Reducing Oversmoothing through Informed Weight Initialization in Graph Neural Networks
Paper and Code
Oct 31, 2024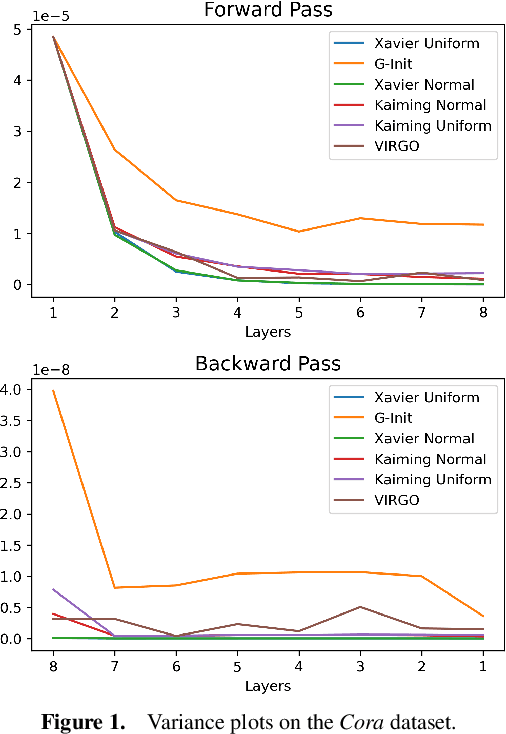
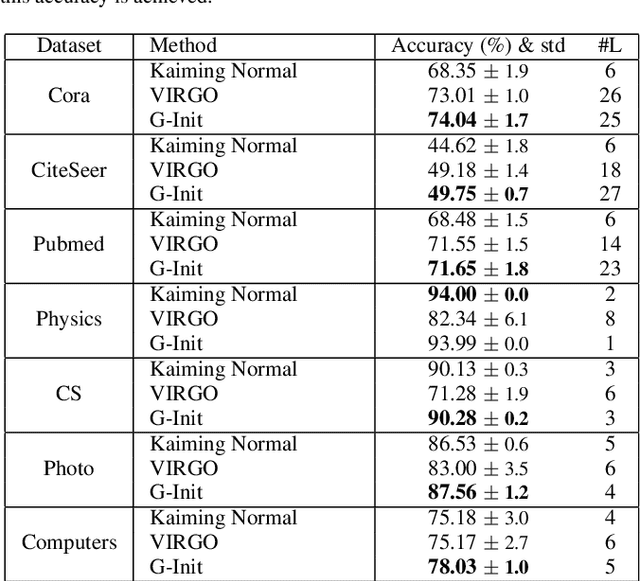
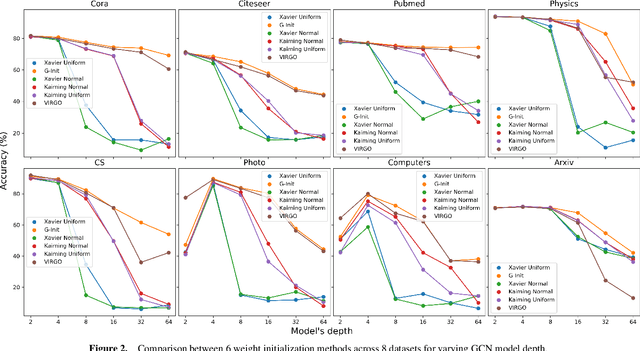

In this work, we generalize the ideas of Kaiming initialization to Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) and propose a new scheme (G-Init) that reduces oversmoothing, leading to very good results in node and graph classification tasks. GNNs are commonly initialized using methods designed for other types of Neural Networks, overlooking the underlying graph topology. We analyze theoretically the variance of signals flowing forward and gradients flowing backward in the class of convolutional GNNs. We then simplify our analysis to the case of the GCN and propose a new initialization method. Our results indicate that the new method (G-Init) reduces oversmoothing in deep GNNs, facilitating their effective use. Experimental validation supports our theoretical findings, demonstrating the advantages of deep networks in scenarios with no feature information for unlabeled nodes (i.e., ``cold start'' scenario).
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge