher's knowledge, despite being 50x and 13x smaller, respectively. Models and code are available at https://github.com/unicamp-dl/InRanker.
BLUEX: A benchmark based on Brazilian Leading Universities Entrance eXams
Jul 11, 2023Abstract:One common trend in recent studies of language models (LMs) is the use of standardized tests for evaluation. However, despite being the fifth most spoken language worldwide, few such evaluations have been conducted in Portuguese. This is mainly due to the lack of high-quality datasets available to the community for carrying out evaluations in Portuguese. To address this gap, we introduce the Brazilian Leading Universities Entrance eXams (BLUEX), a dataset of entrance exams from the two leading universities in Brazil: UNICAMP and USP. The dataset includes annotated metadata for evaluating the performance of NLP models on a variety of subjects. Furthermore, BLUEX includes a collection of recently administered exams that are unlikely to be included in the training data of many popular LMs as of 2023. The dataset is also annotated to indicate the position of images in each question, providing a valuable resource for advancing the state-of-the-art in multimodal language understanding and reasoning. We describe the creation and characteristics of BLUEX and establish a benchmark through experiments with state-of-the-art LMs, demonstrating its potential for advancing the state-of-the-art in natural language understanding and reasoning in Portuguese. The data and relevant code can be found at https://github.com/Portuguese-Benchmark-Datasets/BLUEX
ExaRanker: Explanation-Augmented Neural Ranker
Jan 25, 2023Abstract:Recent work has shown that inducing a large language model (LLM) to generate explanations prior to outputting an answer is an effective strategy to improve performance on a wide range of reasoning tasks. In this work, we show that neural rankers also benefit from explanations. We use LLMs such as GPT-3.5 to augment retrieval datasets with explanations and train a sequence-to-sequence ranking model to output a relevance label and an explanation for a given query-document pair. Our model, dubbed ExaRanker, finetuned on a few thousand examples with synthetic explanations performs on par with models finetuned on 3x more examples without explanations. Furthermore, the ExaRanker model incurs no additional computational cost during ranking and allows explanations to be requested on demand.
NeuralSearchX: Serving a Multi-billion-parameter Reranker for Multilingual Metasearch at a Low Cost
Oct 26, 2022



Abstract:The widespread availability of search API's (both free and commercial) brings the promise of increased coverage and quality of search results for metasearch engines, while decreasing the maintenance costs of the crawling and indexing infrastructures. However, merging strategies frequently comprise complex pipelines that require careful tuning, which is often overlooked in the literature. In this work, we describe NeuralSearchX, a metasearch engine based on a multi-purpose large reranking model to merge results and highlight sentences. Due to the homogeneity of our architecture, we could focus our optimization efforts on a single component. We compare our system with Microsoft's Biomedical Search and show that our design choices led to a much cost-effective system with competitive QPS while having close to state-of-the-art results on a wide range of public benchmarks. Human evaluation on two domain-specific tasks shows that our retrieval system outperformed Google API by a large margin in terms of nDCG@10 scores. By describing our architecture and implementation in detail, we hope that the community will build on our design choices. The system is available at https://neuralsearchx.nsx.ai.
* published as a full paper at the DESIRES 2022 Conference. 13 pages
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge