Georgios Paliouras
A Scalable Approach to Probabilistic Neuro-Symbolic Verification
Feb 05, 2025



Abstract:Neuro-Symbolic Artificial Intelligence (NeSy AI) has emerged as a promising direction for integrating neural learning with symbolic reasoning. In the probabilistic variant of such systems, a neural network first extracts a set of symbols from sub-symbolic input, which are then used by a symbolic component to reason in a probabilistic manner towards answering a query. In this work, we address the problem of formally verifying the robustness of such NeSy probabilistic reasoning systems, therefore paving the way for their safe deployment in critical domains. We analyze the complexity of solving this problem exactly, and show that it is $\mathrm{NP}^{\# \mathrm{P}}$-hard. To overcome this issue, we propose the first approach for approximate, relaxation-based verification of probabilistic NeSy systems. We demonstrate experimentally that the proposed method scales exponentially better than solver-based solutions and apply our technique to a real-world autonomous driving dataset, where we verify a safety property under large input dimensionalities and network sizes.
From Primes to Paths: Enabling Fast Multi-Relational Graph Analysis
Nov 17, 2024Abstract:Multi-relational networks capture intricate relationships in data and have diverse applications across fields such as biomedical, financial, and social sciences. As networks derived from increasingly large datasets become more common, identifying efficient methods for representing and analyzing them becomes crucial. This work extends the Prime Adjacency Matrices (PAMs) framework, which employs prime numbers to represent distinct relations within a network uniquely. This enables a compact representation of a complete multi-relational graph using a single adjacency matrix, which, in turn, facilitates quick computation of multi-hop adjacency matrices. In this work, we enhance the framework by introducing a lossless algorithm for calculating the multi-hop matrices and propose the Bag of Paths (BoP) representation, a versatile feature extraction methodology for various graph analytics tasks, at the node, edge, and graph level. We demonstrate the efficiency of the framework across various tasks and datasets, showing that simple BoP-based models perform comparably to or better than commonly used neural models while offering improved speed and interpretability.
Reducing Oversmoothing through Informed Weight Initialization in Graph Neural Networks
Oct 31, 2024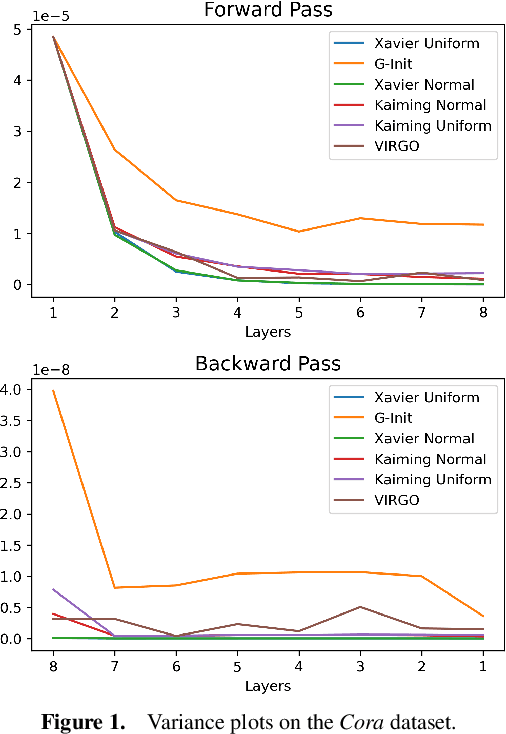
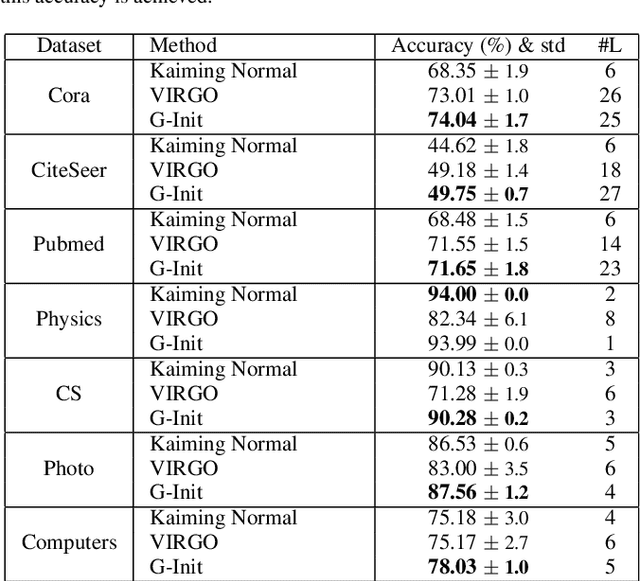
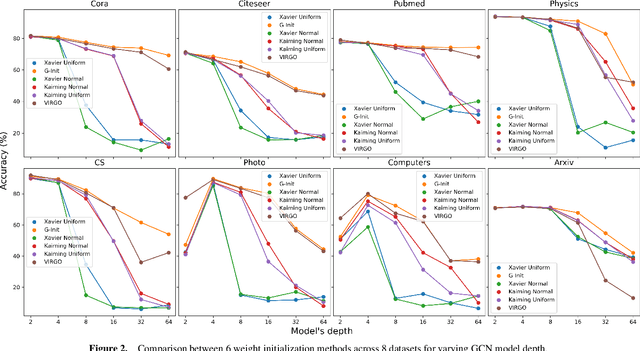

Abstract:In this work, we generalize the ideas of Kaiming initialization to Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) and propose a new scheme (G-Init) that reduces oversmoothing, leading to very good results in node and graph classification tasks. GNNs are commonly initialized using methods designed for other types of Neural Networks, overlooking the underlying graph topology. We analyze theoretically the variance of signals flowing forward and gradients flowing backward in the class of convolutional GNNs. We then simplify our analysis to the case of the GCN and propose a new initialization method. Our results indicate that the new method (G-Init) reduces oversmoothing in deep GNNs, facilitating their effective use. Experimental validation supports our theoretical findings, demonstrating the advantages of deep networks in scenarios with no feature information for unlabeled nodes (i.e., ``cold start'' scenario).
Partially Trained Graph Convolutional Networks Resist Oversmoothing
Oct 17, 2024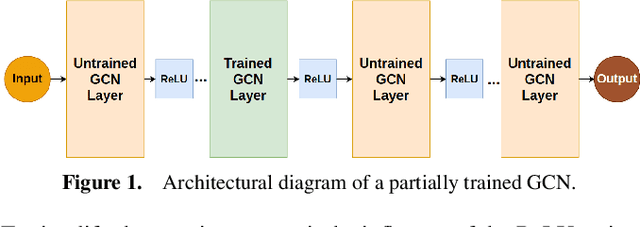
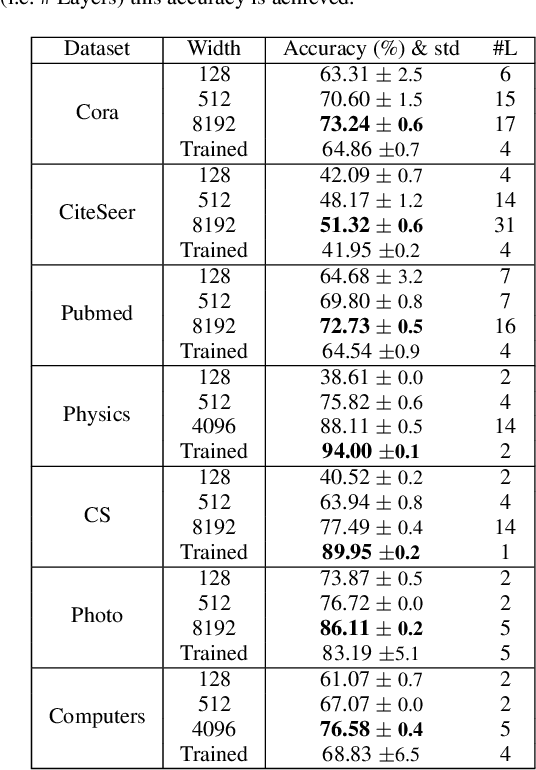


Abstract:In this work we investigate an observation made by Kipf \& Welling, who suggested that untrained GCNs can generate meaningful node embeddings. In particular, we investigate the effect of training only a single layer of a GCN, while keeping the rest of the layers frozen. We propose a basis on which the effect of the untrained layers and their contribution to the generation of embeddings can be predicted. Moreover, we show that network width influences the dissimilarity of node embeddings produced after the initial node features pass through the untrained part of the model. Additionally, we establish a connection between partially trained GCNs and oversmoothing, showing that they are capable of reducing it. We verify our theoretical results experimentally and show the benefits of using deep networks that resist oversmoothing, in a ``cold start'' scenario, where there is a lack of feature information for unlabeled nodes.
Complex Event Recognition with Symbolic Register Transducers: Extended Technical Report
Jul 03, 2024
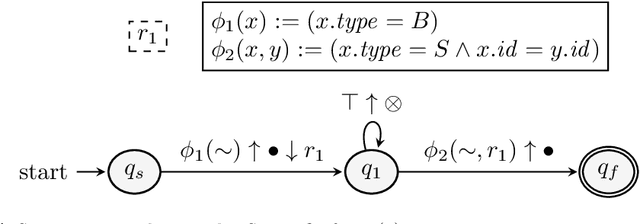


Abstract:We present a system for Complex Event Recognition (CER) based on automata. While multiple such systems have been described in the literature, they typically suffer from a lack of clear and denotational semantics, a limitation which often leads to confusion with respect to their expressive power. In order to address this issue, our system is based on an automaton model which is a combination of symbolic and register automata. We extend previous work on these types of automata, in order to construct a formalism with clear semantics and a corresponding automaton model whose properties can be formally investigated. We call such automata Symbolic Register Transducers (SRT). We show that SRT are closed under various operators, but are not in general closed under complement and they are not determinizable. However, they are closed under these operations when a window operator, quintessential in Complex Event Recognition, is used. We show how SRT can be used in CER in order to detect patterns upon streams of events, using our framework that provides declarative and compositional semantics, and that allows for a systematic treatment of such automata. For SRT to work in pattern detection, we allow them to mark events from the input stream as belonging to a complex event or not, hence the name "transducers". We also present an implementation of SRT which can perform CER. We compare our SRT-based CER engine against other state-of-the-art CER systems and show that it is both more expressive and more efficient.
Overview of BioASQ 2023: The eleventh BioASQ challenge on Large-Scale Biomedical Semantic Indexing and Question Answering
Jul 11, 2023Abstract:This is an overview of the eleventh edition of the BioASQ challenge in the context of the Conference and Labs of the Evaluation Forum (CLEF) 2023. BioASQ is a series of international challenges promoting advances in large-scale biomedical semantic indexing and question answering. This year, BioASQ consisted of new editions of the two established tasks b and Synergy, and a new task (MedProcNER) on semantic annotation of clinical content in Spanish with medical procedures, which have a critical role in medical practice. In this edition of BioASQ, 28 competing teams submitted the results of more than 150 distinct systems in total for the three different shared tasks of the challenge. Similarly to previous editions, most of the participating systems achieved competitive performance, suggesting the continuous advancement of the state-of-the-art in the field.
Financial misstatement detection: a realistic evaluation
May 27, 2023


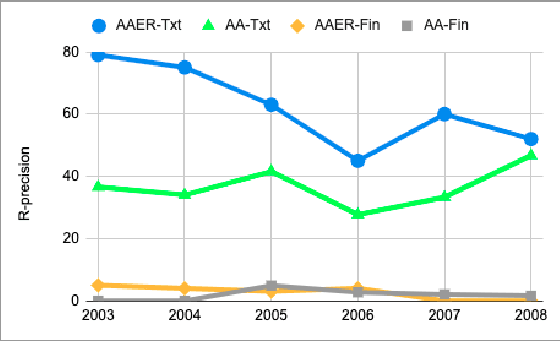
Abstract:In this work, we examine the evaluation process for the task of detecting financial reports with a high risk of containing a misstatement. This task is often referred to, in the literature, as ``misstatement detection in financial reports''. We provide an extensive review of the related literature. We propose a new, realistic evaluation framework for the task which, unlike a large part of the previous work: (a) focuses on the misstatement class and its rarity, (b) considers the dimension of time when splitting data into training and test and (c) considers the fact that misstatements can take a long time to detect. Most importantly, we show that the evaluation process significantly affects system performance, and we analyze the performance of different models and feature types in the new realistic framework.
* 9 pages, ICAIF2021
Analysing Biomedical Knowledge Graphs using Prime Adjacency Matrices
May 17, 2023



Abstract:Most phenomena related to biomedical tasks are inherently complex, and in many cases, are expressed as signals on biomedical Knowledge Graphs (KGs). In this work, we introduce the use of a new representation framework, the Prime Adjacency Matrix (PAM) for biomedical KGs, which allows for very efficient network analysis. PAM utilizes prime numbers to enable representing the whole KG with a single adjacency matrix and the fast computation of multiple properties of the network. We illustrate the applicability of the framework in the biomedical domain by working on different biomedical knowledge graphs and by providing two case studies: one on drug-repurposing for COVID-19 and one on important metapath extraction. We show that we achieve better results than the original proposed workflows, using very simple methods that require no training, in considerably less time.
Large-scale fine-grained semantic indexing of biomedical literature based on weakly-supervised deep learning
Jan 23, 2023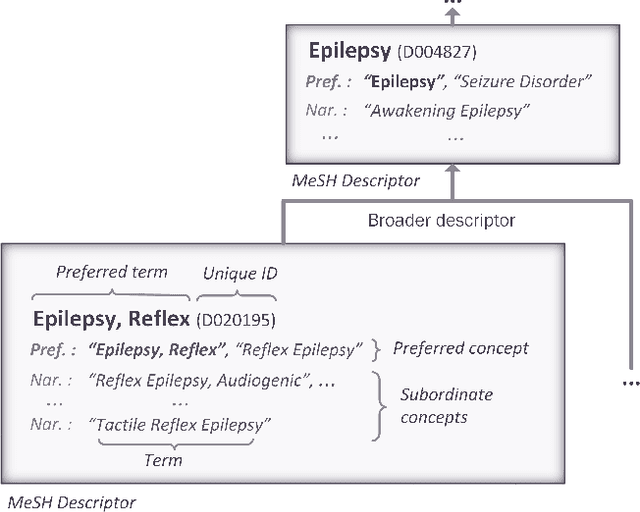
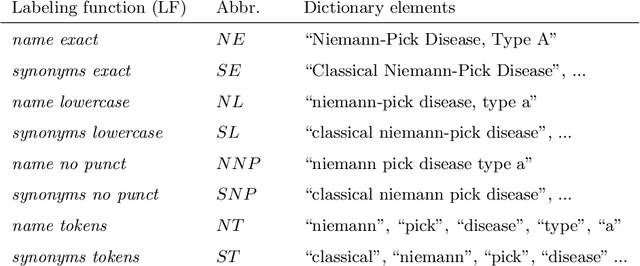
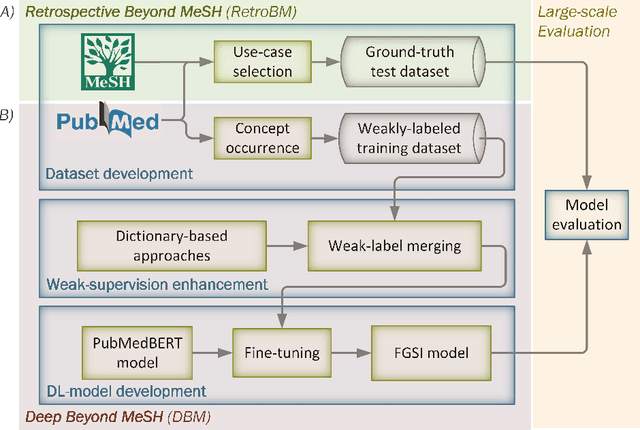
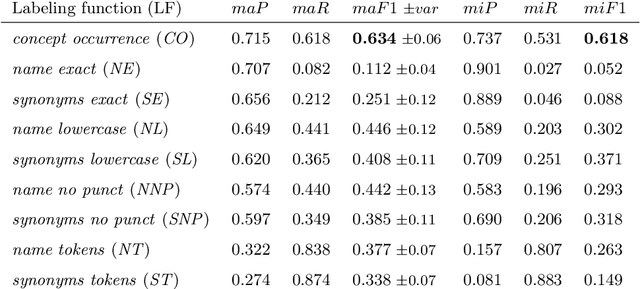
Abstract:Semantic indexing of biomedical literature is usually done at the level of MeSH descriptors, representing topics of interest for the biomedical community. Several related but distinct biomedical concepts are often grouped together in a single coarse-grained descriptor and are treated as a single topic for semantic indexing. This study proposes a new method for the automated refinement of subject annotations at the level of concepts, investigating deep learning approaches. Lacking labelled data for this task, our method relies on weak supervision based on concept occurrence in the abstract of an article. The proposed approach is evaluated on an extended large-scale retrospective scenario, taking advantage of concepts that eventually become MeSH descriptors, for which annotations become available in MEDLINE/PubMed. The results suggest that concept occurrence is a strong heuristic for automated subject annotation refinement and can be further enhanced when combined with dictionary-based heuristics. In addition, such heuristics can be useful as weak supervision for developing deep learning models that can achieve further improvement in some cases.
Overview of BioASQ 2022: The tenth BioASQ challenge on Large-Scale Biomedical Semantic Indexing and Question Answering
Oct 13, 2022Abstract:This paper presents an overview of the tenth edition of the BioASQ challenge in the context of the Conference and Labs of the Evaluation Forum (CLEF) 2022. BioASQ is an ongoing series of challenges that promotes advances in the domain of large-scale biomedical semantic indexing and question answering. In this edition, the challenge was composed of the three established tasks a, b, and Synergy, and a new task named DisTEMIST for automatic semantic annotation and grounding of diseases from clinical content in Spanish, a key concept for semantic indexing and search engines of literature and clinical records. This year, BioASQ received more than 170 distinct systems from 38 teams in total for the four different tasks of the challenge. As in previous years, the majority of the competing systems outperformed the strong baselines, indicating the continuous advancement of the state-of-the-art in this domain.
* 25 pages, 14 tables, 4 figures. arXiv admin note: substantial text overlap with arXiv:2106.14885
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge