David Danks
Causal Graph Recovery in Neuroimaging through Answer Set Programming
Jun 10, 2025Abstract:Learning graphical causal structures from time series data presents significant challenges, especially when the measurement frequency does not match the causal timescale of the system. This often leads to a set of equally possible underlying causal graphs due to information loss from sub-sampling (i.e., not observing all possible states of the system throughout time). Our research addresses this challenge by incorporating the effects of sub-sampling in the derivation of causal graphs, resulting in more accurate and intuitive outcomes. We use a constraint optimization approach, specifically answer set programming (ASP), to find the optimal set of answers. ASP not only identifies the most probable underlying graph, but also provides an equivalence class of possible graphs for expert selection. In addition, using ASP allows us to leverage graph theory to further prune the set of possible solutions, yielding a smaller, more accurate answer set significantly faster than traditional approaches. We validate our approach on both simulated data and empirical structural brain connectivity, and demonstrate its superiority over established methods in these experiments. We further show how our method can be used as a meta-approach on top of established methods to obtain, on average, 12% improvement in F1 score. In addition, we achieved state of the art results in terms of precision and recall of reconstructing causal graph from sub-sampled time series data. Finally, our method shows robustness to varying degrees of sub-sampling on realistic simulations, whereas other methods perform worse for higher rates of sub-sampling.
ION-C: Integration of Overlapping Networks via Constraints
Nov 06, 2024Abstract:In many causal learning problems, variables of interest are often not all measured over the same observations, but are instead distributed across multiple datasets with overlapping variables. Tillman et al. (2008) presented the first algorithm for enumerating the minimal equivalence class of ground-truth DAGs consistent with all input graphs by exploiting local independence relations, called ION. In this paper, this problem is formulated as a more computationally efficient answer set programming (ASP) problem, which we call ION-C, and solved with the ASP system clingo. The ION-C algorithm was run on random synthetic graphs with varying sizes, densities, and degrees of overlap between subgraphs, with overlap having the largest impact on runtime, number of solution graphs, and agreement within the output set. To validate ION-C on real-world data, we ran the algorithm on overlapping graphs learned from data from two successive iterations of the European Social Survey (ESS), using a procedure for conducting joint independence tests to prevent inconsistencies in the input.
Bias Mitigation via Compensation: A Reinforcement Learning Perspective
Apr 30, 2024Abstract:As AI increasingly integrates with human decision-making, we must carefully consider interactions between the two. In particular, current approaches focus on optimizing individual agent actions but often overlook the nuances of collective intelligence. Group dynamics might require that one agent (e.g., the AI system) compensate for biases and errors in another agent (e.g., the human), but this compensation should be carefully developed. We provide a theoretical framework for algorithmic compensation that synthesizes game theory and reinforcement learning principles to demonstrate the natural emergence of deceptive outcomes from the continuous learning dynamics of agents. We provide simulation results involving Markov Decision Processes (MDP) learning to interact. This work then underpins our ethical analysis of the conditions in which AI agents should adapt to biases and behaviors of other agents in dynamic and complex decision-making environments. Overall, our approach addresses the nuanced role of strategic deception of humans, challenging previous assumptions about its detrimental effects. We assert that compensation for others' biases can enhance coordination and ethical alignment: strategic deception, when ethically managed, can positively shape human-AI interactions.
Application of the NIST AI Risk Management Framework to Surveillance Technology
Mar 22, 2024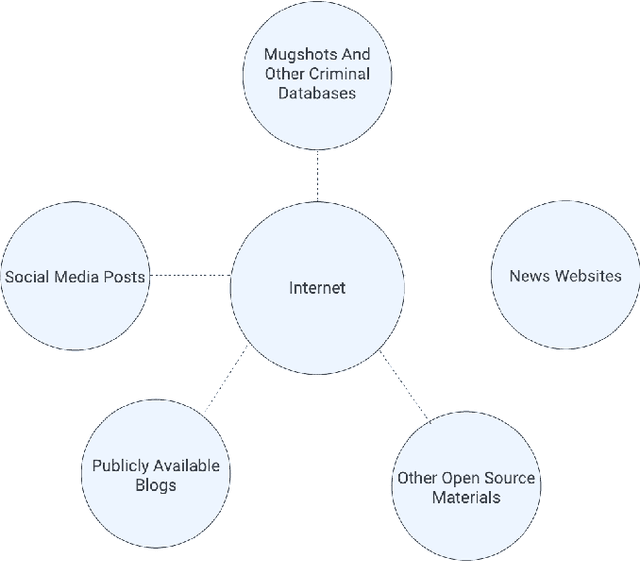
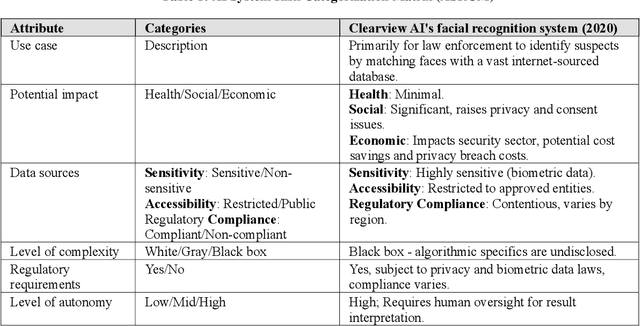
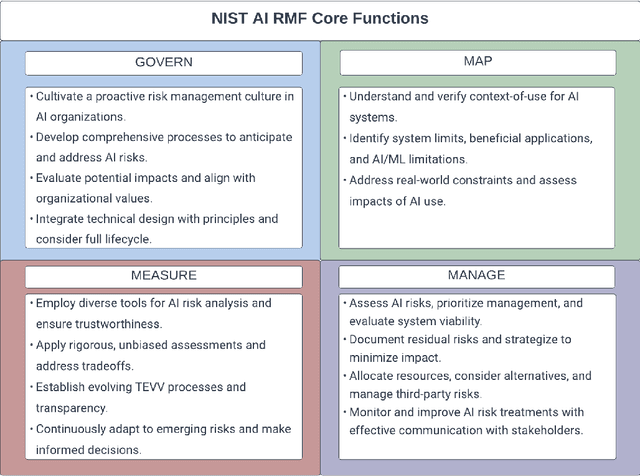
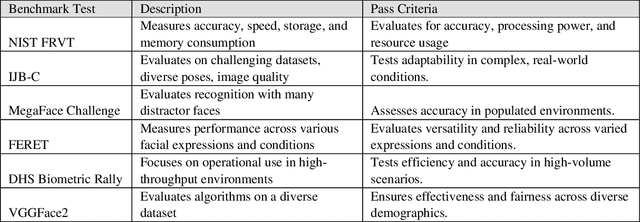
Abstract:This study offers an in-depth analysis of the application and implications of the National Institute of Standards and Technology's AI Risk Management Framework (NIST AI RMF) within the domain of surveillance technologies, particularly facial recognition technology. Given the inherently high-risk and consequential nature of facial recognition systems, our research emphasizes the critical need for a structured approach to risk management in this sector. The paper presents a detailed case study demonstrating the utility of the NIST AI RMF in identifying and mitigating risks that might otherwise remain unnoticed in these technologies. Our primary objective is to develop a comprehensive risk management strategy that advances the practice of responsible AI utilization in feasible, scalable ways. We propose a six-step process tailored to the specific challenges of surveillance technology that aims to produce a more systematic and effective risk management practice. This process emphasizes continual assessment and improvement to facilitate companies in managing AI-related risks more robustly and ensuring ethical and responsible deployment of AI systems. Additionally, our analysis uncovers and discusses critical gaps in the current framework of the NIST AI RMF, particularly concerning its application to surveillance technologies. These insights contribute to the evolving discourse on AI governance and risk management, highlighting areas for future refinement and development in frameworks like the NIST AI RMF.
Commercial AI, Conflict, and Moral Responsibility: A theoretical analysis and practical approach to the moral responsibilities associated with dual-use AI technology
Jan 30, 2024Abstract:This paper presents a theoretical analysis and practical approach to the moral responsibilities when developing AI systems for non-military applications that may nonetheless be used for conflict applications. We argue that AI represents a form of crossover technology that is different from previous historical examples of dual- or multi-use technology as it has a multiplicative effect across other technologies. As a result, existing analyses of ethical responsibilities around dual-use technologies do not necessarily work for AI systems. We instead argue that stakeholders involved in the AI system lifecycle are morally responsible for uses of their systems that are reasonably foreseeable. The core idea is that an agent's moral responsibility for some action is not necessarily determined by their intentions alone; we must also consider what the agent could reasonably have foreseen to be potential outcomes of their action, such as the potential use of a system in conflict even when it is not designed for that. In particular, we contend that it is reasonably foreseeable that: (1) civilian AI systems will be applied to active conflict, including conflict support activities, (2) the use of civilian AI systems in conflict will impact applications of the law of armed conflict, and (3) crossover AI technology will be applied to conflicts that fall short of armed conflict. Given these reasonably foreseeably outcomes, we present three technically feasible actions that developers of civilian AIs can take to potentially mitigate their moral responsibility: (a) establishing systematic approaches to multi-perspective capability testing, (b) integrating digital watermarking in model weight matrices, and (c) utilizing monitoring and reporting mechanisms for conflict-related AI applications.
Beyond Behaviorist Representational Harms: A Plan for Measurement and Mitigation
Jan 25, 2024Abstract:Algorithmic harms are commonly categorized as either allocative or representational. This study specifically addresses the latter, focusing on an examination of current definitions of representational harms to discern what is included and what is not. This analysis motivates our expansion beyond behavioral definitions to encompass harms to cognitive and affective states. The paper outlines high-level requirements for measurement: identifying the necessary expertise to implement this approach and illustrating it through a case study. Our work highlights the unique vulnerabilities of large language models to perpetrating representational harms, particularly when these harms go unmeasured and unmitigated. The work concludes by presenting proposed mitigations and delineating when to employ them. The overarching aim of this research is to establish a framework for broadening the definition of representational harms and to translate insights from fairness research into practical measurement and mitigation praxis.
Fairness Vs. Personalization: Towards Equity in Epistemic Utility
Sep 05, 2023Abstract:The applications of personalized recommender systems are rapidly expanding: encompassing social media, online shopping, search engine results, and more. These systems offer a more efficient way to navigate the vast array of items available. However, alongside this growth, there has been increased recognition of the potential for algorithmic systems to exhibit and perpetuate biases, risking unfairness in personalized domains. In this work, we explicate the inherent tension between personalization and conventional implementations of fairness. As an alternative, we propose equity to achieve fairness in the context of epistemic utility. We provide a mapping between goals and practical implementations and detail policy recommendations across key stakeholders to forge a path towards achieving fairness in personalized systems.
Constraint-Based Causal Structure Learning from Undersampled Graphs
May 18, 2022



Abstract:Graphical structures estimated by causal learning algorithms from time series data can provide highly misleading causal information if the causal timescale of the generating process fails to match the measurement timescale of the data. Although this problem has been recently recognized, practitioners have limited resources to respond to it, and so must continue using models that they know are likely misleading. Existing methods either (a) require that the difference between causal and measurement timescales is known; or (b) can handle only very small number of random variables when the timescale difference is unknown; or (c) apply to only pairs of variables, though with fewer assumptions about prior knowledge; or (d) return impractically too many solutions. This paper addresses all four challenges. We combine constraint programming with both theoretical insights into the problem structure and prior information about admissible causal interactions. The resulting system provides a practical approach that scales to significantly larger sets (>100) of random variables, does not require precise knowledge of the timescale difference, supports edge misidentification and parametric connection strengths, and can provide the optimum choice among many possible solutions. The cumulative impact of these improvements is gain of multiple orders of magnitude in speed and informativeness.
Dynamic Certification for Autonomous Systems
Mar 21, 2022
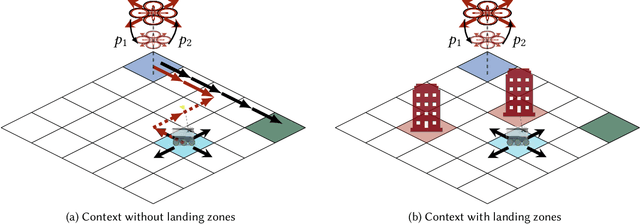
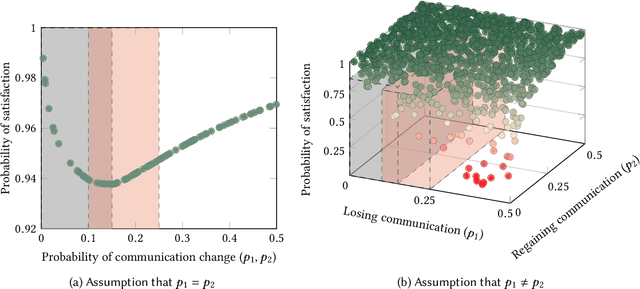
Abstract:Autonomous systems are often deployed in complex sociotechnical environments, such as public roads, where they must behave safely and securely. Unlike many traditionally engineered systems, autonomous systems are expected to behave predictably in varying "open world" environmental contexts that cannot be fully specified formally. As a result, assurance about autonomous systems requires us to develop new certification methods and mathematical tools that can bound the uncertainty engendered by these diverse deployment scenarios, rather than relying on static tools.
Causal Discovery from Subsampled Time Series Data by Constraint Optimization
Jul 13, 2016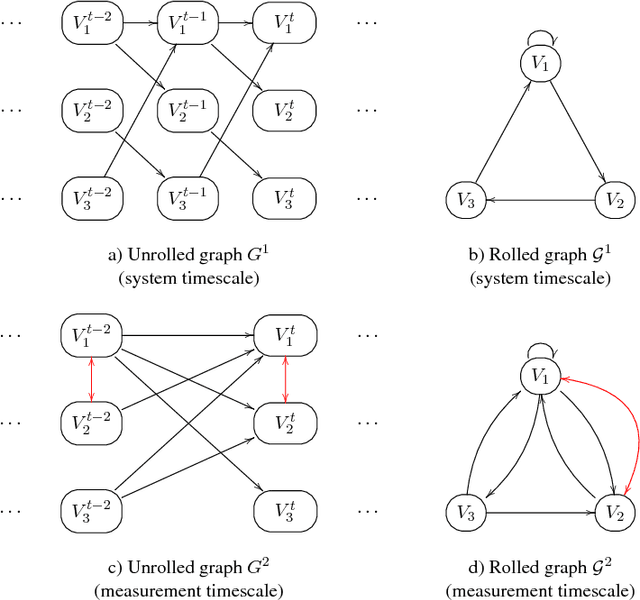
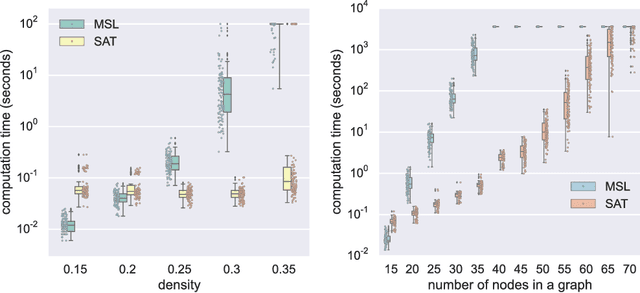
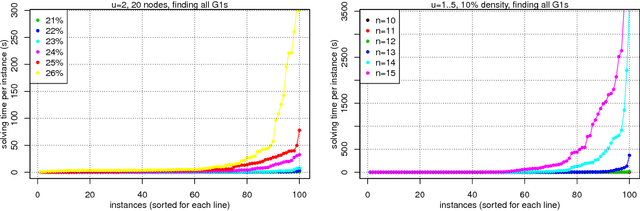
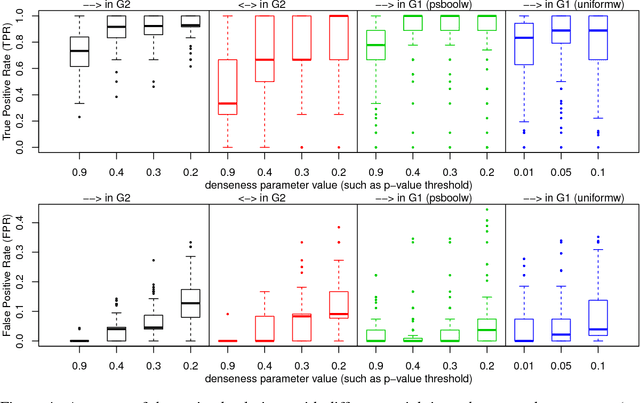
Abstract:This paper focuses on causal structure estimation from time series data in which measurements are obtained at a coarser timescale than the causal timescale of the underlying system. Previous work has shown that such subsampling can lead to significant errors about the system's causal structure if not properly taken into account. In this paper, we first consider the search for the system timescale causal structures that correspond to a given measurement timescale structure. We provide a constraint satisfaction procedure whose computational performance is several orders of magnitude better than previous approaches. We then consider finite-sample data as input, and propose the first constraint optimization approach for recovering the system timescale causal structure. This algorithm optimally recovers from possible conflicts due to statistical errors. More generally, these advances allow for a robust and non-parametric estimation of system timescale causal structures from subsampled time series data.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge