Hideo Saito
VIOLA: Towards Video In-Context Learning with Minimal Annotations
Jan 22, 2026Abstract:Generalizing Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) to novel video domains is essential for real-world deployment but remains challenging due to the scarcity of labeled data. While In-Context Learning (ICL) offers a training-free adaptation path, standard methods rely on large annotated pools, which are often impractical in specialized environments like industrial or surgical settings since they require the experts' annotations. To bridge this gap, we introduce VIOLA (Video In-cOntext Learning with minimal Annotation), a label-efficient framework that synergizes minimal expert supervision with abundant unlabeled data. First, to maximize the efficiency of a strict annotation budget, we propose density-uncertainty-weighted sampling. Unlike standard diversity or uncertainty strategies that risk selecting visual outliers, our method leverages density estimation to identify samples that are simultaneously diverse, representative, and informative. Second, to utilize the remaining unlabeled data without noise propagation, we construct a hybrid pool and introduce confidence-aware retrieval and confidence-aware prompting. These mechanisms explicitly model label reliability, retrieving demonstrations based on a composite score of similarity and confidence while enabling the MLLM to adaptively distinguish between verified ground truths and noisy pseudo-labels. Extensive experiments across nine diverse benchmarks using four MLLMs demonstrate that our framework significantly outperforms various baselines in low-resource settings, achieving robust adaptation with minimal annotation costs.
Prime and Reach: Synthesising Body Motion for Gaze-Primed Object Reach
Dec 18, 2025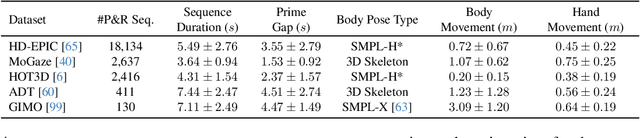



Abstract:Human motion generation is a challenging task that aims to create realistic motion imitating natural human behaviour. We focus on the well-studied behaviour of priming an object/location for pick up or put down -- that is, the spotting of an object/location from a distance, known as gaze priming, followed by the motion of approaching and reaching the target location. To that end, we curate, for the first time, 23.7K gaze-primed human motion sequences for reaching target object locations from five publicly available datasets, i.e., HD-EPIC, MoGaze, HOT3D, ADT, and GIMO. We pre-train a text-conditioned diffusion-based motion generation model, then fine-tune it conditioned on goal pose or location, on our curated sequences. Importantly, we evaluate the ability of the generated motion to imitate natural human movement through several metrics, including the 'Reach Success' and a newly introduced 'Prime Success' metric. On the largest dataset, HD-EPIC, our model achieves 60% prime success and 89% reach success when conditioned on the goal object location.
Disturbance-Free Surgical Video Generation from Multi-Camera Shadowless Lamps for Open Surgery
Dec 09, 2025



Abstract:Video recordings of open surgeries are greatly required for education and research purposes. However, capturing unobstructed videos is challenging since surgeons frequently block the camera field of view. To avoid occlusion, the positions and angles of the camera must be frequently adjusted, which is highly labor-intensive. Prior work has addressed this issue by installing multiple cameras on a shadowless lamp and arranging them to fully surround the surgical area. This setup increases the chances of some cameras capturing an unobstructed view. However, manual image alignment is needed in post-processing since camera configurations change every time surgeons move the lamp for optimal lighting. This paper aims to fully automate this alignment task. The proposed method identifies frames in which the lighting system moves, realigns them, and selects the camera with the least occlusion to generate a video that consistently presents the surgical field from a fixed perspective. A user study involving surgeons demonstrated that videos generated by our method were superior to those produced by conventional methods in terms of the ease of confirming the surgical area and the comfort during video viewing. Additionally, our approach showed improvements in video quality over existing techniques. Furthermore, we implemented several synthesis options for the proposed view-synthesis method and conducted a user study to assess surgeons' preferences for each option.
Hand Held Multi-Object Tracking Dataset in American Football
Nov 12, 2025



Abstract:Multi-Object Tracking (MOT) plays a critical role in analyzing player behavior from videos, enabling performance evaluation. Current MOT methods are often evaluated using publicly available datasets. However, most of these focus on everyday scenarios such as pedestrian tracking or are tailored to specific sports, including soccer and basketball. Despite the inherent challenges of tracking players in American football, such as frequent occlusion and physical contact, no standardized dataset has been publicly available, making fair comparisons between methods difficult. To address this gap, we constructed the first dedicated detection and tracking dataset for the American football players and conducted a comparative evaluation of various detection and tracking methods. Our results demonstrate that accurate detection and tracking can be achieved even in crowded scenarios. Fine-tuning detection models improved performance over pre-trained models. Furthermore, when these fine-tuned detectors and re-identification models were integrated into tracking systems, we observed notable improvements in tracking accuracy compared to existing approaches. This work thus enables robust detection and tracking of American football players in challenging, high-density scenarios previously underserved by conventional methods.
Human Preference-Aligned Concept Customization Benchmark via Decomposed Evaluation
Sep 03, 2025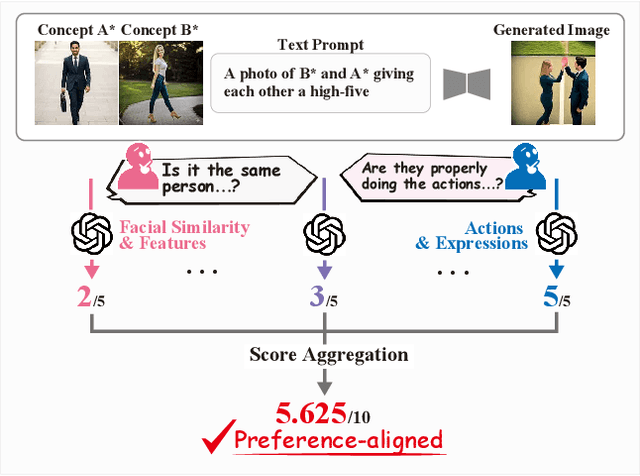

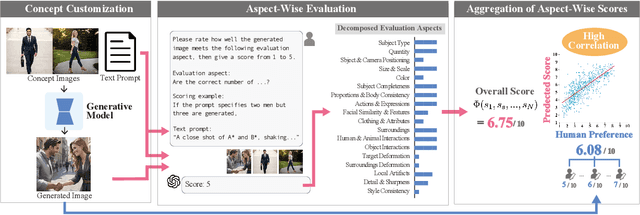

Abstract:Evaluating concept customization is challenging, as it requires a comprehensive assessment of fidelity to generative prompts and concept images. Moreover, evaluating multiple concepts is considerably more difficult than evaluating a single concept, as it demands detailed assessment not only for each individual concept but also for the interactions among concepts. While humans can intuitively assess generated images, existing metrics often provide either overly narrow or overly generalized evaluations, resulting in misalignment with human preference. To address this, we propose Decomposed GPT Score (D-GPTScore), a novel human-aligned evaluation method that decomposes evaluation criteria into finer aspects and incorporates aspect-wise assessments using Multimodal Large Language Model (MLLM). Additionally, we release Human Preference-Aligned Concept Customization Benchmark (CC-AlignBench), a benchmark dataset containing both single- and multi-concept tasks, enabling stage-wise evaluation across a wide difficulty range -- from individual actions to multi-person interactions. Our method significantly outperforms existing approaches on this benchmark, exhibiting higher correlation with human preferences. This work establishes a new standard for evaluating concept customization and highlights key challenges for future research. The benchmark and associated materials are available at https://github.com/ReinaIshikawa/D-GPTScore.
SoccerNet 2025 Challenges Results
Aug 26, 2025Abstract:The SoccerNet 2025 Challenges mark the fifth annual edition of the SoccerNet open benchmarking effort, dedicated to advancing computer vision research in football video understanding. This year's challenges span four vision-based tasks: (1) Team Ball Action Spotting, focused on detecting ball-related actions in football broadcasts and assigning actions to teams; (2) Monocular Depth Estimation, targeting the recovery of scene geometry from single-camera broadcast clips through relative depth estimation for each pixel; (3) Multi-View Foul Recognition, requiring the analysis of multiple synchronized camera views to classify fouls and their severity; and (4) Game State Reconstruction, aimed at localizing and identifying all players from a broadcast video to reconstruct the game state on a 2D top-view of the field. Across all tasks, participants were provided with large-scale annotated datasets, unified evaluation protocols, and strong baselines as starting points. This report presents the results of each challenge, highlights the top-performing solutions, and provides insights into the progress made by the community. The SoccerNet Challenges continue to serve as a driving force for reproducible, open research at the intersection of computer vision, artificial intelligence, and sports. Detailed information about the tasks, challenges, and leaderboards can be found at https://www.soccer-net.org, with baselines and development kits available at https://github.com/SoccerNet.
User-in-the-Loop View Sampling with Error Peaking Visualization
Jun 26, 2025



Abstract:Augmented reality (AR) provides ways to visualize missing view samples for novel view synthesis. Existing approaches present 3D annotations for new view samples and task users with taking images by aligning the AR display. This data collection task is known to be mentally demanding and limits capture areas to pre-defined small areas due to the ideal but restrictive underlying sampling theory. To free users from 3D annotations and limited scene exploration, we propose using locally reconstructed light fields and visualizing errors to be removed by inserting new views. Our results show that the error-peaking visualization is less invasive, reduces disappointment in final results, and is satisfactory with fewer view samples in our mobile view synthesis system. We also show that our approach can contribute to recent radiance field reconstruction for larger scenes, such as 3D Gaussian splatting.
The Invisible EgoHand: 3D Hand Forecasting through EgoBody Pose Estimation
Apr 11, 2025Abstract:Forecasting hand motion and pose from an egocentric perspective is essential for understanding human intention. However, existing methods focus solely on predicting positions without considering articulation, and only when the hands are visible in the field of view. This limitation overlooks the fact that approximate hand positions can still be inferred even when they are outside the camera's view. In this paper, we propose a method to forecast the 3D trajectories and poses of both hands from an egocentric video, both in and out of the field of view. We propose a diffusion-based transformer architecture for Egocentric Hand Forecasting, EgoH4, which takes as input the observation sequence and camera poses, then predicts future 3D motion and poses for both hands of the camera wearer. We leverage full-body pose information, allowing other joints to provide constraints on hand motion. We denoise the hand and body joints along with a visibility predictor for hand joints and a 3D-to-2D reprojection loss that minimizes the error when hands are in-view. We evaluate EgoH4 on the Ego-Exo4D dataset, combining subsets with body and hand annotations. We train on 156K sequences and evaluate on 34K sequences, respectively. EgoH4 improves the performance by 3.4cm and 5.1cm over the baseline in terms of ADE for hand trajectory forecasting and MPJPE for hand pose forecasting. Project page: https://masashi-hatano.github.io/EgoH4/
EgoSurgery-HTS: A Dataset for Egocentric Hand-Tool Segmentation in Open Surgery Videos
Mar 24, 2025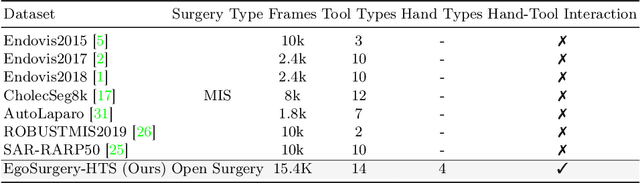
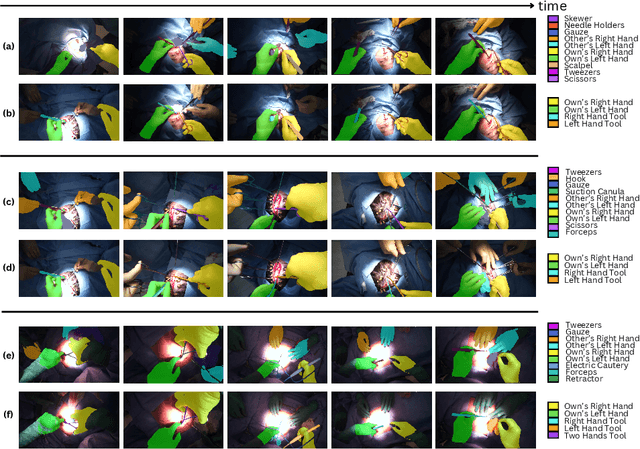

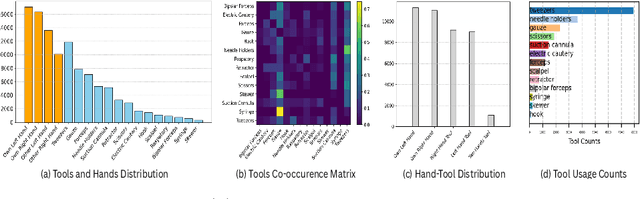
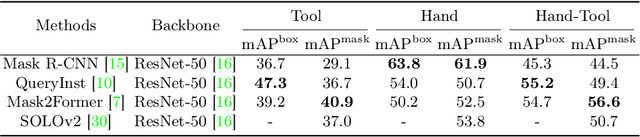
Abstract:Egocentric open-surgery videos capture rich, fine-grained details essential for accurately modeling surgical procedures and human behavior in the operating room. A detailed, pixel-level understanding of hands and surgical tools is crucial for interpreting a surgeon's actions and intentions. We introduce EgoSurgery-HTS, a new dataset with pixel-wise annotations and a benchmark suite for segmenting surgical tools, hands, and interacting tools in egocentric open-surgery videos. Specifically, we provide a labeled dataset for (1) tool instance segmentation of 14 distinct surgical tools, (2) hand instance segmentation, and (3) hand-tool segmentation to label hands and the tools they manipulate. Using EgoSurgery-HTS, we conduct extensive evaluations of state-of-the-art segmentation methods and demonstrate significant improvements in the accuracy of hand and hand-tool segmentation in egocentric open-surgery videos compared to existing datasets. The dataset will be released at https://github.com/Fujiry0/EgoSurgery.
High-Quality Virtual Single-Viewpoint Surgical Video: Geometric Autocalibration of Multiple Cameras in Surgical Lights
Mar 05, 2025Abstract:Occlusion-free video generation is challenging due to surgeons' obstructions in the camera field of view. Prior work has addressed this issue by installing multiple cameras on a surgical light, hoping some cameras will observe the surgical field with less occlusion. However, this special camera setup poses a new imaging challenge since camera configurations can change every time surgeons move the light, and manual image alignment is required. This paper proposes an algorithm to automate this alignment task. The proposed method detects frames where the lighting system moves, realigns them, and selects the camera with the least occlusion. This algorithm results in a stabilized video with less occlusion. Quantitative results show that our method outperforms conventional approaches. A user study involving medical doctors also confirmed the superiority of our method.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge