Kevin R. B. Butler
Analyzing the AI Nudification Application Ecosystem
Nov 14, 2024



Abstract:Given a source image of a clothed person (an image subject), AI-based nudification applications can produce nude (undressed) images of that person. Moreover, not only do such applications exist, but there is ample evidence of the use of such applications in the real world and without the consent of an image subject. Still, despite the growing awareness of the existence of such applications and their potential to violate the rights of image subjects and cause downstream harms, there has been no systematic study of the nudification application ecosystem across multiple applications. We conduct such a study here, focusing on 20 popular and easy-to-find nudification websites. We study the positioning of these web applications (e.g., finding that most sites explicitly target the nudification of women, not all people), the features that they advertise (e.g., ranging from undressing-in-place to the rendering of image subjects in sexual positions, as well as differing user-privacy options), and their underlying monetization infrastructure (e.g., credit cards and cryptocurrencies). We believe this work will empower future, data-informed conversations -- within the scientific, technical, and policy communities -- on how to better protect individuals' rights and minimize harm in the face of modern (and future) AI-based nudification applications. Content warning: This paper includes descriptions of web applications that can be used to create synthetic non-consensual explicit AI-created imagery (SNEACI). This paper also includes an artistic rendering of a user interface for such an application.
Hard-label Manifolds: Unexpected Advantages of Query Efficiency for Finding On-manifold Adversarial Examples
Mar 04, 2021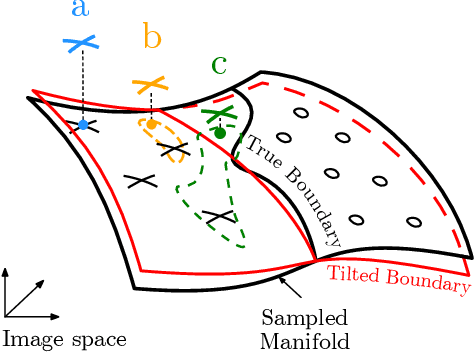
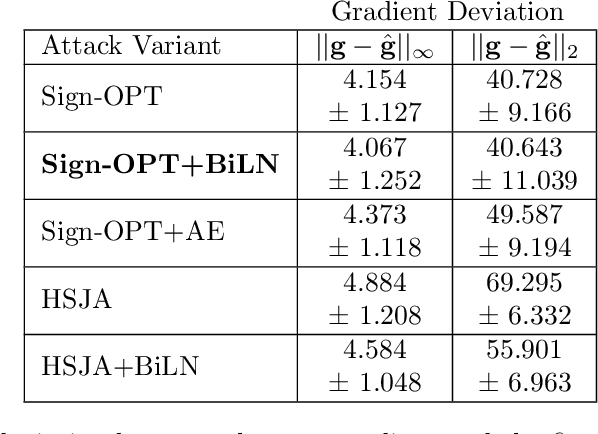
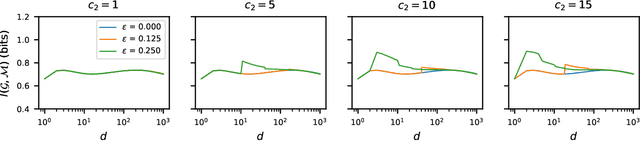
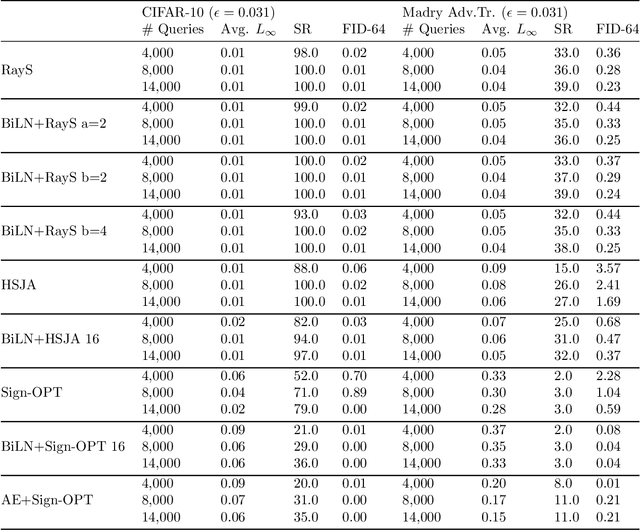
Abstract:Designing deep networks robust to adversarial examples remains an open problem. Likewise, recent zeroth order hard-label attacks on image classification models have shown comparable performance to their first-order, gradient-level alternatives. It was recently shown in the gradient-level setting that regular adversarial examples leave the data manifold, while their on-manifold counterparts are in fact generalization errors. In this paper, we argue that query efficiency in the zeroth-order setting is connected to an adversary's traversal through the data manifold. To explain this behavior, we propose an information-theoretic argument based on a noisy manifold distance oracle, which leaks manifold information through the adversary's gradient estimate. Through numerical experiments of manifold-gradient mutual information, we show this behavior acts as a function of the effective problem dimensionality and number of training points. On real-world datasets and multiple zeroth-order attacks using dimension-reduction, we observe the same universal behavior to produce samples closer to the data manifold. This results in up to two-fold decrease in the manifold distance measure, regardless of the model robustness. Our results suggest that taking the manifold-gradient mutual information into account can thus inform better robust model design in the future, and avoid leakage of the sensitive data manifold.
Practical Hidden Voice Attacks against Speech and Speaker Recognition Systems
Mar 18, 2019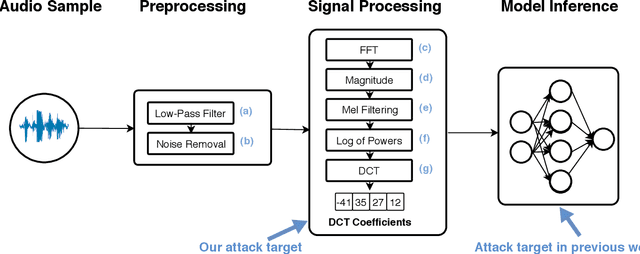
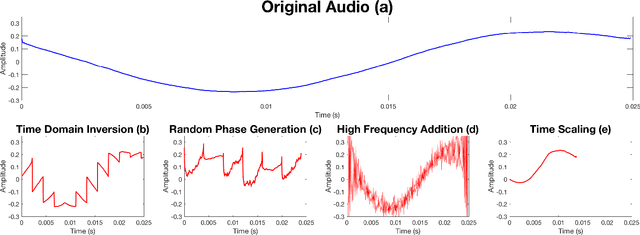
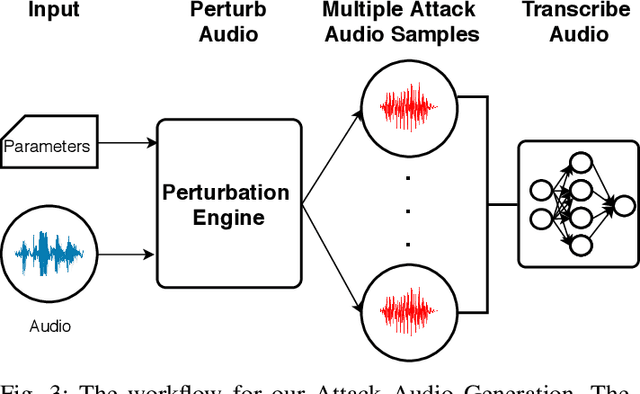
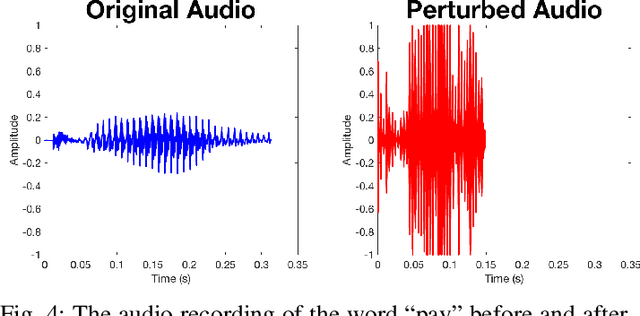
Abstract:Voice Processing Systems (VPSes), now widely deployed, have been made significantly more accurate through the application of recent advances in machine learning. However, adversarial machine learning has similarly advanced and has been used to demonstrate that VPSes are vulnerable to the injection of hidden commands - audio obscured by noise that is correctly recognized by a VPS but not by human beings. Such attacks, though, are often highly dependent on white-box knowledge of a specific machine learning model and limited to specific microphones and speakers, making their use across different acoustic hardware platforms (and thus their practicality) limited. In this paper, we break these dependencies and make hidden command attacks more practical through model-agnostic (blackbox) attacks, which exploit knowledge of the signal processing algorithms commonly used by VPSes to generate the data fed into machine learning systems. Specifically, we exploit the fact that multiple source audio samples have similar feature vectors when transformed by acoustic feature extraction algorithms (e.g., FFTs). We develop four classes of perturbations that create unintelligible audio and test them against 12 machine learning models, including 7 proprietary models (e.g., Google Speech API, Bing Speech API, IBM Speech API, Azure Speaker API, etc), and demonstrate successful attacks against all targets. Moreover, we successfully use our maliciously generated audio samples in multiple hardware configurations, demonstrating effectiveness across both models and real systems. In so doing, we demonstrate that domain-specific knowledge of audio signal processing represents a practical means of generating successful hidden voice command attacks.
Explainable Black-Box Attacks Against Model-based Authentication
Sep 28, 2018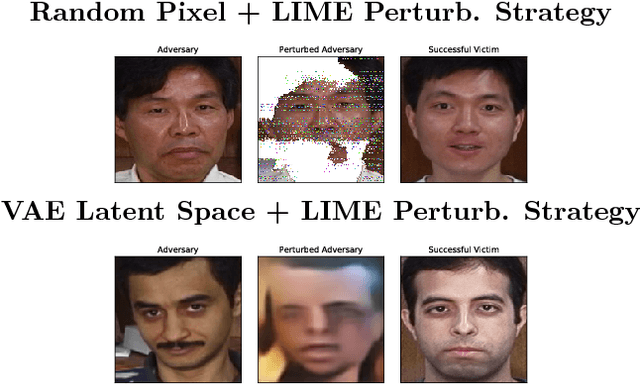
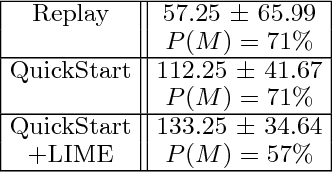
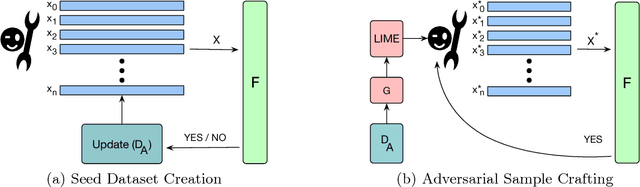
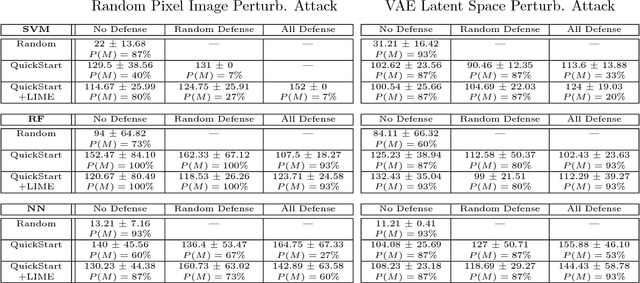
Abstract:Establishing unique identities for both humans and end systems has been an active research problem in the security community, giving rise to innovative machine learning-based authentication techniques. Although such techniques offer an automated method to establish identity, they have not been vetted against sophisticated attacks that target their core machine learning technique. This paper demonstrates that mimicking the unique signatures generated by host fingerprinting and biometric authentication systems is possible. We expose the ineffectiveness of underlying machine learning classification models by constructing a blind attack based around the query synthesis framework and utilizing Explainable-AI (XAI) techniques. We launch an attack in under 130 queries on a state-of-the-art face authentication system, and under 100 queries on a host authentication system. We examine how these attacks can be defended against and explore their limitations. XAI provides an effective means for adversaries to infer decision boundaries and provides a new way forward in constructing attacks against systems using machine learning models for authentication.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge