Huamin Feng
Alleviating Structural Distribution Shift in Graph Anomaly Detection
Jan 25, 2024


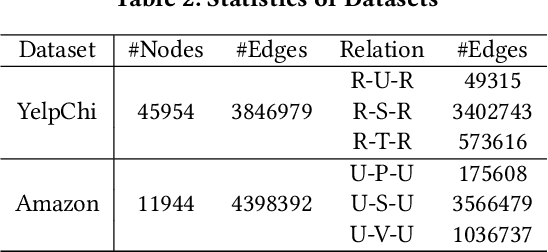
Abstract:Graph anomaly detection (GAD) is a challenging binary classification problem due to its different structural distribution between anomalies and normal nodes -- abnormal nodes are a minority, therefore holding high heterophily and low homophily compared to normal nodes. Furthermore, due to various time factors and the annotation preferences of human experts, the heterophily and homophily can change across training and testing data, which is called structural distribution shift (SDS) in this paper. The mainstream methods are built on graph neural networks (GNNs), benefiting the classification of normals from aggregating homophilous neighbors, yet ignoring the SDS issue for anomalies and suffering from poor generalization. This work solves the problem from a feature view. We observe that the degree of SDS varies between anomalies and normal nodes. Hence to address the issue, the key lies in resisting high heterophily for anomalies meanwhile benefiting the learning of normals from homophily. We tease out the anomaly features on which we constrain to mitigate the effect of heterophilous neighbors and make them invariant. We term our proposed framework as Graph Decomposition Network (GDN). Extensive experiments are conducted on two benchmark datasets, and the proposed framework achieves a remarkable performance boost in GAD, especially in an SDS environment where anomalies have largely different structural distribution across training and testing environments. Codes are open-sourced in https://github.com/blacksingular/wsdm_GDN.
Rumor Detection with Self-supervised Learning on Texts and Social Graph
Apr 19, 2022



Abstract:Rumor detection has become an emerging and active research field in recent years. At the core is to model the rumor characteristics inherent in rich information, such as propagation patterns in social network and semantic patterns in post content, and differentiate them from the truth. However, existing works on rumor detection fall short in modeling heterogeneous information, either using one single information source only (e.g. social network, or post content) or ignoring the relations among multiple sources (e.g. fusing social and content features via simple concatenation). Therefore, they possibly have drawbacks in comprehensively understanding the rumors, and detecting them accurately. In this work, we explore contrastive self-supervised learning on heterogeneous information sources, so as to reveal their relations and characterize rumors better. Technically, we supplement the main supervised task of detection with an auxiliary self-supervised task, which enriches post representations via post self-discrimination. Specifically, given two heterogeneous views of a post (i.e. representations encoding social patterns and semantic patterns), the discrimination is done by maximizing the mutual information between different views of the same post compared to that of other posts. We devise cluster-wise and instance-wise approaches to generate the views and conduct the discrimination, considering different relations of information sources. We term this framework as Self-supervised Rumor Detection (SRD). Extensive experiments on three real-world datasets validate the effectiveness of SRD for automatic rumor detection on social media.
Temporal RoI Align for Video Object Recognition
Sep 11, 2021



Abstract:Video object detection is challenging in the presence of appearance deterioration in certain video frames. Therefore, it is a natural choice to aggregate temporal information from other frames of the same video into the current frame. However, RoI Align, as one of the most core procedures of video detectors, still remains extracting features from a single-frame feature map for proposals, making the extracted RoI features lack temporal information from videos. In this work, considering the features of the same object instance are highly similar among frames in a video, a novel Temporal RoI Align operator is proposed to extract features from other frames feature maps for current frame proposals by utilizing feature similarity. The proposed Temporal RoI Align operator can extract temporal information from the entire video for proposals. We integrate it into single-frame video detectors and other state-of-the-art video detectors, and conduct quantitative experiments to demonstrate that the proposed Temporal RoI Align operator can consistently and significantly boost the performance. Besides, the proposed Temporal RoI Align can also be applied into video instance segmentation. Codes are available at https://github.com/open-mmlab/mmtracking
Reversible Watermarking in Deep Convolutional Neural Networks for Integrity Authentication
Apr 09, 2021



Abstract:Deep convolutional neural networks have made outstanding contributions in many fields such as computer vision in the past few years and many researchers published well-trained network for downloading. But recent studies have shown serious concerns about integrity due to model-reuse attacks and backdoor attacks. In order to protect these open-source networks, many algorithms have been proposed such as watermarking. However, these existing algorithms modify the contents of the network permanently and are not suitable for integrity authentication. In this paper, we propose a reversible watermarking algorithm for integrity authentication. Specifically, we present the reversible watermarking problem of deep convolutional neural networks and utilize the pruning theory of model compression technology to construct a host sequence used for embedding watermarking information by histogram shift. As shown in the experiments, the influence of embedding reversible watermarking on the classification performance is less than 0.5% and the parameters of the model can be fully recovered after extracting the watermarking. At the same time, the integrity of the model can be verified by applying the reversible watermarking: if the model is modified illegally, the authentication information generated by original model will be absolutely different from the extracted watermarking information.
Deep Model Intellectual Property Protection via Deep Watermarking
Mar 08, 2021



Abstract:Despite the tremendous success, deep neural networks are exposed to serious IP infringement risks. Given a target deep model, if the attacker knows its full information, it can be easily stolen by fine-tuning. Even if only its output is accessible, a surrogate model can be trained through student-teacher learning by generating many input-output training pairs. Therefore, deep model IP protection is important and necessary. However, it is still seriously under-researched. In this work, we propose a new model watermarking framework for protecting deep networks trained for low-level computer vision or image processing tasks. Specifically, a special task-agnostic barrier is added after the target model, which embeds a unified and invisible watermark into its outputs. When the attacker trains one surrogate model by using the input-output pairs of the barrier target model, the hidden watermark will be learned and extracted afterwards. To enable watermarks from binary bits to high-resolution images, a deep invisible watermarking mechanism is designed. By jointly training the target model and watermark embedding, the extra barrier can even be absorbed into the target model. Through extensive experiments, we demonstrate the robustness of the proposed framework, which can resist attacks with different network structures and objective functions.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge