Gelei Xu
Patient-Conditioned Adaptive Offsets for Reliable Diagnosis across Subgroups
Jan 19, 2026Abstract:AI models for medical diagnosis often exhibit uneven performance across patient populations due to heterogeneity in disease prevalence, imaging appearance, and clinical risk profiles. Existing algorithmic fairness approaches typically seek to reduce such disparities by suppressing sensitive attributes. However, in medical settings these attributes often carry essential diagnostic information, and removing them can degrade accuracy and reliability, particularly in high-stakes applications. In contrast, clinical decision making explicitly incorporates patient context when interpreting diagnostic evidence, suggesting a different design direction for subgroup-aware models. In this paper, we introduce HyperAdapt, a patient-conditioned adaptation framework that improves subgroup reliability while maintaining a shared diagnostic model. Clinically relevant attributes such as age and sex are encoded into a compact embedding and used to condition a hypernetwork-style module, which generates small residual modulation parameters for selected layers of a shared backbone. This design preserves the general medical knowledge learned by the backbone while enabling targeted adjustments that reflect patient-specific variability. To ensure efficiency and robustness, adaptations are constrained through low-rank and bottlenecked parameterizations, limiting both model complexity and computational overhead. Experiments across multiple public medical imaging benchmarks demonstrate that the proposed approach consistently improves subgroup-level performance without sacrificing overall accuracy. On the PAD-UFES-20 dataset, our method outperforms the strongest competing baseline by 4.1% in recall and 4.4% in F1 score, with larger gains observed for underrepresented patient populations.
H-CNN-ViT: A Hierarchical Gated Attention Multi-Branch Model for Bladder Cancer Recurrence Prediction
Nov 19, 2025Abstract:Bladder cancer is one of the most prevalent malignancies worldwide, with a recurrence rate of up to 78%, necessitating accurate post-operative monitoring for effective patient management. Multi-sequence contrast-enhanced MRI is commonly used for recurrence detection; however, interpreting these scans remains challenging, even for experienced radiologists, due to post-surgical alterations such as scarring, swelling, and tissue remodeling. AI-assisted diagnostic tools have shown promise in improving bladder cancer recurrence prediction, yet progress in this field is hindered by the lack of dedicated multi-sequence MRI datasets for recurrence assessment study. In this work, we first introduce a curated multi-sequence, multi-modal MRI dataset specifically designed for bladder cancer recurrence prediction, establishing a valuable benchmark for future research. We then propose H-CNN-ViT, a new Hierarchical Gated Attention Multi-Branch model that enables selective weighting of features from the global (ViT) and local (CNN) paths based on contextual demands, achieving a balanced and targeted feature fusion. Our multi-branch architecture processes each modality independently, ensuring that the unique properties of each imaging channel are optimally captured and integrated. Evaluated on our dataset, H-CNN-ViT achieves an AUC of 78.6%, surpassing state-of-the-art models. Our model is publicly available at https://github.com/XLIAaron/H-CNN-ViT.
AT-CXR: Uncertainty-Aware Agentic Triage for Chest X-rays
Aug 26, 2025Abstract:Agentic AI is advancing rapidly, yet truly autonomous medical-imaging triage, where a system decides when to stop, escalate, or defer under real constraints, remains relatively underexplored. To address this gap, we introduce AT-CXR, an uncertainty-aware agent for chest X-rays. The system estimates per-case confidence and distributional fit, then follows a stepwise policy to issue an automated decision or abstain with a suggested label for human intervention. We evaluate two router designs that share the same inputs and actions: a deterministic rule-based router and an LLM-decided router. Across five-fold evaluation on a balanced subset of NIH ChestX-ray14 dataset, both variants outperform strong zero-shot vision-language models and state-of-the-art supervised classifiers, achieving higher full-coverage accuracy and superior selective-prediction performance, evidenced by a lower area under the risk-coverage curve (AURC) and a lower error rate at high coverage, while operating with lower latency that meets practical clinical constraints. The two routers provide complementary operating points, enabling deployments to prioritize maximal throughput or maximal accuracy. Our code is available at https://github.com/XLIAaron/uncertainty-aware-cxr-agent.
The Cost of Local and Global Fairness in Federated Learning
Mar 27, 2025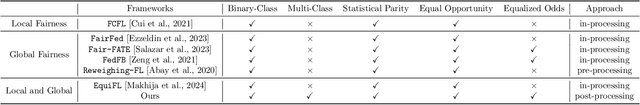

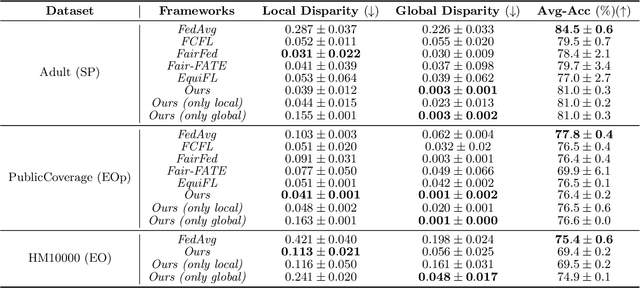
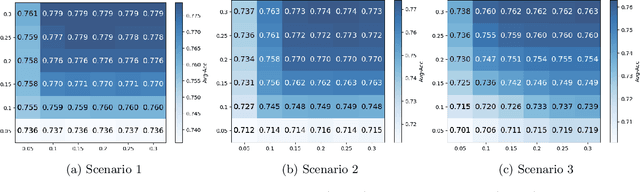
Abstract:With the emerging application of Federated Learning (FL) in finance, hiring and healthcare, FL models are regulated to be fair, preventing disparities with respect to legally protected attributes such as race or gender. Two concepts of fairness are important in FL: global and local fairness. Global fairness addresses the disparity across the entire population and local fairness is concerned with the disparity within each client. Prior fair FL frameworks have improved either global or local fairness without considering both. Furthermore, while the majority of studies on fair FL focuses on binary settings, many real-world applications are multi-class problems. This paper proposes a framework that investigates the minimum accuracy lost for enforcing a specified level of global and local fairness in multi-class FL settings. Our framework leads to a simple post-processing algorithm that derives fair outcome predictors from the Bayesian optimal score functions. Experimental results show that our algorithm outperforms the current state of the art (SOTA) with regard to the accuracy-fairness tradoffs, computational and communication costs. Codes are available at: https://github.com/papersubmission678/The-cost-of-local-and-global-fairness-in-FL .
Tiny-Align: Bridging Automatic Speech Recognition and Large Language Model on the Edge
Nov 21, 2024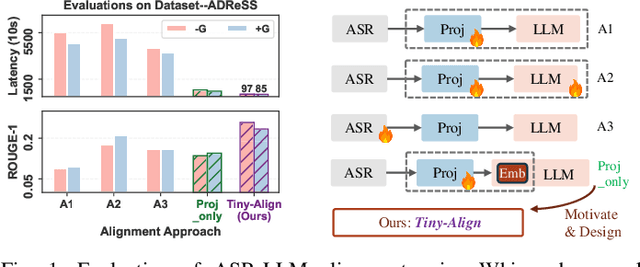
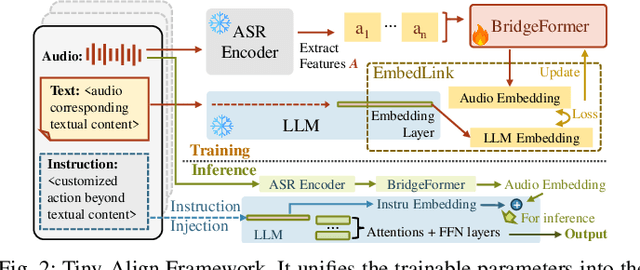
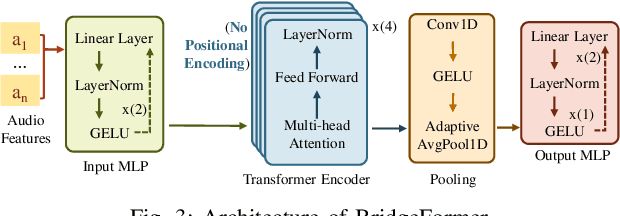
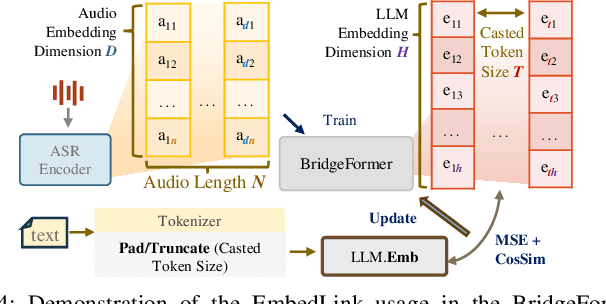
Abstract:The combination of Large Language Models (LLM) and Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR), when deployed on edge devices (called edge ASR-LLM), can serve as a powerful personalized assistant to enable audio-based interaction for users. Compared to text-based interaction, edge ASR-LLM allows accessible and natural audio interactions. Unfortunately, existing ASR-LLM models are mainly trained in high-performance computing environments and produce substantial model weights, making them difficult to deploy on edge devices. More importantly, to better serve users' personalized needs, the ASR-LLM must be able to learn from each distinct user, given that audio input often contains highly personalized characteristics that necessitate personalized on-device training. Since individually fine-tuning the ASR or LLM often leads to suboptimal results due to modality-specific limitations, end-to-end training ensures seamless integration of audio features and language understanding (cross-modal alignment), ultimately enabling a more personalized and efficient adaptation on edge devices. However, due to the complex training requirements and substantial computational demands of existing approaches, cross-modal alignment between ASR audio and LLM can be challenging on edge devices. In this work, we propose a resource-efficient cross-modal alignment framework that bridges ASR and LLMs on edge devices to handle personalized audio input. Our framework enables efficient ASR-LLM alignment on resource-constrained devices like NVIDIA Jetson Orin (8GB RAM), achieving 50x training time speedup while improving the alignment quality by more than 50\%. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first work to study efficient ASR-LLM alignment on resource-constrained edge devices.
An Adaptive System for Wearable Devices to Detect Stress Using Physiological Signals
Jul 21, 2024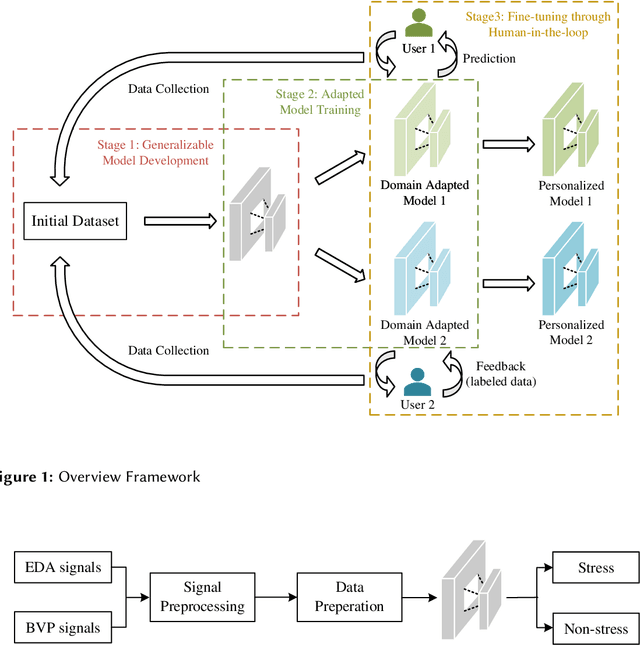
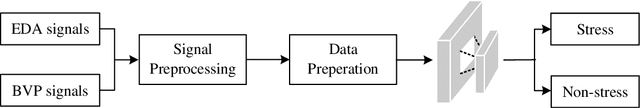
Abstract:Timely stress detection is crucial for protecting vulnerable groups from long-term detrimental effects by enabling early intervention. Wearable devices, by collecting real-time physiological signals, offer a solution for accurate stress detection accommodating individual differences. This position paper introduces an adaptive framework for personalized stress detection using PPG and EDA signals. Unlike traditional methods that rely on a generalized model, which may suffer performance drops when applied to new users due to domain shifts, this framework aims to provide each user with a personalized model for higher stress detection accuracy. The framework involves three stages: developing a generalized model offline with an initial dataset, adapting the model to the user's unlabeled data, and fine-tuning it with a small set of labeled data obtained through user interaction. This approach not only offers a foundation for mobile applications that provide personalized stress detection and intervention but also has the potential to address a wider range of mental health issues beyond stress detection using physiological signals.
Enabling On-Device Learning via Experience Replay with Efficient Dataset Condensation
May 25, 2024Abstract:Upon deployment to edge devices, it is often desirable for a model to further learn from streaming data to improve accuracy. However, extracting representative features from such data is challenging because it is typically unlabeled, non-independent and identically distributed (non-i.i.d), and is seen only once. To mitigate this issue, a common strategy is to maintain a small data buffer on the edge device to hold the most representative data for further learning. As most data is either never stored or quickly discarded, identifying the most representative data to avoid significant information loss becomes critical. In this paper, we propose an on-device framework that addresses this issue by condensing incoming data into more informative samples. Specifically, to effectively handle unlabeled incoming data, we propose a pseudo-labeling technique designed for unlabeled on-device learning environments. Additionally, we develop a dataset condensation technique that only requires little computation resources. To counteract the effects of noisy labels during the condensation process, we further utilize a contrastive learning objective to improve the purity of class data within the buffer. Our empirical results indicate substantial improvements over existing methods, particularly when buffer capacity is severely restricted. For instance, with a buffer capacity of just one sample per class, our method achieves an accuracy that outperforms the best existing baseline by 58.4% on the CIFAR-10 dataset.
Achieving Fairness in Dermatological Disease Diagnosis through Automatic Weight Adjusting Federated Learning and Personalization
Aug 23, 2022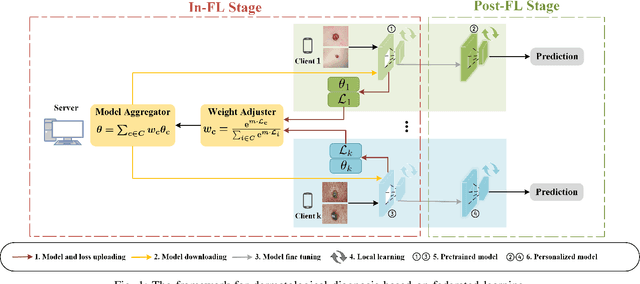
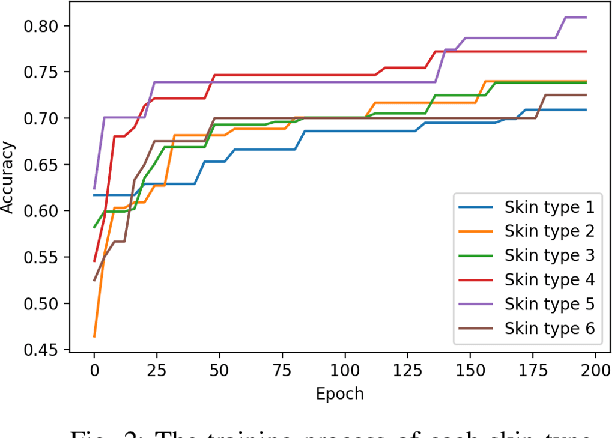
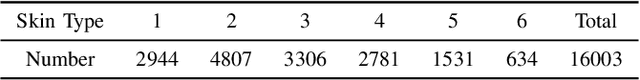
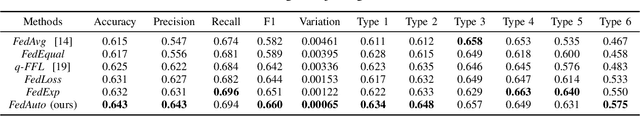
Abstract:Dermatological diseases pose a major threat to the global health, affecting almost one-third of the world's population. Various studies have demonstrated that early diagnosis and intervention are often critical to prognosis and outcome. To this end, the past decade has witnessed the rapid evolvement of deep learning based smartphone apps, which allow users to conveniently and timely identify issues that have emerged around their skins. In order to collect sufficient data needed by deep learning and at the same time protect patient privacy, federated learning is often used, where individual clients aggregate a global model while keeping datasets local. However, existing federated learning frameworks are mostly designed to optimize the overall performance, while common dermatological datasets are heavily imbalanced. When applying federated learning to such datasets, significant disparities in diagnosis accuracy may occur. To address such a fairness issue, this paper proposes a fairness-aware federated learning framework for dermatological disease diagnosis. The framework is divided into two stages: In the first in-FL stage, clients with different skin types are trained in a federated learning process to construct a global model for all skin types. An automatic weight aggregator is used in this process to assign higher weights to the client with higher loss, and the intensity of the aggregator is determined by the level of difference between losses. In the latter post-FL stage, each client fine-tune its personalized model based on the global model in the in-FL stage. To achieve better fairness, models from different epochs are selected for each client to keep the accuracy difference of different skin types within 0.05. Experiments indicate that our proposed framework effectively improves both fairness and accuracy compared with the state-of-the-art.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge