Frederick Shic
Gaze Behavior During a Long-Term, In-Home, Social Robot Intervention for Children with ASD
Jan 05, 2025



Abstract:Atypical gaze behavior is a diagnostic hallmark of Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD), playing a substantial role in the social and communicative challenges that individuals with ASD face. This study explores the impacts of a month-long, in-home intervention designed to promote triadic interactions between a social robot, a child with ASD, and their caregiver. Our results indicate that the intervention successfully promoted appropriate gaze behavior, encouraging children with ASD to follow the robot's gaze, resulting in more frequent and prolonged instances of spontaneous eye contact and joint attention with their caregivers. Additionally, we observed specific timelines for behavioral variability and novelty effects among users. Furthermore, diagnostic measures for ASD emerged as strong predictors of gaze patterns for both caregivers and children. These results deepen our understanding of ASD gaze patterns and highlight the potential for clinical relevance of robot-assisted interventions.
Towards mitigating uncann(eye)ness in face swaps via gaze-centric loss terms
Feb 05, 2024Abstract:Advances in face swapping have enabled the automatic generation of highly realistic faces. Yet face swaps are perceived differently than when looking at real faces, with key differences in viewer behavior surrounding the eyes. Face swapping algorithms generally place no emphasis on the eyes, relying on pixel or feature matching losses that consider the entire face to guide the training process. We further investigate viewer perception of face swaps, focusing our analysis on the presence of an uncanny valley effect. We additionally propose a novel loss equation for the training of face swapping models, leveraging a pretrained gaze estimation network to directly improve representation of the eyes. We confirm that viewed face swaps do elicit uncanny responses from viewers. Our proposed improvements significant reduce viewing angle errors between face swaps and their source material. Our method additionally reduces the prevalence of the eyes as a deciding factor when viewers perform deepfake detection tasks. Our findings have implications on face swapping for special effects, as digital avatars, as privacy mechanisms, and more; negative responses from users could limit effectiveness in said applications. Our gaze improvements are a first step towards alleviating negative viewer perceptions via a targeted approach.
Introducing Explicit Gaze Constraints to Face Swapping
May 25, 2023



Abstract:Face swapping combines one face's identity with another face's non-appearance attributes (expression, head pose, lighting) to generate a synthetic face. This technology is rapidly improving, but falls flat when reconstructing some attributes, particularly gaze. Image-based loss metrics that consider the full face do not effectively capture the perceptually important, yet spatially small, eye regions. Improving gaze in face swaps can improve naturalness and realism, benefiting applications in entertainment, human computer interaction, and more. Improved gaze will also directly improve Deepfake detection efforts, serving as ideal training data for classifiers that rely on gaze for classification. We propose a novel loss function that leverages gaze prediction to inform the face swap model during training and compare against existing methods. We find all methods to significantly benefit gaze in resulting face swaps.
Practical Digital Disguises: Leveraging Face Swaps to Protect Patient Privacy
Apr 13, 2022
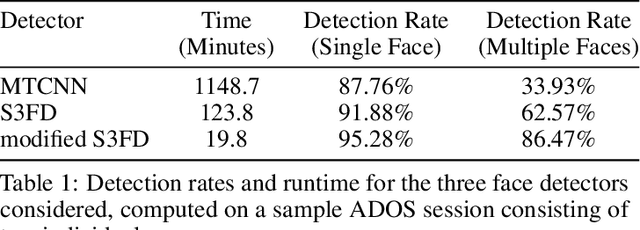
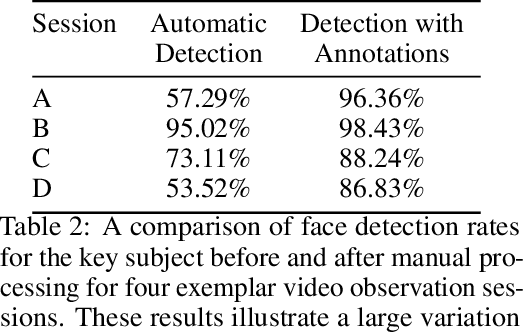
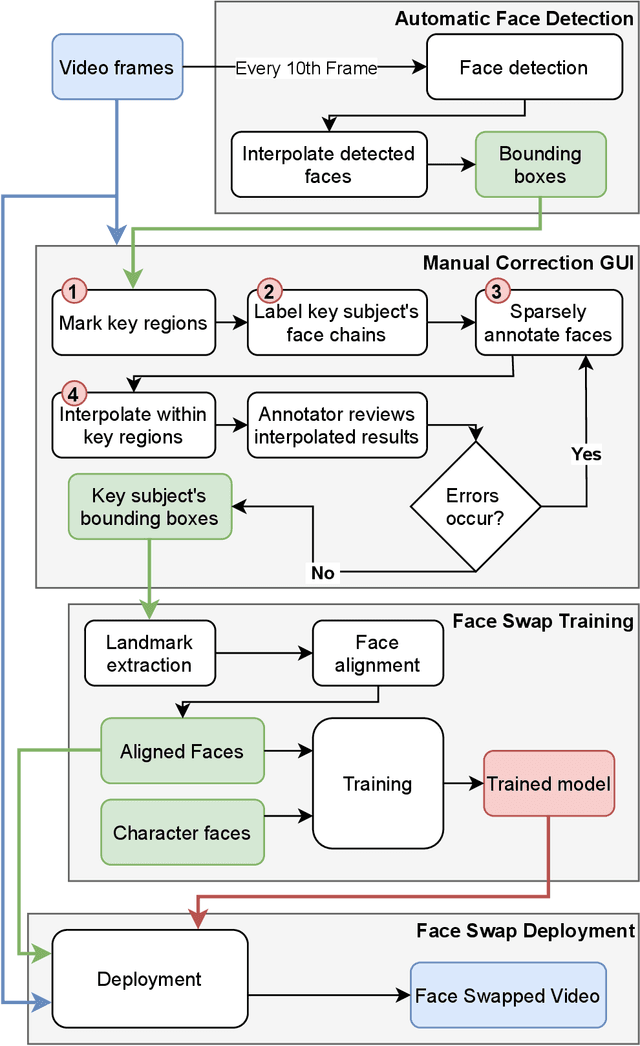
Abstract:With rapid advancements in image generation technology, face swapping for privacy protection has emerged as an active area of research. The ultimate benefit is improved access to video datasets, e.g. in healthcare settings. Recent literature has proposed deep network-based architectures to perform facial swaps and reported the associated reduction in facial recognition accuracy. However, there is not much reporting on how well these methods preserve the types of semantic information needed for the privatized videos to remain useful for their intended application. Our main contribution is a novel end-to-end face swapping pipeline for recorded videos of standardized assessments of autism symptoms in children. Through this design, we are the first to provide a methodology for assessing the privacy-utility trade-offs for the face swapping approach to patient privacy protection. Our methodology can show, for example, that current deep network based face swapping is bottle-necked by face detection in real world videos, and the extent to which gaze and expression information is preserved by face swaps relative to baseline privatization methods such as blurring.
Learning Oculomotor Behaviors from Scanpath
Aug 11, 2021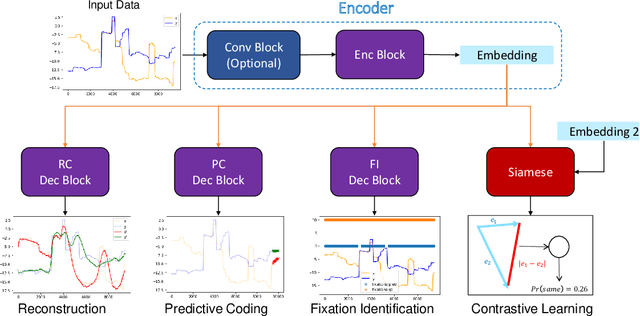
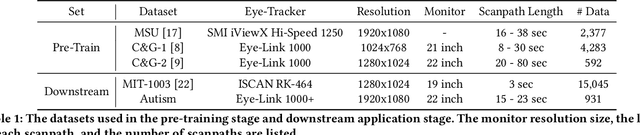
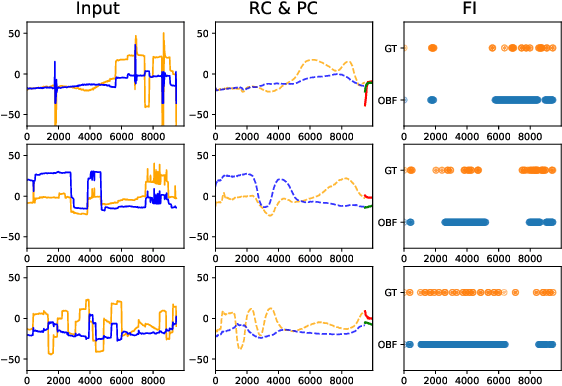
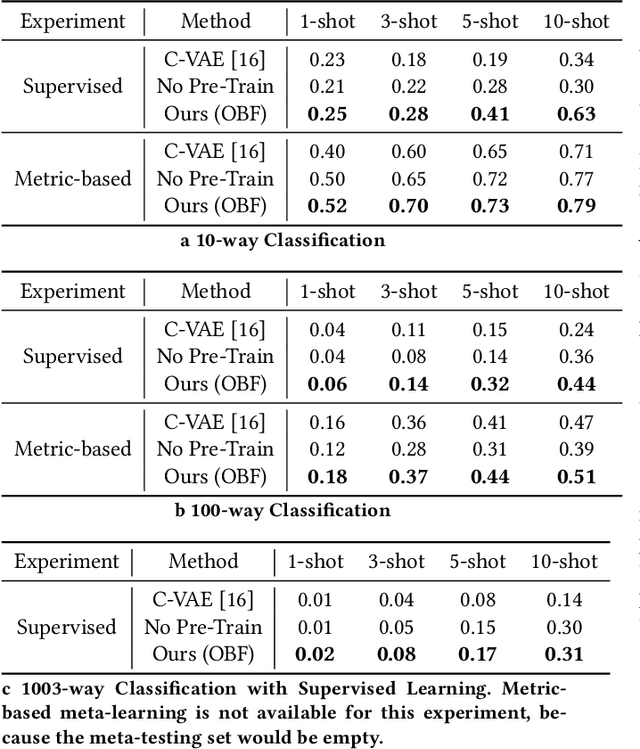
Abstract:Identifying oculomotor behaviors relevant for eye-tracking applications is a critical but often challenging task. Aiming to automatically learn and extract knowledge from existing eye-tracking data, we develop a novel method that creates rich representations of oculomotor scanpaths to facilitate the learning of downstream tasks. The proposed stimulus-agnostic Oculomotor Behavior Framework (OBF) model learns human oculomotor behaviors from unsupervised and semi-supervised tasks, including reconstruction, predictive coding, fixation identification, and contrastive learning tasks. The resultant pre-trained OBF model can be used in a variety of applications. Our pre-trained model outperforms baseline approaches and traditional scanpath methods in autism spectrum disorder and viewed-stimulus classification tasks. Ablation experiments further show our proposed method could achieve even better results with larger model sizes and more diverse eye-tracking training datasets, supporting the model's potential for future eye-tracking applications. Open source code: http://github.com/BeibinLi/OBF.
Sparsely Grouped Input Variables for Neural Networks
Nov 29, 2019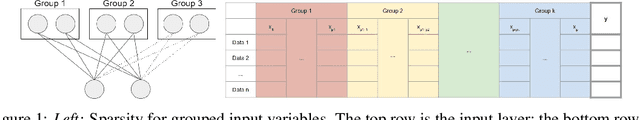

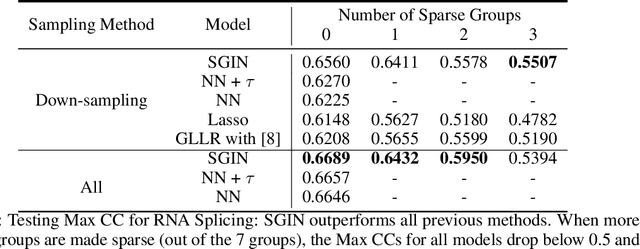
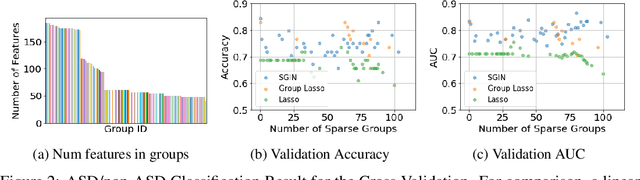
Abstract:In genomic analysis, biomarker discovery, image recognition, and other systems involving machine learning, input variables can often be organized into different groups by their source or semantic category. Eliminating some groups of variables can expedite the process of data acquisition and avoid over-fitting. Researchers have used the group lasso to ensure group sparsity in linear models and have extended it to create compact neural networks in meta-learning. Different from previous studies, we use multi-layer non-linear neural networks to find sparse groups for input variables. We propose a new loss function to regularize parameters for grouped input variables, design a new optimization algorithm for this loss function, and test these methods in three real-world settings. We achieve group sparsity for three datasets, maintaining satisfying results while excluding one nucleotide position from an RNA splicing experiment, excluding 89.9% of stimuli from an eye-tracking experiment, and excluding 60% of image rows from an experiment on the MNIST dataset.
A Facial Affect Analysis System for Autism Spectrum Disorder
Apr 07, 2019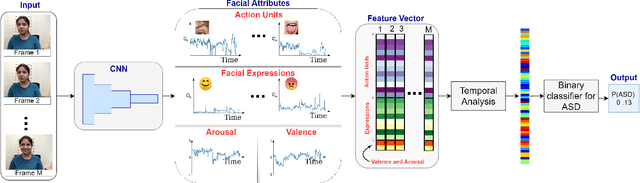
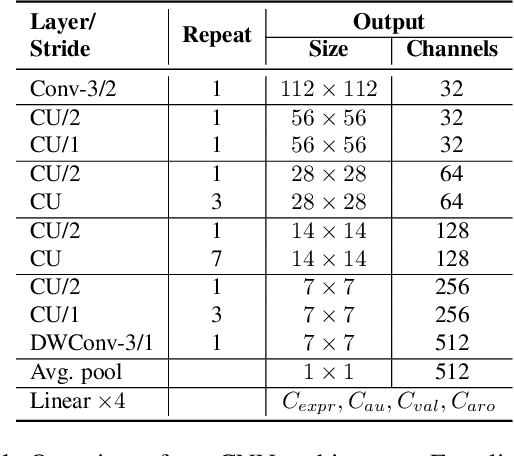
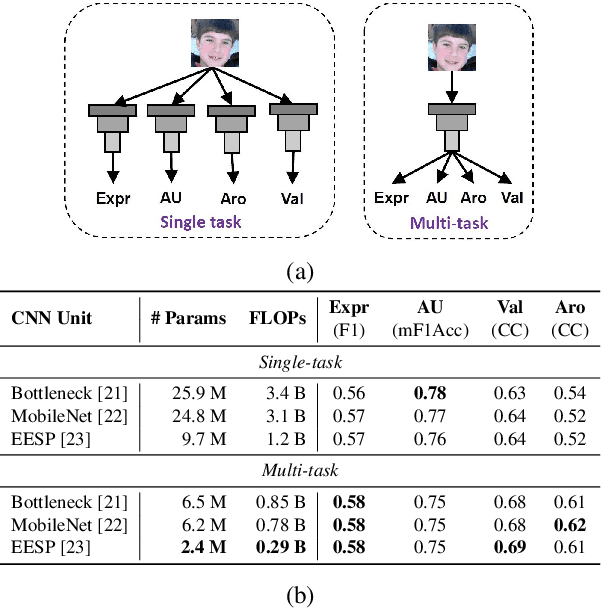
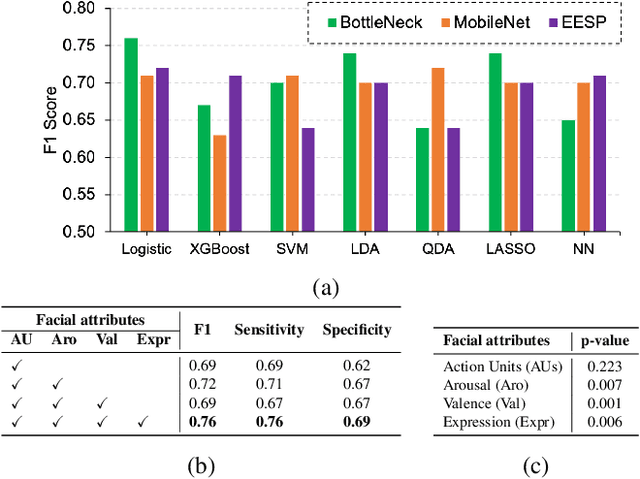
Abstract:In this paper, we introduce an end-to-end machine learning-based system for classifying autism spectrum disorder (ASD) using facial attributes such as expressions, action units, arousal, and valence. Our system classifies ASD using representations of different facial attributes from convolutional neural networks, which are trained on images in the wild. Our experimental results show that different facial attributes used in our system are statistically significant and improve sensitivity, specificity, and F1 score of ASD classification by a large margin. In particular, the addition of different facial attributes improves the performance of ASD classification by about 7% which achieves a F1 score of 76%.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge