Howard Morgan
TransAnaNet: Transformer-based Anatomy Change Prediction Network for Head and Neck Cancer Patient Radiotherapy
May 09, 2024



Abstract:Early identification of head and neck cancer (HNC) patients who would experience significant anatomical change during radiotherapy (RT) is important to optimize patient clinical benefit and treatment resources. This study aims to assess the feasibility of using a vision-transformer (ViT) based neural network to predict RT-induced anatomic change in HNC patients. We retrospectively included 121 HNC patients treated with definitive RT/CRT. We collected the planning CT (pCT), planned dose, CBCTs acquired at the initial treatment (CBCT01) and fraction 21 (CBCT21), and primary tumor volume (GTVp) and involved nodal volume (GTVn) delineated on both pCT and CBCTs for model construction and evaluation. A UNet-style ViT network was designed to learn spatial correspondence and contextual information from embedded CT, dose, CBCT01, GTVp, and GTVn image patches. The model estimated the deformation vector field between CBCT01 and CBCT21 as the prediction of anatomic change, and deformed CBCT01 was used as the prediction of CBCT21. We also generated binary masks of GTVp, GTVn, and patient body for volumetric change evaluation. The predicted image from the proposed method yielded the best similarity to the real image (CBCT21) over pCT, CBCT01, and predicted CBCTs from other comparison models. The average MSE and SSIM between the normalized predicted CBCT to CBCT21 are 0.009 and 0.933, while the average dice coefficient between body mask, GTVp mask, and GTVn mask are 0.972, 0.792, and 0.821 respectively. The proposed method showed promising performance for predicting radiotherapy-induced anatomic change, which has the potential to assist in the decision-making of HNC Adaptive RT.
Deep Learning (DL)-based Automatic Segmentation of the Internal Pudendal Artery (IPA) for Reduction of Erectile Dysfunction in Definitive Radiotherapy of Localized Prostate Cancer
Feb 03, 2023Abstract:Background and purpose: Radiation-induced erectile dysfunction (RiED) is commonly seen in prostate cancer patients. Clinical trials have been developed in multiple institutions to investigate whether dose-sparing to the internal-pudendal-arteries (IPA) will improve retention of sexual potency. The IPA is usually not considered a conventional organ-at-risk (OAR) due to segmentation difficulty. In this work, we propose a deep learning (DL)-based auto-segmentation model for the IPA that utilizes CT and MRI or CT alone as the input image modality to accommodate variation in clinical practice. Materials and methods: 86 patients with CT and MRI images and noisy IPA labels were recruited in this study. We split the data into 42/14/30 for model training, testing, and a clinical observer study, respectively. There were three major innovations in this model: 1) we designed an architecture with squeeze-and-excite blocks and modality attention for effective feature extraction and production of accurate segmentation, 2) a novel loss function was used for training the model effectively with noisy labels, and 3) modality dropout strategy was used for making the model capable of segmentation in the absence of MRI. Results: The DSC, ASD, and HD95 values for the test dataset were 62.2%, 2.54mm, and 7mm, respectively. AI segmented contours were dosimetrically equivalent to the expert physician's contours. The observer study showed that expert physicians' scored AI contours (mean=3.7) higher than inexperienced physicians' contours (mean=3.1). When inexperienced physicians started with AI contours, the score improved to 3.7. Conclusion: The proposed model achieved good quality IPA contours to improve uniformity of segmentation and to facilitate introduction of standardized IPA segmentation into clinical trials and practice.
Exploring the combination of deep-learning based direct segmentation and deformable image registration for cone-beam CT based auto-segmentation for adaptive radiotherapy
Jun 07, 2022



Abstract:CBCT-based online adaptive radiotherapy (ART) calls for accurate auto-segmentation models to reduce the time cost for physicians to edit contours, since the patient is immobilized on the treatment table waiting for treatment to start. However, auto-segmentation of CBCT images is a difficult task, majorly due to low image quality and lack of true labels for training a deep learning (DL) model. Meanwhile CBCT auto-segmentation in ART is a unique task compared to other segmentation problems, where manual contours on planning CT (pCT) are available. To make use of this prior knowledge, we propose to combine deformable image registration (DIR) and direct segmentation (DS) on CBCT for head and neck patients. First, we use deformed pCT contours derived from multiple DIR methods between pCT and CBCT as pseudo labels for training. Second, we use deformed pCT contours as bounding box to constrain the region of interest for DS. Meanwhile deformed pCT contours are used as pseudo labels for training, but are generated from different DIR algorithms from bounding box. Third, we fine-tune the model with bounding box on true labels. We found that DS on CBCT trained with pseudo labels and without utilizing any prior knowledge has very poor segmentation performance compared to DIR-only segmentation. However, adding deformed pCT contours as bounding box in the DS network can dramatically improve segmentation performance, comparable to DIR-only segmentation. The DS model with bounding box can be further improved by fine-tuning it with some real labels. Experiments showed that 7 out of 19 structures have at least 0.2 dice similarity coefficient increase compared to DIR-only segmentation. Utilizing deformed pCT contours as pseudo labels for training and as bounding box for shape and location feature extraction in a DS model is a good way to combine DIR and DS.
Segmentation by Test-Time Optimization (TTO) for CBCT-based Adaptive Radiation Therapy
Feb 08, 2022



Abstract:Online adaptive radiotherapy (ART) requires accurate and efficient auto-segmentation of target volumes and organs-at-risk (OARs) in mostly cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT) images. Propagating expert-drawn contours from the pre-treatment planning CT (pCT) through traditional or deep learning (DL) based deformable image registration (DIR) can achieve improved results in many situations. Typical DL-based DIR models are population based, that is, trained with a dataset for a population of patients, so they may be affected by the generalizability problem. In this paper, we propose a method called test-time optimization (TTO) to refine a pre-trained DL-based DIR population model, first for each individual test patient, and then progressively for each fraction of online ART treatment. Our proposed method is less susceptible to the generalizability problem, and thus can improve overall performance of different DL-based DIR models by improving model accuracy, especially for outliers. Our experiments used data from 239 patients with head and neck squamous cell carcinoma to test the proposed method. Firstly, we trained a population model with 200 patients, and then applied TTO to the remaining 39 test patients by refining the trained population model to obtain 39 individualized models. We compared each of the individualized models with the population model in terms of segmentation accuracy. The number of patients with at least 0.05 DSC improvement or 2 mm HD95 improvement by TTO averaged over the 17 selected structures for the state-of-the-art architecture Voxelmorph is 10 out of 39 test patients. The average time for deriving the individualized model using TTO from the pre-trained population model is approximately four minutes. When adapting the individualized model to a later fraction of the same patient, the average time is reduced to about one minute and the accuracy is slightly improved.
PSA-Net: Deep Learning based Physician Style-Aware Segmentation Network for Post-Operative Prostate Cancer Clinical Target Volume
Feb 15, 2021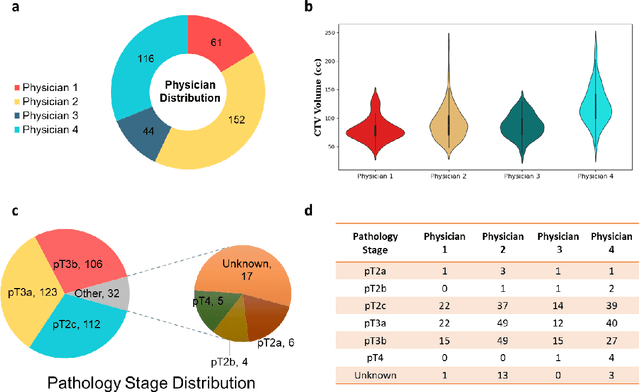
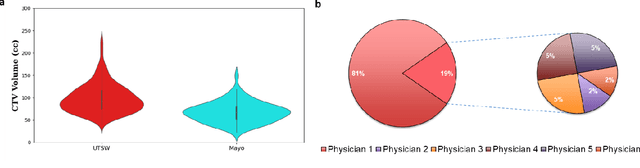
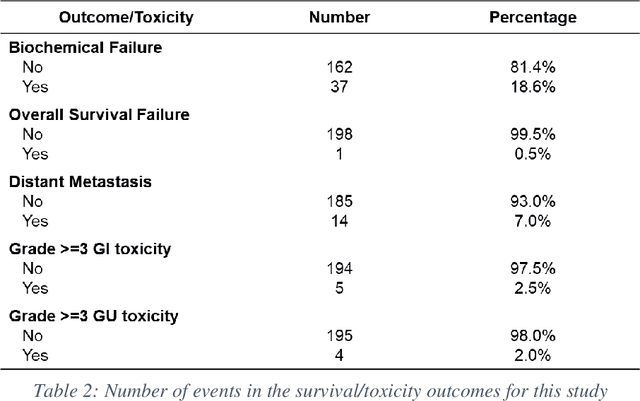
Abstract:Automatic segmentation of medical images with DL algorithms has proven to be highly successful. With most of these algorithms, inter-observer variation is an acknowledged problem, leading to sub-optimal results. This problem is even more significant in post-operative clinical target volume (post-op CTV) segmentation due to the absence of macroscopic visual tumor in the image. This study, using post-op CTV segmentation as the test bed, tries to determine if physician styles are consistent and learnable, if there is an impact of physician styles on treatment outcome and toxicity; and how to explicitly deal with physician styles in DL algorithms to facilitate its clinical acceptance. A classifier is trained to identify which physician has contoured the CTV from just the contour and corresponding CT scan, to determine if physician styles are consistent and learnable. Next, we evaluate if adapting automatic segmentation to physician styles would be clinically feasible based on a lack of difference between outcomes. For modeling different physician styles of CTV segmentation, a concept called physician style-aware (PSA) segmentation is proposed which is an encoder-multidecoder network trained with perceptual loss. With the proposed physician style-aware network (PSA-Net), Dice similarity coefficient (DSC) accuracy increases on an average of 3.4% for all physicians from a general model that is not style adapted. We show that stylistic contouring variations also exist between institutions that follow the same segmentation guidelines and show the effectiveness of the proposed method in adapting to new institutional styles. We observed an accuracy improvement of 5% in terms of DSC when adapting to the style of a separate institution.
Dosimetric impact of physician style variations in contouring CTV for post-operative prostate cancer: A deep learning based simulation study
Feb 01, 2021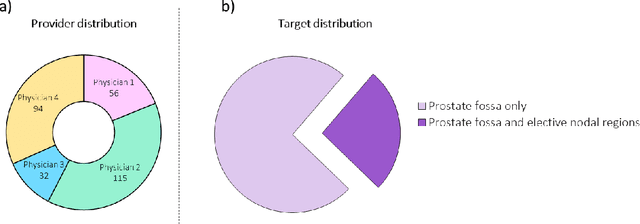
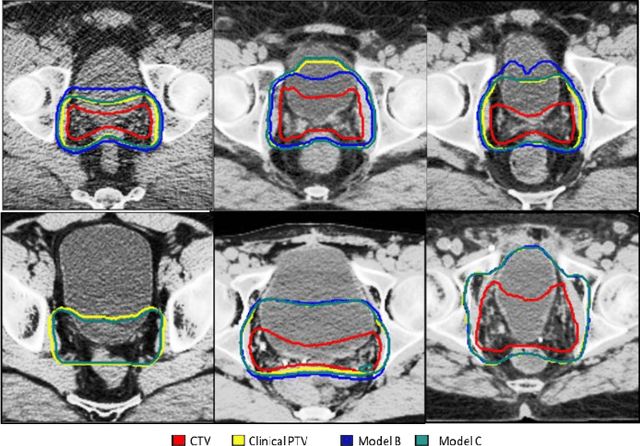
Abstract:In tumor segmentation, inter-observer variation is acknowledged to be a significant problem. This is even more significant in clinical target volume (CTV) segmentation, specifically, in post-operative settings, where a gross tumor does not exist. In this scenario, CTV is not an anatomically established structure but rather one determined by the physician based on the clinical guideline used, the preferred trade off between tumor control and toxicity, their experience, training background etc... This results in high inter-observer variability between physicians. Inter-observer variability has been considered an issue, however its dosimetric consequence is still unclear, due to the absence of multiple physician CTV contours for each patient and the significant amount of time required for dose planning. In this study, we analyze the impact that these physician stylistic variations have on organs-at-risk (OAR) dose by simulating the clinical workflow using deep learning. For a given patient previously treated by one physician, we use DL-based tools to simulate how other physicians would contour the CTV and how the corresponding dose distributions should look like for this patient. To simulate multiple physician styles, we use a previously developed in-house CTV segmentation model that can produce physician style-aware segmentations. The corresponding dose distribution is predicted using another in-house deep learning tool, which, averaging across all structures, is capable of predicting dose within 3% of the prescription dose on the test data. For every test patient, four different physician-style CTVs are considered and four different dose distributions are analyzed. OAR dose metrics are compared, showing that even though physician style variations results in organs getting different doses, all the important dose metrics except Maximum Dose point are within the clinically acceptable limit.
A deep learning-based framework for segmenting invisible clinical target volumes with estimated uncertainties for post-operative prostate cancer radiotherapy
Apr 28, 2020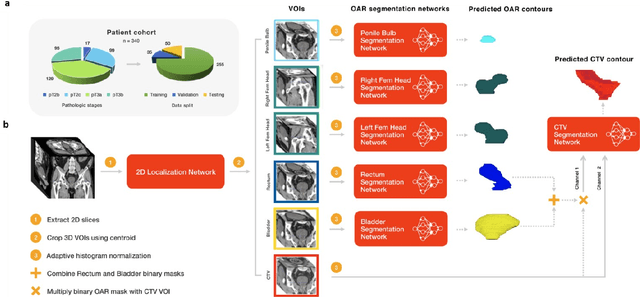
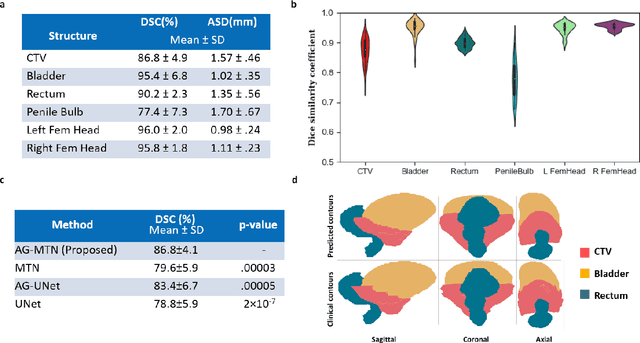
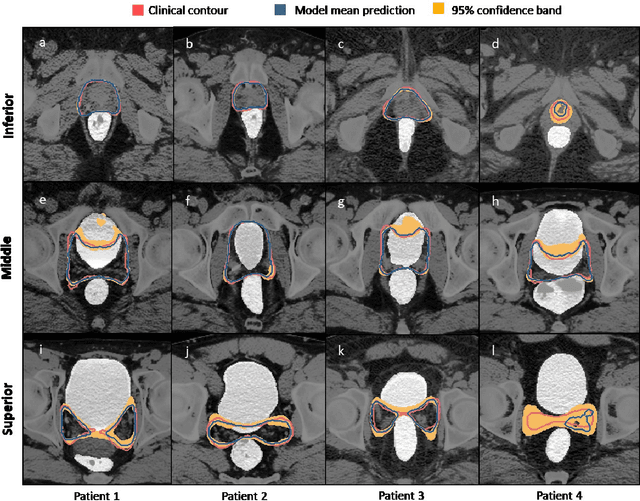
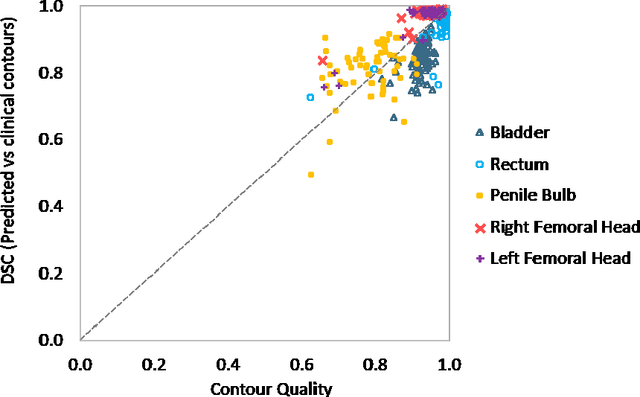
Abstract:In post-operative radiotherapy for prostate cancer, the cancerous prostate gland has been surgically removed, so the clinical target volume (CTV) to be irradiated encompasses the microscopic spread of tumor cells, which cannot be visualized in typical clinical images such as computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging. In current clinical practice, physicians segment CTVs manually based on their relationship with nearby organs and other clinical information, per clinical guidelines. Automating post-operative prostate CTV segmentation with traditional image segmentation methods has been a major challenge. Here, we propose a deep learning model to overcome this problem by segmenting nearby organs first, then using their relationship with the CTV to assist CTV segmentation. The model proposed is trained using labels clinically approved and used for patient treatment, which are subject to relatively large inter-physician variations due to the absence of a visual ground truth. The model achieves an average Dice similarity coefficient (DSC) of 0.87 on a holdout dataset of 50 patients, much better than established methods, such as atlas-based methods (DSC<0.7). The uncertainties associated with automatically segmented CTV contours are also estimated to help physicians inspect and revise the contours, especially in areas with large inter-physician variations. We also use a 4-point grading system to show that the clinical quality of the automatically segmented CTV contours is equal to that of approved clinical contours manually drawn by physicians.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge