Martin Krallinger
SynCABEL: Synthetic Contextualized Augmentation for Biomedical Entity Linking
Jan 27, 2026Abstract:We present SynCABEL (Synthetic Contextualized Augmentation for Biomedical Entity Linking), a framework that addresses a central bottleneck in supervised biomedical entity linking (BEL): the scarcity of expert-annotated training data. SynCABEL leverages large language models to generate context-rich synthetic training examples for all candidate concepts in a target knowledge base, providing broad supervision without manual annotation. We demonstrate that SynCABEL, when combined with decoder-only models and guided inference establish new state-of-the-art results across three widely used multilingual benchmarks: MedMentions for English, QUAERO for French, and SPACCC for Spanish. Evaluating data efficiency, we show that SynCABEL reaches the performance of full human supervision using up to 60% less annotated data, substantially reducing reliance on labor-intensive and costly expert labeling. Finally, acknowledging that standard evaluation based on exact code matching often underestimates clinically valid predictions due to ontology redundancy, we introduce an LLM-as-a-judge protocol. This analysis reveals that SynCABEL significantly improves the rate of clinically valid predictions. Our synthetic datasets, models, and code are released to support reproducibility and future research.
ClinLinker: Medical Entity Linking of Clinical Concept Mentions in Spanish
Apr 09, 2024Abstract:Advances in natural language processing techniques, such as named entity recognition and normalization to widely used standardized terminologies like UMLS or SNOMED-CT, along with the digitalization of electronic health records, have significantly advanced clinical text analysis. This study presents ClinLinker, a novel approach employing a two-phase pipeline for medical entity linking that leverages the potential of in-domain adapted language models for biomedical text mining: initial candidate retrieval using a SapBERT-based bi-encoder and subsequent re-ranking with a cross-encoder, trained by following a contrastive-learning strategy to be tailored to medical concepts in Spanish. This methodology, focused initially on content in Spanish, substantially outperforming multilingual language models designed for the same purpose. This is true even for complex scenarios involving heterogeneous medical terminologies and being trained on a subset of the original data. Our results, evaluated using top-k accuracy at 25 and other top-k metrics, demonstrate our approach's performance on two distinct clinical entity linking Gold Standard corpora, DisTEMIST (diseases) and MedProcNER (clinical procedures), outperforming previous benchmarks by 40 points in DisTEMIST and 43 points in MedProcNER, both normalized to SNOMED-CT codes. These findings highlight our approach's ability to address language-specific nuances and set a new benchmark in entity linking, offering a potent tool for enhancing the utility of digital medical records. The resulting system is of practical value, both for large scale automatic generation of structured data derived from clinical records, as well as for exhaustive extraction and harmonization of predefined clinical variables of interest.
Overview of BioASQ 2023: The eleventh BioASQ challenge on Large-Scale Biomedical Semantic Indexing and Question Answering
Jul 11, 2023Abstract:This is an overview of the eleventh edition of the BioASQ challenge in the context of the Conference and Labs of the Evaluation Forum (CLEF) 2023. BioASQ is a series of international challenges promoting advances in large-scale biomedical semantic indexing and question answering. This year, BioASQ consisted of new editions of the two established tasks b and Synergy, and a new task (MedProcNER) on semantic annotation of clinical content in Spanish with medical procedures, which have a critical role in medical practice. In this edition of BioASQ, 28 competing teams submitted the results of more than 150 distinct systems in total for the three different shared tasks of the challenge. Similarly to previous editions, most of the participating systems achieved competitive performance, suggesting the continuous advancement of the state-of-the-art in the field.
Overview of BioASQ 2022: The tenth BioASQ challenge on Large-Scale Biomedical Semantic Indexing and Question Answering
Oct 13, 2022Abstract:This paper presents an overview of the tenth edition of the BioASQ challenge in the context of the Conference and Labs of the Evaluation Forum (CLEF) 2022. BioASQ is an ongoing series of challenges that promotes advances in the domain of large-scale biomedical semantic indexing and question answering. In this edition, the challenge was composed of the three established tasks a, b, and Synergy, and a new task named DisTEMIST for automatic semantic annotation and grounding of diseases from clinical content in Spanish, a key concept for semantic indexing and search engines of literature and clinical records. This year, BioASQ received more than 170 distinct systems from 38 teams in total for the four different tasks of the challenge. As in previous years, the majority of the competing systems outperformed the strong baselines, indicating the continuous advancement of the state-of-the-art in this domain.
* 25 pages, 14 tables, 4 figures. arXiv admin note: substantial text overlap with arXiv:2106.14885
Spanish Biomedical Crawled Corpus: A Large, Diverse Dataset for Spanish Biomedical Language Models
Sep 16, 2021
Abstract:We introduce CoWeSe (the Corpus Web Salud Espa\~nol), the largest Spanish biomedical corpus to date, consisting of 4.5GB (about 750M tokens) of clean plain text. CoWeSe is the result of a massive crawler on 3000 Spanish domains executed in 2020. The corpus is openly available and already preprocessed. CoWeSe is an important resource for biomedical and health NLP in Spanish and has already been employed to train domain-specific language models and to produce word embbedings. We released the CoWeSe corpus under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International license, both in Zenodo (\url{https://zenodo.org/record/4561971\#.YTI5SnVKiEA}).
Overview of BioASQ 2020: The eighth BioASQ challenge on Large-Scale Biomedical Semantic Indexing and Question Answering
Jun 28, 2021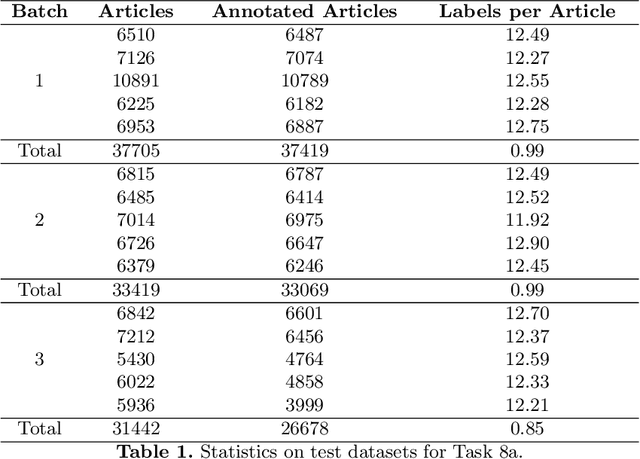
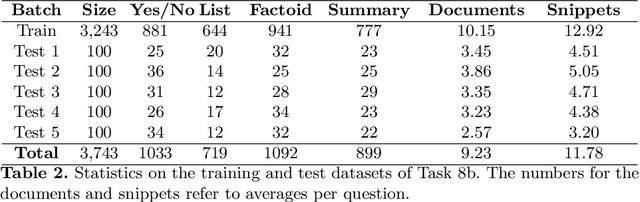
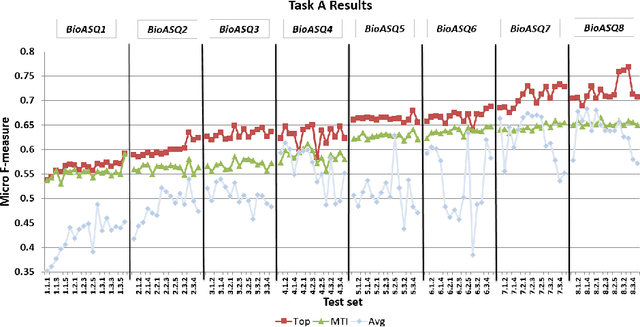
Abstract:In this paper, we present an overview of the eighth edition of the BioASQ challenge, which ran as a lab in the Conference and Labs of the Evaluation Forum (CLEF) 2020. BioASQ is a series of challenges aiming at the promotion of systems and methodologies for large-scale biomedical semantic indexing and question answering. To this end, shared tasks are organized yearly since 2012, where different teams develop systems that compete on the same demanding benchmark datasets that represent the real information needs of experts in the biomedical domain. This year, the challenge has been extended with the introduction of a new task on medical semantic indexing in Spanish. In total, 34 teams with more than 100 systems participated in the three tasks of the challenge. As in previous years, the results of the evaluation reveal that the top-performing systems managed to outperform the strong baselines, which suggests that state-of-the-art systems keep pushing the frontier of research through continuous improvements.
* 21 pages, 10 tables, 3 figures
Overview of BioASQ 2021: The ninth BioASQ challenge on Large-Scale Biomedical Semantic Indexing and Question Answering
Jun 28, 2021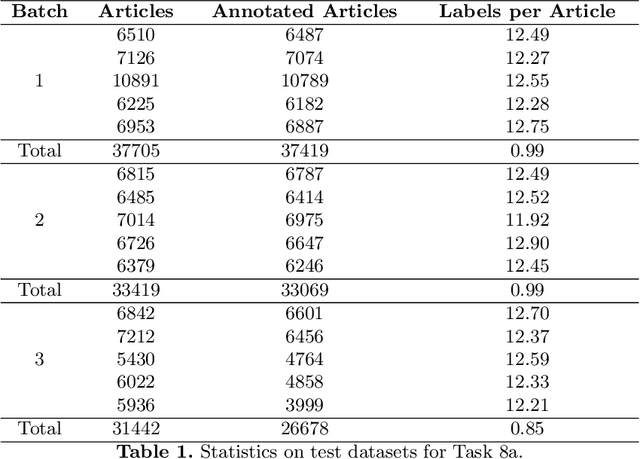
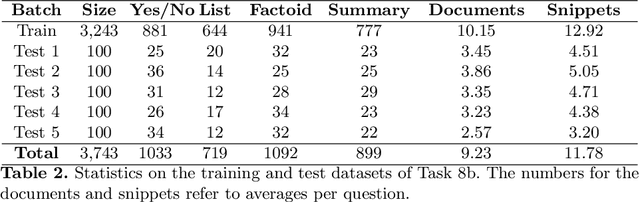
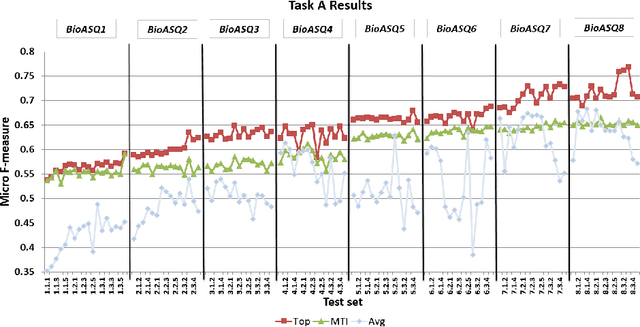
Abstract:Advancing the state-of-the-art in large-scale biomedical semantic indexing and question answering is the main focus of the BioASQ challenge. BioASQ organizes respective tasks where different teams develop systems that are evaluated on the same benchmark datasets that represent the real information needs of experts in the biomedical domain. This paper presents an overview of the ninth edition of the BioASQ challenge in the context of the Conference and Labs of the Evaluation Forum (CLEF) 2021. In this year, a new question answering task, named Synergy, is introduced to support researchers studying the COVID-19 disease and measure the ability of the participating teams to discern information while the problem is still developing. In total, 42 teams with more than 170 systems were registered to participate in the four tasks of the challenge. The evaluation results, similarly to previous years, show a performance gain against the baselines which indicates the continuous improvement of the state-of-the-art in this field.
BVS Corpus: A Multilingual Parallel Corpus of Biomedical Scientific Texts
May 05, 2019



Abstract:The BVS database (Health Virtual Library) is a centralized source of biomedical information for Latin America and Carib, created in 1998 and coordinated by BIREME (Biblioteca Regional de Medicina) in agreement with the Pan American Health Organization (OPAS). Abstracts are available in English, Spanish, and Portuguese, with a subset in more than one language, thus being a possible source of parallel corpora. In this article, we present the development of parallel corpora from BVS in three languages: English, Portuguese, and Spanish. Sentences were automatically aligned using the Hunalign algorithm for EN/ES and EN/PT language pairs, and for a subset of trilingual articles also. We demonstrate the capabilities of our corpus by training a Neural Machine Translation (OpenNMT) system for each language pair, which outperformed related works on scientific biomedical articles. Sentence alignment was also manually evaluated, presenting an average 96% of correctly aligned sentences across all languages. Our parallel corpus is freely available, with complementary information regarding article metadata.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge