Hadi Abdullah
Watch What You Pretrain For: Targeted, Transferable Adversarial Examples on Self-Supervised Speech Recognition models
Sep 29, 2022



Abstract:A targeted adversarial attack produces audio samples that can force an Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR) system to output attacker-chosen text. To exploit ASR models in real-world, black-box settings, an adversary can leverage the transferability property, i.e. that an adversarial sample produced for a proxy ASR can also fool a different remote ASR. However recent work has shown that transferability against large ASR models is very difficult. In this work, we show that modern ASR architectures, specifically ones based on Self-Supervised Learning, are in fact vulnerable to transferability. We successfully demonstrate this phenomenon by evaluating state-of-the-art self-supervised ASR models like Wav2Vec2, HuBERT, Data2Vec and WavLM. We show that with low-level additive noise achieving a 30dB Signal-Noise Ratio, we can achieve target transferability with up to 80% accuracy. Next, we 1) use an ablation study to show that Self-Supervised learning is the main cause of that phenomenon, and 2) we provide an explanation for this phenomenon. Through this we show that modern ASR architectures are uniquely vulnerable to adversarial security threats.
Attacks as Defenses: Designing Robust Audio CAPTCHAs Using Attacks on Automatic Speech Recognition Systems
Mar 10, 2022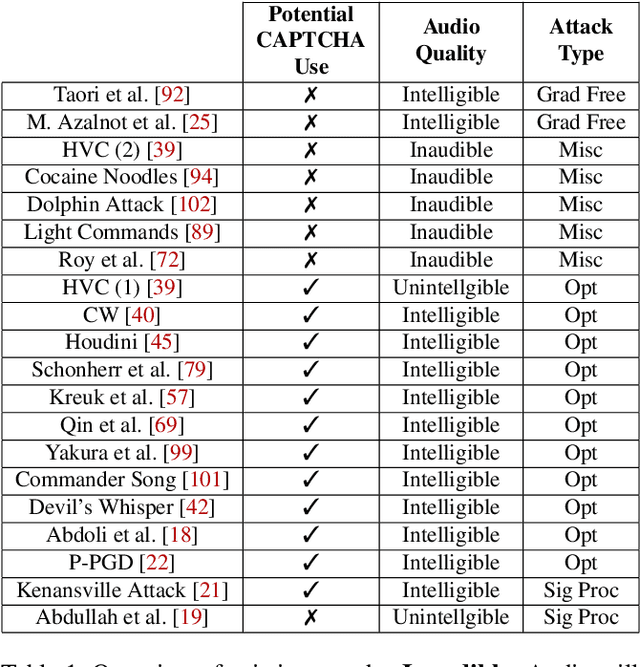
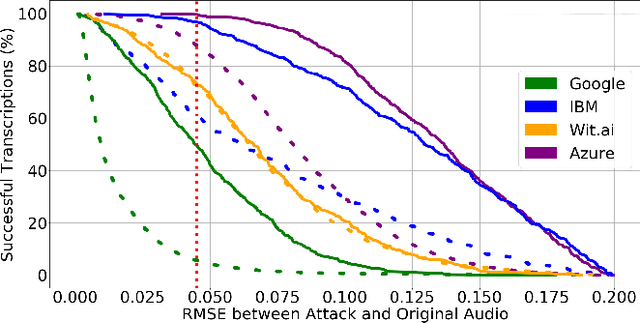

Abstract:Audio CAPTCHAs are supposed to provide a strong defense for online resources; however, advances in speech-to-text mechanisms have rendered these defenses ineffective. Audio CAPTCHAs cannot simply be abandoned, as they are specifically named by the W3C as important enablers of accessibility. Accordingly, demonstrably more robust audio CAPTCHAs are important to the future of a secure and accessible Web. We look to recent literature on attacks on speech-to-text systems for inspiration for the construction of robust, principle-driven audio defenses. We begin by comparing 20 recent attack papers, classifying and measuring their suitability to serve as the basis of new "robust to transcription" but "easy for humans to understand" CAPTCHAs. After showing that none of these attacks alone are sufficient, we propose a new mechanism that is both comparatively intelligible (evaluated through a user study) and hard to automatically transcribe (i.e., $P({\rm transcription}) = 4 \times 10^{-5}$). Finally, we demonstrate that our audio samples have a high probability of being detected as CAPTCHAs when given to speech-to-text systems ($P({\rm evasion}) = 1.77 \times 10^{-4}$). In so doing, we not only demonstrate a CAPTCHA that is approximately four orders of magnitude more difficult to crack, but that such systems can be designed based on the insights gained from attack papers using the differences between the ways that humans and computers process audio.
Beyond $L_p$ clipping: Equalization-based Psychoacoustic Attacks against ASRs
Oct 25, 2021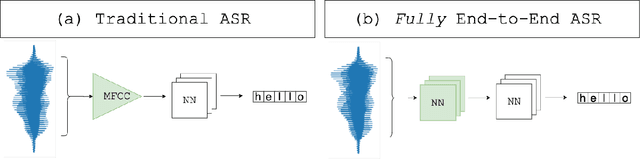
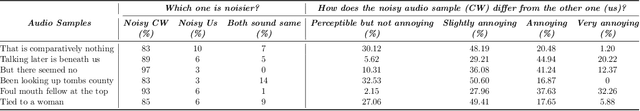
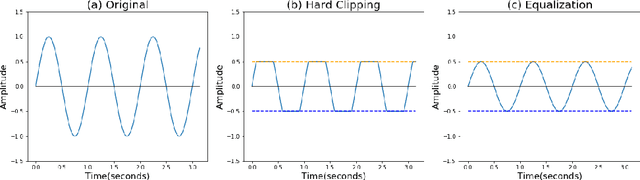
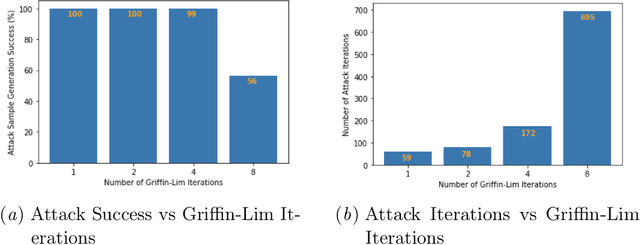
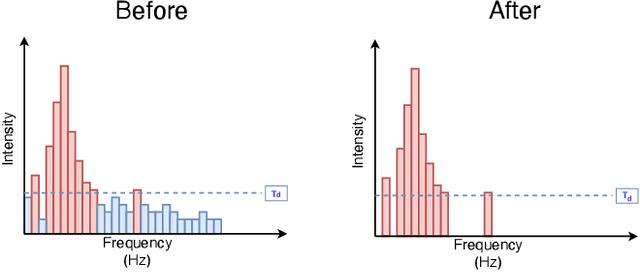
Abstract:Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR) systems convert speech into text and can be placed into two broad categories: traditional and fully end-to-end. Both types have been shown to be vulnerable to adversarial audio examples that sound benign to the human ear but force the ASR to produce malicious transcriptions. Of these attacks, only the "psychoacoustic" attacks can create examples with relatively imperceptible perturbations, as they leverage the knowledge of the human auditory system. Unfortunately, existing psychoacoustic attacks can only be applied against traditional models, and are obsolete against the newer, fully end-to-end ASRs. In this paper, we propose an equalization-based psychoacoustic attack that can exploit both traditional and fully end-to-end ASRs. We successfully demonstrate our attack against real-world ASRs that include DeepSpeech and Wav2Letter. Moreover, we employ a user study to verify that our method creates low audible distortion. Specifically, 80 of the 100 participants voted in favor of all our attack audio samples as less noisier than the existing state-of-the-art attack. Through this, we demonstrate both types of existing ASR pipelines can be exploited with minimum degradation to attack audio quality.
SoK: The Faults in our ASRs: An Overview of Attacks against Automatic Speech Recognition and Speaker Identification Systems
Jul 21, 2020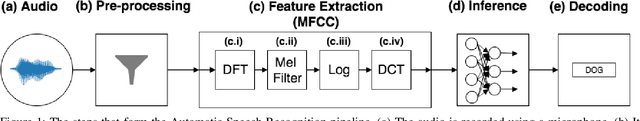
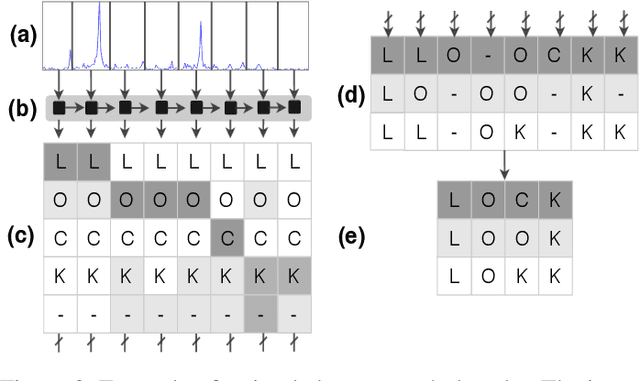
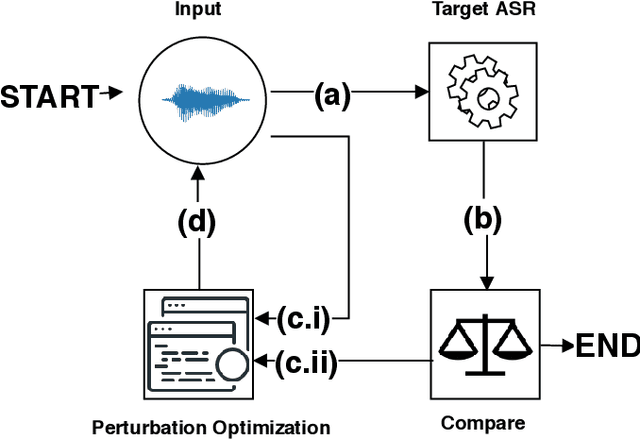
Abstract:Speech and speaker recognition systems are employed in a variety of applications, from personal assistants to telephony surveillance and biometric authentication. The wide deployment of these systems has been made possible by the improved accuracy in neural networks. Like other systems based on neural networks, recent research has demonstrated that speech and speaker recognition systems are vulnerable to attacks using manipulated inputs. However, as we demonstrate in this paper, the end-to-end architecture of speech and speaker systems and the nature of their inputs make attacks and defenses against them substantially different than those in the image space. We demonstrate this first by systematizing existing research in this space and providing a taxonomy through which the community can evaluate future work. We then demonstrate experimentally that attacks against these models almost universally fail to transfer. In so doing, we argue that substantial additional work is required to provide adequate mitigations in this space.
Hear "No Evil", See "Kenansville": Efficient and Transferable Black-Box Attacks on Speech Recognition and Voice Identification Systems
Oct 11, 2019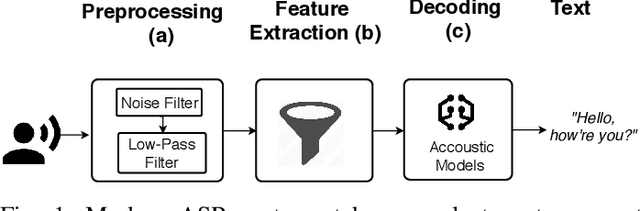
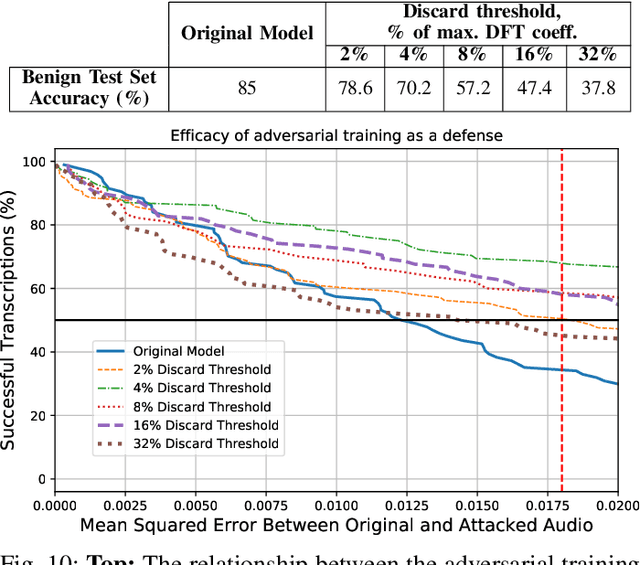
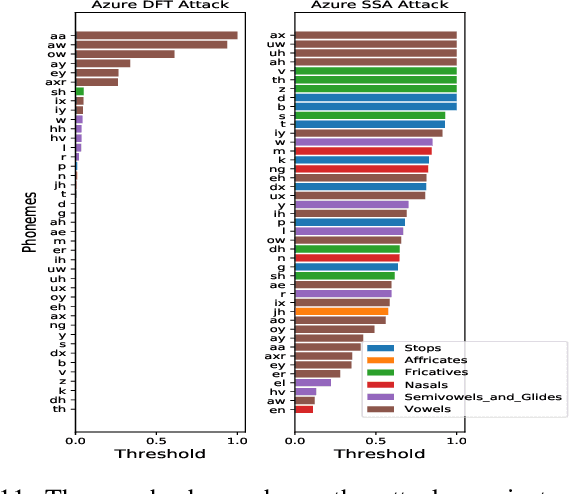
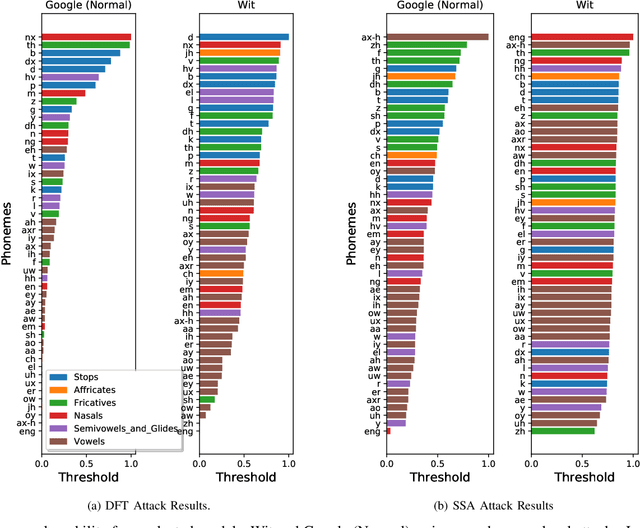
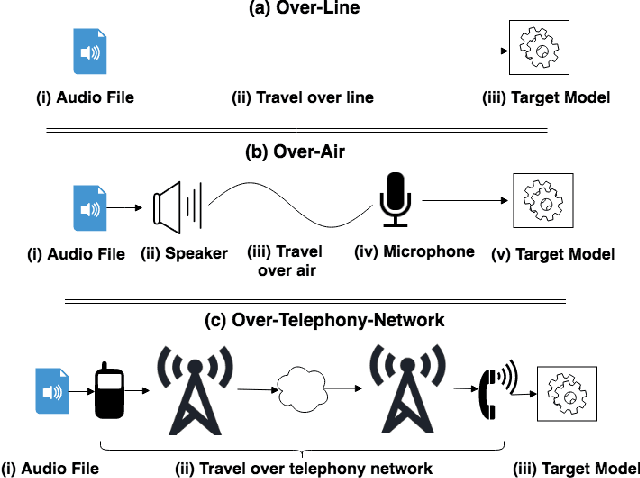
Abstract:Automatic speech recognition and voice identification systems are being deployed in a wide array of applications, from providing control mechanisms to devices lacking traditional interfaces, to the automatic transcription of conversations and authentication of users. Many of these applications have significant security and privacy considerations. We develop attacks that force mistranscription and misidentification in state of the art systems, with minimal impact on human comprehension. Processing pipelines for modern systems are comprised of signal preprocessing and feature extraction steps, whose output is fed to a machine-learned model. Prior work has focused on the models, using white-box knowledge to tailor model-specific attacks. We focus on the pipeline stages before the models, which (unlike the models) are quite similar across systems. As such, our attacks are black-box and transferable, and demonstrably achieve mistranscription and misidentification rates as high as 100% by modifying only a few frames of audio. We perform a study via Amazon Mechanical Turk demonstrating that there is no statistically significant difference between human perception of regular and perturbed audio. Our findings suggest that models may learn aspects of speech that are generally not perceived by human subjects, but that are crucial for model accuracy. We also find that certain English language phonemes (in particular, vowels) are significantly more susceptible to our attack. We show that the attacks are effective when mounted over cellular networks, where signals are subject to degradation due to transcoding, jitter, and packet loss.
Practical Hidden Voice Attacks against Speech and Speaker Recognition Systems
Mar 18, 2019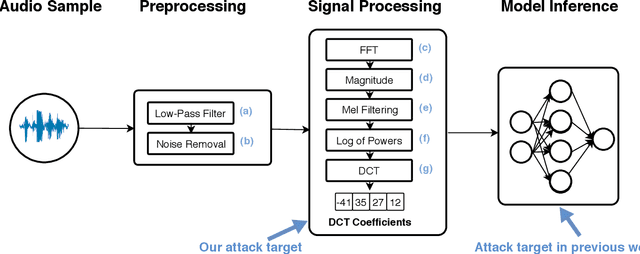
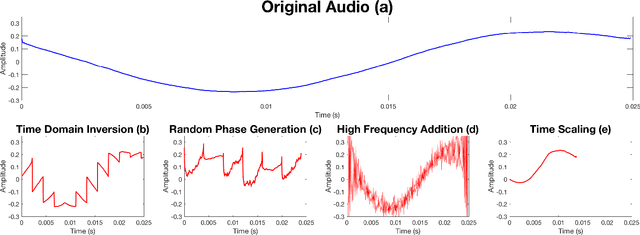
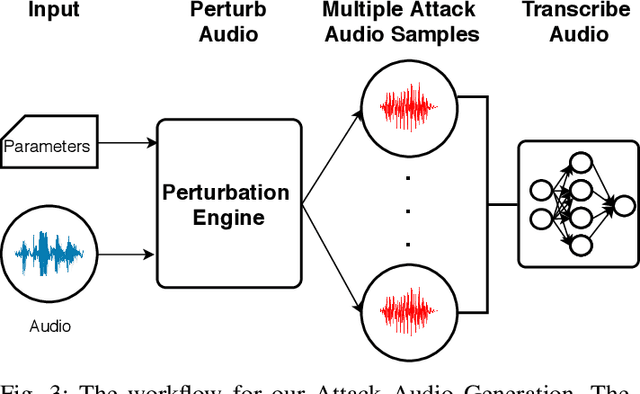
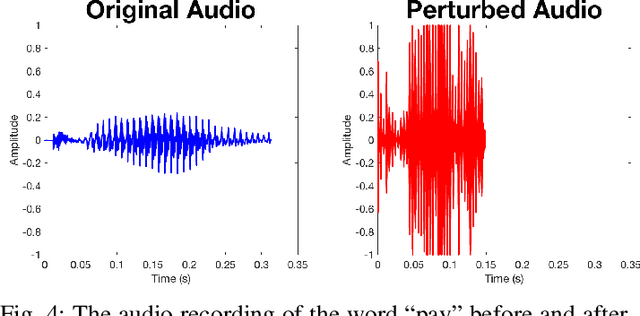
Abstract:Voice Processing Systems (VPSes), now widely deployed, have been made significantly more accurate through the application of recent advances in machine learning. However, adversarial machine learning has similarly advanced and has been used to demonstrate that VPSes are vulnerable to the injection of hidden commands - audio obscured by noise that is correctly recognized by a VPS but not by human beings. Such attacks, though, are often highly dependent on white-box knowledge of a specific machine learning model and limited to specific microphones and speakers, making their use across different acoustic hardware platforms (and thus their practicality) limited. In this paper, we break these dependencies and make hidden command attacks more practical through model-agnostic (blackbox) attacks, which exploit knowledge of the signal processing algorithms commonly used by VPSes to generate the data fed into machine learning systems. Specifically, we exploit the fact that multiple source audio samples have similar feature vectors when transformed by acoustic feature extraction algorithms (e.g., FFTs). We develop four classes of perturbations that create unintelligible audio and test them against 12 machine learning models, including 7 proprietary models (e.g., Google Speech API, Bing Speech API, IBM Speech API, Azure Speaker API, etc), and demonstrate successful attacks against all targets. Moreover, we successfully use our maliciously generated audio samples in multiple hardware configurations, demonstrating effectiveness across both models and real systems. In so doing, we demonstrate that domain-specific knowledge of audio signal processing represents a practical means of generating successful hidden voice command attacks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge