Huanjun Deng
DXQ-Net: Differentiable LiDAR-Camera Extrinsic Calibration Using Quality-aware Flow
Mar 17, 2022



Abstract:Accurate LiDAR-camera extrinsic calibration is a precondition for many multi-sensor systems in mobile robots. Most calibration methods rely on laborious manual operations and calibration targets. While working online, the calibration methods should be able to extract information from the environment to construct the cross-modal data association. Convolutional neural networks (CNNs) have powerful feature extraction ability and have been used for calibration. However, most of the past methods solve the extrinsic as a regression task, without considering the geometric constraints involved. In this paper, we propose a novel end-to-end extrinsic calibration method named DXQ-Net, using a differentiable pose estimation module for generalization. We formulate a probabilistic model for LiDAR-camera calibration flow, yielding a prediction of uncertainty to measure the quality of LiDAR-camera data association. Testing experiments illustrate that our method achieves a competitive with other methods for the translation component and state-of-the-art performance for the rotation component. Generalization experiments illustrate that the generalization performance of our method is significantly better than other deep learning-based methods.
DuMLP-Pin: A Dual-MLP-dot-product Permutation-invariant Network for Set Feature Extraction
Mar 08, 2022



Abstract:Existing permutation-invariant methods can be divided into two categories according to the aggregation scope, i.e. global aggregation and local one. Although the global aggregation methods, e. g., PointNet and Deep Sets, get involved in simpler structures, their performance is poorer than the local aggregation ones like PointNet++ and Point Transformer. It remains an open problem whether there exists a global aggregation method with a simple structure, competitive performance, and even much fewer parameters. In this paper, we propose a novel global aggregation permutation-invariant network based on dual MLP dot-product, called DuMLP-Pin, which is capable of being employed to extract features for set inputs, including unordered or unstructured pixel, attribute, and point cloud data sets. We strictly prove that any permutation-invariant function implemented by DuMLP-Pin can be decomposed into two or more permutation-equivariant ones in a dot-product way as the cardinality of the given input set is greater than a threshold. We also show that the DuMLP-Pin can be viewed as Deep Sets with strong constraints under certain conditions. The performance of DuMLP-Pin is evaluated on several different tasks with diverse data sets. The experimental results demonstrate that our DuMLP-Pin achieves the best results on the two classification problems for pixel sets and attribute sets. On both the point cloud classification and the part segmentation, the accuracy of DuMLP-Pin is very close to the so-far best-performing local aggregation method with only a 1-2% difference, while the number of required parameters is significantly reduced by more than 85% in classification and 69% in segmentation, respectively. The code is publicly available on https://github.com/JaronTHU/DuMLP-Pin.
Translation Invariant Global Estimation of Heading Angle Using Sinogram of LiDAR Point Cloud
Mar 02, 2022



Abstract:Global point cloud registration is an essential module for localization, of which the main difficulty exists in estimating the rotation globally without initial value. With the aid of gravity alignment, the degree of freedom in point cloud registration could be reduced to 4DoF, in which only the heading angle is required for rotation estimation. In this paper, we propose a fast and accurate global heading angle estimation method for gravity-aligned point clouds. Our key idea is that we generate a translation invariant representation based on Radon Transform, allowing us to solve the decoupled heading angle globally with circular cross-correlation. Besides, for heading angle estimation between point clouds with different distributions, we implement this heading angle estimator as a differentiable module to train a feature extraction network end- to-end. The experimental results validate the effectiveness of the proposed method in heading angle estimation and show better performance compared with other methods.
PSF-LO: Parameterized Semantic Features Based Lidar Odometry
Oct 31, 2020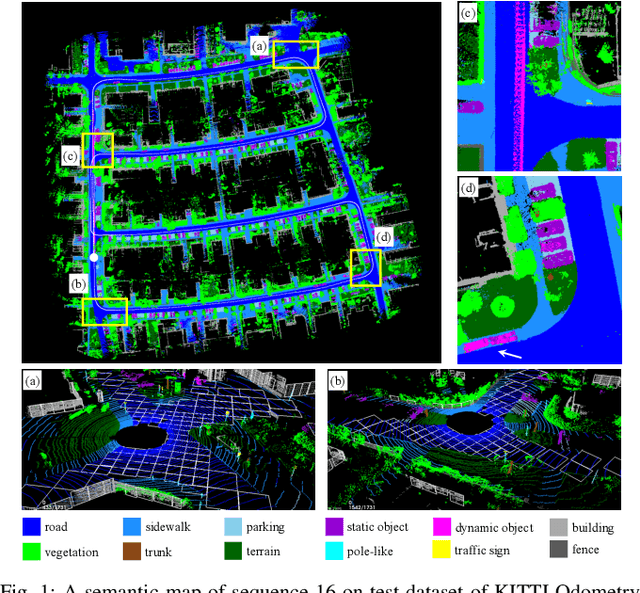
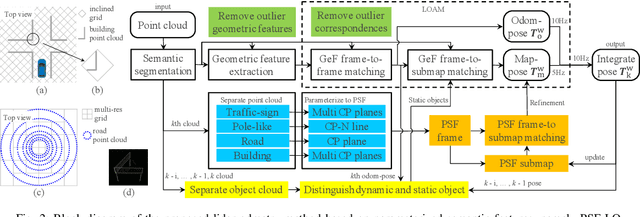
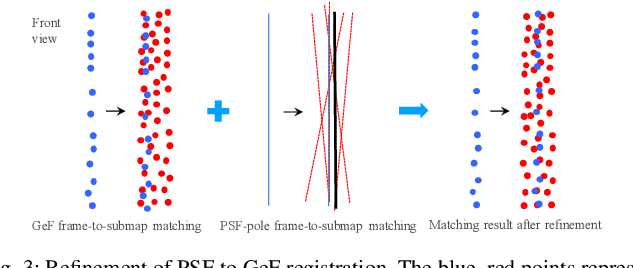
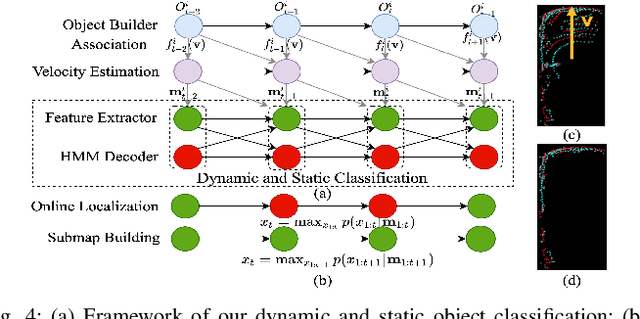
Abstract:Lidar odometry (LO) is a key technology in numerous reliable and accurate localization and mapping systems of autonomous driving. The state-of-the-art LO methods generally leverage geometric information to perform point cloud registration. Furthermore, obtaining point cloud semantic information which can describe the environment more abundantly will help for the registration. We present a novel semantic lidar odometry method based on self-designed parameterized semantic features (PSFs) to achieve low-drift ego-motion estimation for autonomous vehicle in realtime. We first use a convolutional neural network-based algorithm to obtain point-wise semantics from the input laser point cloud, and then use semantic labels to separate the road, building, traffic sign and pole-like point cloud and fit them separately to obtain corresponding PSFs. A fast PSF-based matching enable us to refine geometric features (GeFs) registration, reducing the impact of blurred submap surface on the accuracy of GeFs matching. Besides, we design an efficient method to accurately recognize and remove the dynamic objects while retaining static ones in the semantic point cloud, which are beneficial to further improve the accuracy of LO. We evaluated our method, namely PSF-LO, on the public dataset KITTI Odometry Benchmark and ranked #1 among semantic lidar methods with an average translation error of 0.82% in the test dataset at the time of writing.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge