Minah Kim
Learning Oculomotor Behaviors from Scanpath
Aug 11, 2021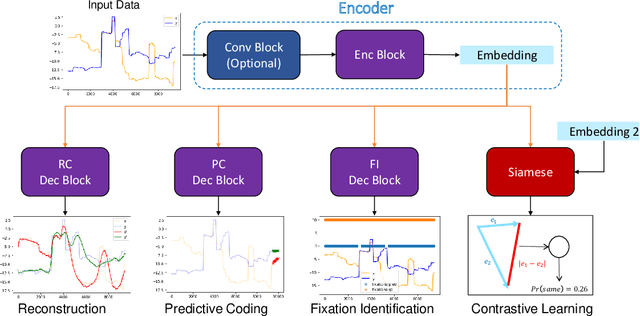
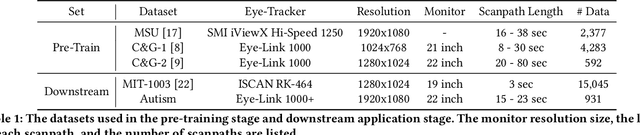
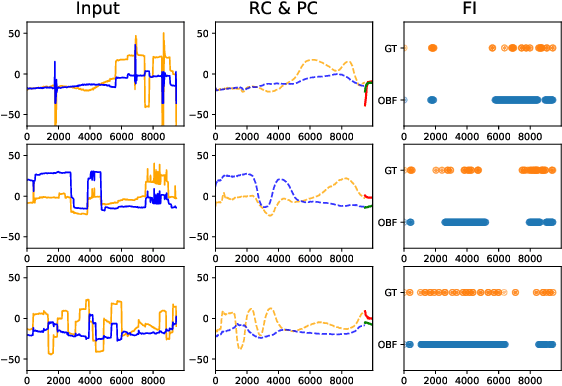
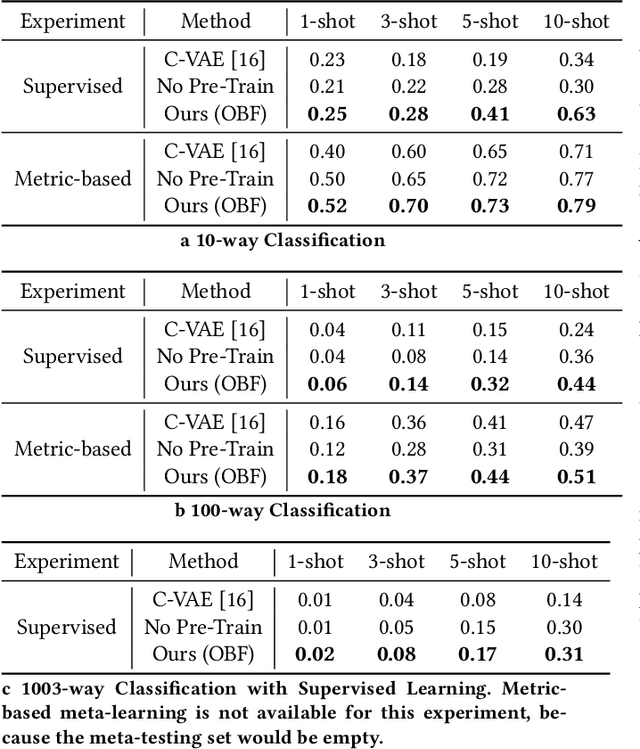
Abstract:Identifying oculomotor behaviors relevant for eye-tracking applications is a critical but often challenging task. Aiming to automatically learn and extract knowledge from existing eye-tracking data, we develop a novel method that creates rich representations of oculomotor scanpaths to facilitate the learning of downstream tasks. The proposed stimulus-agnostic Oculomotor Behavior Framework (OBF) model learns human oculomotor behaviors from unsupervised and semi-supervised tasks, including reconstruction, predictive coding, fixation identification, and contrastive learning tasks. The resultant pre-trained OBF model can be used in a variety of applications. Our pre-trained model outperforms baseline approaches and traditional scanpath methods in autism spectrum disorder and viewed-stimulus classification tasks. Ablation experiments further show our proposed method could achieve even better results with larger model sizes and more diverse eye-tracking training datasets, supporting the model's potential for future eye-tracking applications. Open source code: http://github.com/BeibinLi/OBF.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge