Frederick Eberhardt
Lost in Aggregation: The Causal Interpretation of the IV Estimand
Jan 17, 2026Abstract:Instrumental variable based estimation of a causal effect has emerged as a standard approach to mitigate confounding bias in the social sciences and epidemiology, where conducting randomized experiments can be too costly or impossible. However, justifying the validity of the instrument often poses a significant challenge. In this work, we highlight a problem generally neglected in arguments for instrumental variable validity: the presence of an ''aggregate treatment variable'', where the treatment (e.g., education, GDP, caloric intake) is composed of finer-grained components that each may have a different effect on the outcome. We show that the causal effect of an aggregate treatment is generally ambiguous, as it depends on how interventions on the aggregate are instantiated at the component level, formalized through the aggregate-constrained component intervention distribution. We then characterize conditions on the interventional distribution and the aggregate setting under which standard instrumental variable estimators identify the aggregate effect. The contrived nature of these conditions implies major limitations on the interpretation of instrumental variable estimates based on aggregate treatments and highlights the need for a broader justificatory base for the exclusion restriction in such settings.
When the Coffee Feature Activates on Coffins: An Analysis of Feature Extraction and Steering for Mechanistic Interpretability
Jan 06, 2026Abstract:Recent work by Anthropic on Mechanistic interpretability claims to understand and control Large Language Models by extracting human-interpretable features from their neural activation patterns using sparse autoencoders (SAEs). If successful, this approach offers one of the most promising routes for human oversight in AI safety. We conduct an initial stress-test of these claims by replicating their main results with open-source SAEs for Llama 3.1. While we successfully reproduce basic feature extraction and steering capabilities, our investigation suggests that major caution is warranted regarding the generalizability of these claims. We find that feature steering exhibits substantial fragility, with sensitivity to layer selection, steering magnitude, and context. We observe non-standard activation behavior and demonstrate the difficulty to distinguish thematically similar features from one another. While SAE-based interpretability produces compelling demonstrations in selected cases, current methods often fall short of the systematic reliability required for safety-critical applications. This suggests a necessary shift in focus from prioritizing interpretability of internal representations toward reliable prediction and control of model output. Our work contributes to a more nuanced understanding of what mechanistic interpretability has achieved and highlights fundamental challenges for AI safety that remain unresolved.
Lower Bounds on the Size of Markov Equivalence Classes
Jun 26, 2025Abstract:Causal discovery algorithms typically recover causal graphs only up to their Markov equivalence classes unless additional parametric assumptions are made. The sizes of these equivalence classes reflect the limits of what can be learned about the underlying causal graph from purely observational data. Under the assumptions of acyclicity, causal sufficiency, and a uniform model prior, Markov equivalence classes are known to be small on average. In this paper, we show that this is no longer the case when any of these assumptions is relaxed. Specifically, we prove exponentially large lower bounds for the expected size of Markov equivalence classes in three settings: sparse random directed acyclic graphs, uniformly random acyclic directed mixed graphs, and uniformly random directed cyclic graphs.
Modeling Discrimination with Causal Abstraction
Jan 14, 2025Abstract:A person is directly racially discriminated against only if her race caused her worse treatment. This implies that race is an attribute sufficiently separable from other attributes to isolate its causal role. But race is embedded in a nexus of social factors that resist isolated treatment. If race is socially constructed, in what sense can it cause worse treatment? Some propose that the perception of race, rather than race itself, causes worse treatment. Others suggest that since causal models require modularity, i.e. the ability to isolate causal effects, attempts to causally model discrimination are misguided. This paper addresses the problem differently. We introduce a framework for reasoning about discrimination, in which race is a high-level abstraction of lower-level features. In this framework, race can be modeled as itself causing worse treatment. Modularity is ensured by allowing assumptions about social construction to be precisely and explicitly stated, via an alignment between race and its constituents. Such assumptions can then be subjected to normative and empirical challenges, which lead to different views of when discrimination occurs. By distinguishing constitutive and causal relations, the abstraction framework pinpoints disagreements in the current literature on modeling discrimination, while preserving a precise causal account of discrimination.
Controlling for discrete unmeasured confounding in nonlinear causal models
Aug 10, 2024



Abstract:Unmeasured confounding is a major challenge for identifying causal relationships from non-experimental data. Here, we propose a method that can accommodate unmeasured discrete confounding. Extending recent identifiability results in deep latent variable models, we show theoretically that confounding can be detected and corrected under the assumption that the observed data is a piecewise affine transformation of a latent Gaussian mixture model and that the identity of the mixture components is confounded. We provide a flow-based algorithm to estimate this model and perform deconfounding. Experimental results on synthetic and real-world data provide support for the effectiveness of our approach.
Approximate Causal Abstraction
Jun 29, 2019


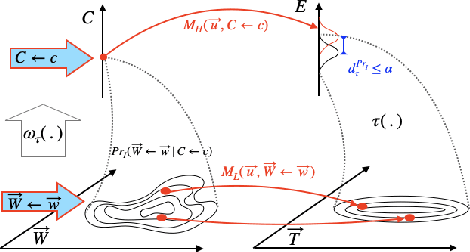
Abstract:Scientific models describe natural phenomena at different levels of abstraction. Abstract descriptions can provide the basis for interventions on the system and explanation of observed phenomena at a level of granularity that is coarser than the most fundamental account of the system. Beckers and Halpern (2019), building on work of Rubenstein et al. (2017), developed an account of abstraction for causal models that is exact. Here we extend this account to the more realistic case where an abstract causal model offers only an approximation of the underlying system. We show how the resulting account handles the discrepancy that can arise between low- and high-level causal models of the same system, and in the process provide an account of how one causal model approximates another, a topic of independent interest. Finally, we extend the account of approximate abstractions to probabilistic causal models, indicating how and where uncertainty can enter into an approximate abstraction.
ASP-based Discovery of Semi-Markovian Causal Models under Weaker Assumptions
Jun 06, 2019



Abstract:In recent years the possibility of relaxing the so-called Faithfulness assumption in automated causal discovery has been investigated. The investigation showed (1) that the Faithfulness assumption can be weakened in various ways that in an important sense preserve its power, and (2) that weakening of Faithfulness may help to speed up methods based on Answer Set Programming. However, this line of work has so far only considered the discovery of causal models without latent variables. In this paper, we study weakenings of Faithfulness for constraint-based discovery of semi-Markovian causal models, which accommodate the possibility of latent variables, and show that both (1) and (2) remain the case in this more realistic setting.
Fast Conditional Independence Test for Vector Variables with Large Sample Sizes
Apr 08, 2018
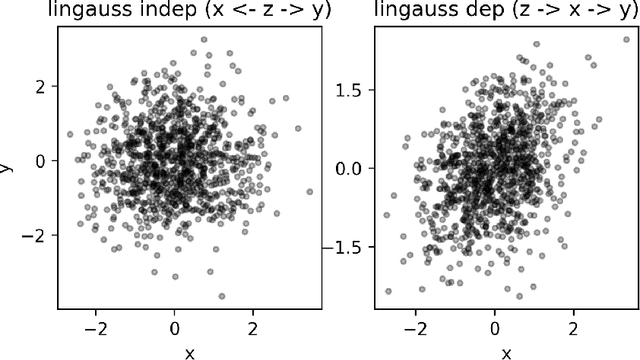

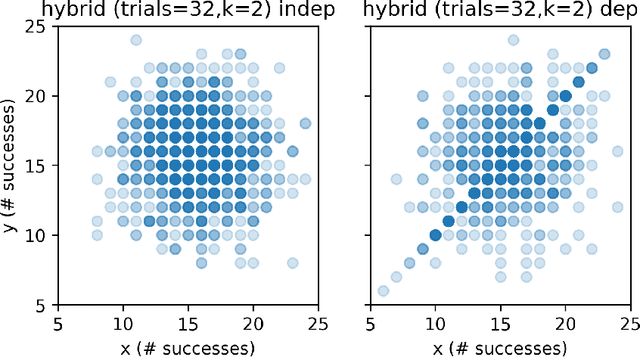
Abstract:We present and evaluate the Fast (conditional) Independence Test (FIT) -- a nonparametric conditional independence test. The test is based on the idea that when $P(X \mid Y, Z) = P(X \mid Y)$, $Z$ is not useful as a feature to predict $X$, as long as $Y$ is also a regressor. On the contrary, if $P(X \mid Y, Z) \neq P(X \mid Y)$, $Z$ might improve prediction results. FIT applies to thousand-dimensional random variables with a hundred thousand samples in a fraction of the time required by alternative methods. We provide an extensive evaluation that compares FIT to six extant nonparametric independence tests. The evaluation shows that FIT has low probability of making both Type I and Type II errors compared to other tests, especially as the number of available samples grows. Our implementation of FIT is publicly available.
Estimating Causal Direction and Confounding of Two Discrete Variables
Nov 04, 2016


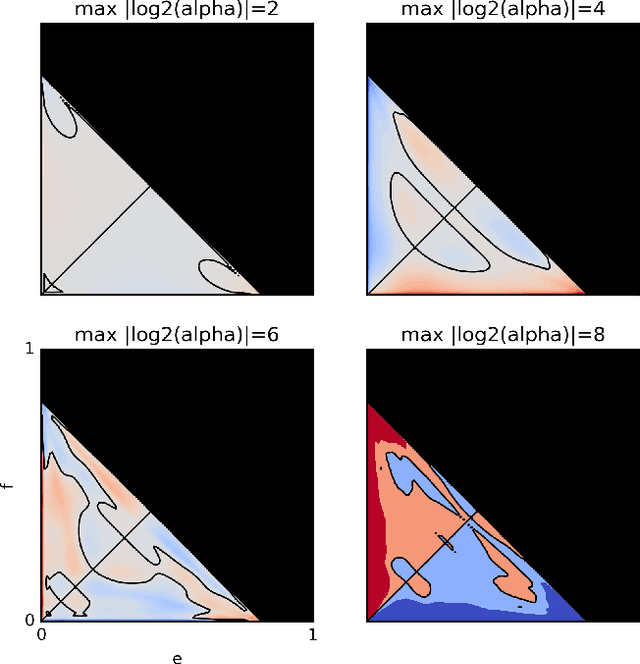
Abstract:We propose a method to classify the causal relationship between two discrete variables given only the joint distribution of the variables, acknowledging that the method is subject to an inherent baseline error. We assume that the causal system is acyclicity, but we do allow for hidden common causes. Our algorithm presupposes that the probability distributions $P(C)$ of a cause $C$ is independent from the probability distribution $P(E\mid C)$ of the cause-effect mechanism. While our classifier is trained with a Bayesian assumption of flat hyperpriors, we do not make this assumption about our test data. This work connects to recent developments on the identifiability of causal models over continuous variables under the assumption of "independent mechanisms". Carefully-commented Python notebooks that reproduce all our experiments are available online at http://vision.caltech.edu/~kchalupk/code.html.
Causal Discovery from Subsampled Time Series Data by Constraint Optimization
Jul 13, 2016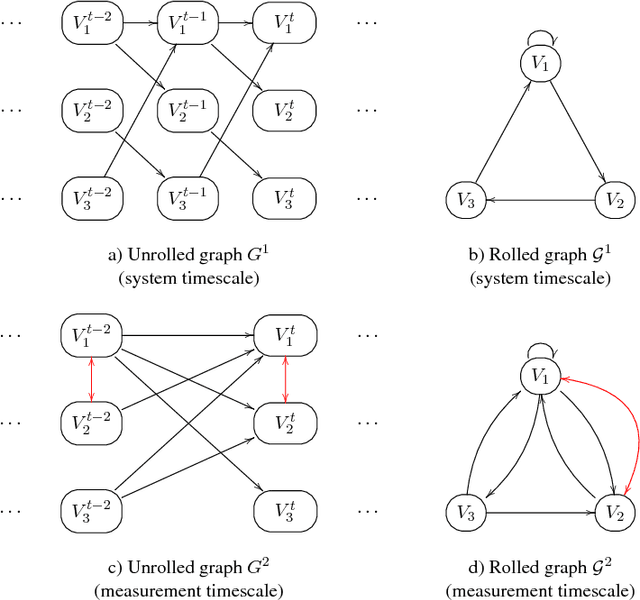
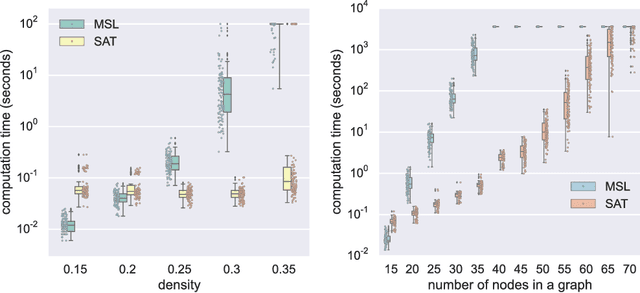
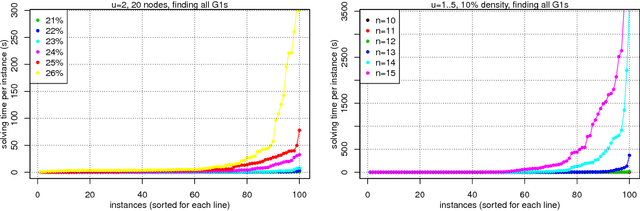
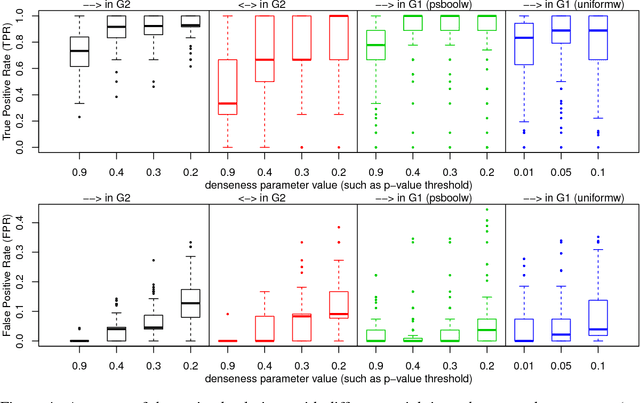
Abstract:This paper focuses on causal structure estimation from time series data in which measurements are obtained at a coarser timescale than the causal timescale of the underlying system. Previous work has shown that such subsampling can lead to significant errors about the system's causal structure if not properly taken into account. In this paper, we first consider the search for the system timescale causal structures that correspond to a given measurement timescale structure. We provide a constraint satisfaction procedure whose computational performance is several orders of magnitude better than previous approaches. We then consider finite-sample data as input, and propose the first constraint optimization approach for recovering the system timescale causal structure. This algorithm optimally recovers from possible conflicts due to statistical errors. More generally, these advances allow for a robust and non-parametric estimation of system timescale causal structures from subsampled time series data.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge