Elissa M. Redmiles
"Unlimited Realm of Exploration and Experimentation": Methods and Motivations of AI-Generated Sexual Content Creators
Jan 28, 2026Abstract:AI-generated media is radically changing the way content is both consumed and produced on the internet, and in no place is this potentially more visible than in sexual content. AI-generated sexual content (AIG-SC) is increasingly enabled by an ecosystem of individual AI developers, specialized third-party applications, and foundation model providers. AIG-SC raises a number of concerns from old debates about the line between pornography and obscenity, to newer debates about fair use and labor displacement (in this case, of sex workers), and spurred new regulations to curb the spread of non-consensual intimate imagery (NCII) created using the same technology used to create AIG-SC. However, despite the growing prevalence of AIG-SC, little is known about its creators, their motivations, and what types of content they produce. To inform effective governance in this space, we perform an in-depth study to understand what AIG-SC creators make, along with how and why they make it. Interviews of 28 AIG-SC creators, ranging from hobbyists to entrepreneurs to those who moderate communities of hundreds of thousands of other creators, reveal a wide spectrum of motivations, including sexual exploration, creative expression, technical experimentation, and in a handful of cases, the creation of NCII.
Analyzing the AI Nudification Application Ecosystem
Nov 14, 2024



Abstract:Given a source image of a clothed person (an image subject), AI-based nudification applications can produce nude (undressed) images of that person. Moreover, not only do such applications exist, but there is ample evidence of the use of such applications in the real world and without the consent of an image subject. Still, despite the growing awareness of the existence of such applications and their potential to violate the rights of image subjects and cause downstream harms, there has been no systematic study of the nudification application ecosystem across multiple applications. We conduct such a study here, focusing on 20 popular and easy-to-find nudification websites. We study the positioning of these web applications (e.g., finding that most sites explicitly target the nudification of women, not all people), the features that they advertise (e.g., ranging from undressing-in-place to the rendering of image subjects in sexual positions, as well as differing user-privacy options), and their underlying monetization infrastructure (e.g., credit cards and cryptocurrencies). We believe this work will empower future, data-informed conversations -- within the scientific, technical, and policy communities -- on how to better protect individuals' rights and minimize harm in the face of modern (and future) AI-based nudification applications. Content warning: This paper includes descriptions of web applications that can be used to create synthetic non-consensual explicit AI-created imagery (SNEACI). This paper also includes an artistic rendering of a user interface for such an application.
How good is good enough for COVID19 apps? The influence of benefits, accuracy, and privacy on willingness to adopt
May 18, 2020
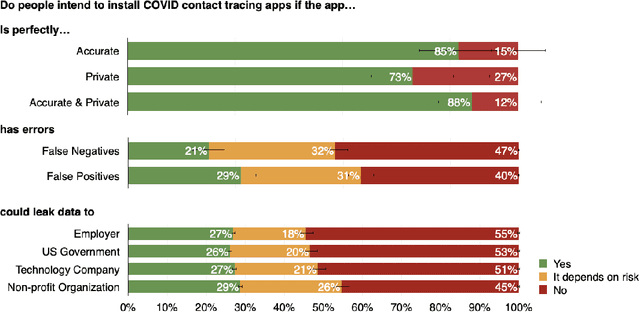
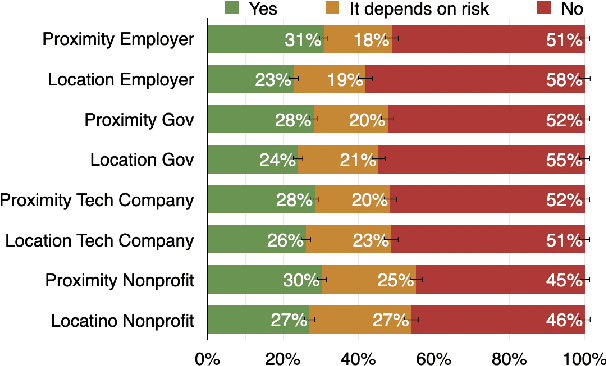
Abstract:A growing number of contact tracing apps are being developed to complement manual contact tracing. A key question is whether users will be willing to adopt these contact tracing apps. In this work, we survey over 4,500 Americans to evaluate (1) the effect of both accuracy and privacy concerns on reported willingness to install COVID19 contact tracing apps and (2) how different groups of users weight accuracy vs. privacy. Drawing on our findings from these first two research questions, we (3) quantitatively model how the amount of public health benefit (reduction in infection rate), amount of individual benefit (true-positive detection of exposures to COVID), and degree of privacy risk in a hypothetical contact tracing app may influence American's willingness to install. Our work takes a descriptive ethics approach toward offering implications for the development of policy and app designs related to COVID19.
Dimensions of Diversity in Human Perceptions of Algorithmic Fairness
May 02, 2020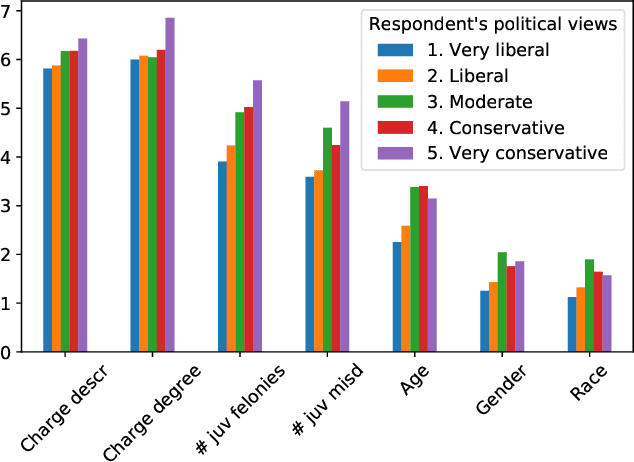
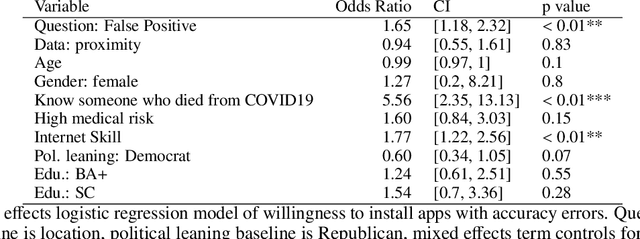
Abstract:Algorithms are increasingly involved in making decisions that affect human lives. Prior work has explored how people believe algorithmic decisions should be made, but there is little understanding of which individual factors relate to variance in these beliefs across people. As an increasing emphasis is put on oversight boards and regulatory bodies, it is important to understand the biases that may affect human judgements about the fairness of algorithms. Building on factors found in moral foundations theory and egocentric fairness literature, we explore how people's perceptions of fairness relate to their (i) demographics (age, race, gender, political view), and (ii) personal experiences with the algorithmic task being evaluated. Specifically, we study human beliefs about the fairness of using different features in an algorithm designed to assist judges in making decisions about granting bail. Our analysis suggests that political views and certain demographic factors, such as age and gender, exhibit a significant relation to people's beliefs about fairness. Additionally, we find that people beliefs about the fairness of using demographic features such as age, gender and race, for making bail decisions about others, vary egocentrically: that is they vary depending on their own age, gender and race respectively.
Human Perceptions of Fairness in Algorithmic Decision Making: A Case Study of Criminal Risk Prediction
Feb 26, 2018
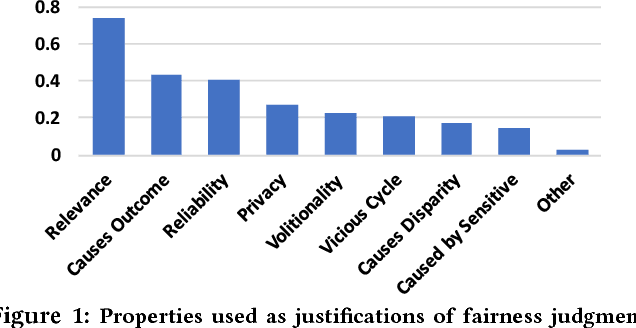
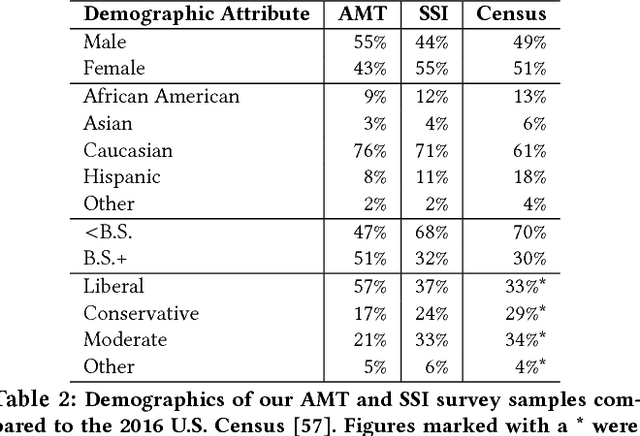
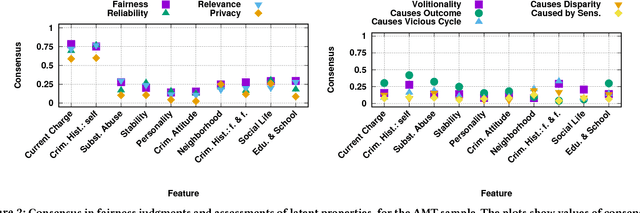
Abstract:As algorithms are increasingly used to make important decisions that affect human lives, ranging from social benefit assignment to predicting risk of criminal recidivism, concerns have been raised about the fairness of algorithmic decision making. Most prior works on algorithmic fairness normatively prescribe how fair decisions ought to be made. In contrast, here, we descriptively survey users for how they perceive and reason about fairness in algorithmic decision making. A key contribution of this work is the framework we propose to understand why people perceive certain features as fair or unfair to be used in algorithms. Our framework identifies eight properties of features, such as relevance, volitionality and reliability, as latent considerations that inform people's moral judgments about the fairness of feature use in decision-making algorithms. We validate our framework through a series of scenario-based surveys with 576 people. We find that, based on a person's assessment of the eight latent properties of a feature in our exemplar scenario, we can accurately (> 85%) predict if the person will judge the use of the feature as fair. Our findings have important implications. At a high-level, we show that people's unfairness concerns are multi-dimensional and argue that future studies need to address unfairness concerns beyond discrimination. At a low-level, we find considerable disagreements in people's fairness judgments. We identify root causes of the disagreements, and note possible pathways to resolve them.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge