Florian André
Multi-Modal Dataset Creation for Federated~Learning with DICOM Structured Reports
Jul 12, 2024



Abstract:Purpose: Federated training is often hindered by heterogeneous datasets due to divergent data storage options, inconsistent naming schemes, varied annotation procedures, and disparities in label quality. This is particularly evident in the emerging multi-modal learning paradigms, where dataset harmonization including a uniform data representation and filtering options are of paramount importance. Methods: DICOM structured reports enable the standardized linkage of arbitrary information beyond the imaging domain and can be used within Python deep learning pipelines with highdicom. Building on this, we developed an open platform for data integration and interactive filtering capabilities that simplifies the process of assembling multi-modal datasets. Results: In this study, we extend our prior work by showing its applicability to more and divergent data types, as well as streamlining datasets for federated training within an established consortium of eight university hospitals in Germany. We prove its concurrent filtering ability by creating harmonized multi-modal datasets across all locations for predicting the outcome after minimally invasive heart valve replacement. The data includes DICOM data (i.e. computed tomography images, electrocardiography scans) as well as annotations (i.e. calcification segmentations, pointsets and pacemaker dependency), and metadata (i.e. prosthesis and diagnoses). Conclusion: Structured reports bridge the traditional gap between imaging systems and information systems. Utilizing the inherent DICOM reference system arbitrary data types can be queried concurrently to create meaningful cohorts for clinical studies. The graphical interface as well as example structured report templates will be made publicly available.
Federated Foundation Model for Cardiac CT Imaging
Jul 10, 2024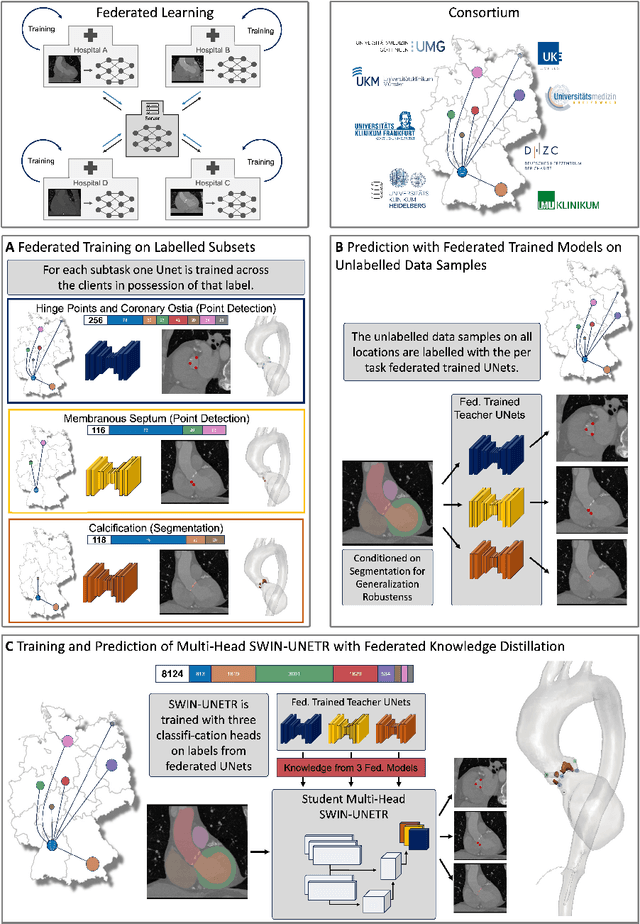
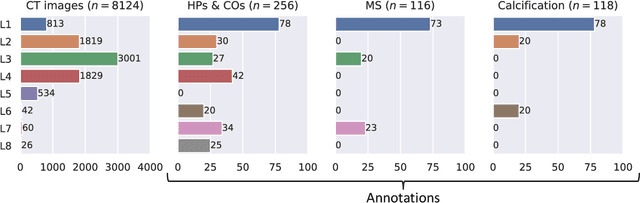
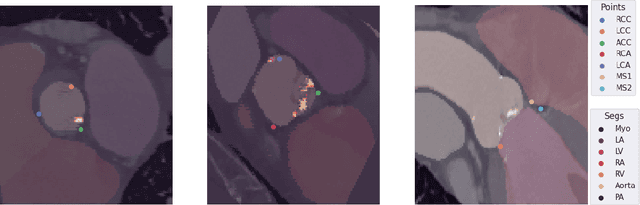

Abstract:Federated learning (FL) is a renowned technique for utilizing decentralized data while preserving privacy. However, real-world applications often involve inherent challenges such as partially labeled datasets, where not all clients possess expert annotations of all labels of interest, leaving large portions of unlabeled data unused. In this study, we conduct the largest federated cardiac CT imaging analysis to date, focusing on partially labeled datasets ($n=8,124$) of Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation (TAVI) patients over eight hospital clients. Transformer architectures, which are the major building blocks of current foundation models, have shown superior performance when trained on larger cohorts than traditional CNNs. However, when trained on small task-specific labeled sample sizes, it is currently not feasible to exploit their underlying attention mechanism for improved performance. Therefore, we developed a two-stage semi-supervised learning strategy that distills knowledge from several task-specific CNNs (landmark detection and segmentation of calcification) into a single transformer model by utilizing large amounts of unlabeled data typically residing unused in hospitals to mitigate these issues. This method not only improves the predictive accuracy and generalizability of transformer-based architectures but also facilitates the simultaneous learning of all partial labels within a single transformer model across the federation. Additionally, we show that our transformer-based model extracts more meaningful features for further downstream tasks than the UNet-based one by only training the last layer to also solve segmentation of coronary arteries. We make the code and weights of the final model openly available, which can serve as a foundation model for further research in cardiac CT imaging.
Content-Aware Differential Privacy with Conditional Invertible Neural Networks
Jul 29, 2022
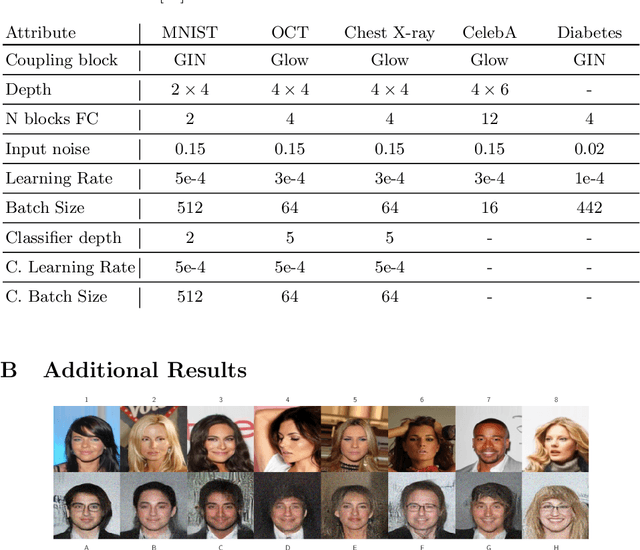
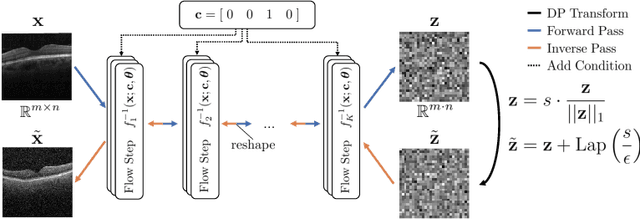

Abstract:Differential privacy (DP) has arisen as the gold standard in protecting an individual's privacy in datasets by adding calibrated noise to each data sample. While the application to categorical data is straightforward, its usability in the context of images has been limited. Contrary to categorical data the meaning of an image is inherent in the spatial correlation of neighboring pixels making the simple application of noise infeasible. Invertible Neural Networks (INN) have shown excellent generative performance while still providing the ability to quantify the exact likelihood. Their principle is based on transforming a complicated distribution into a simple one e.g. an image into a spherical Gaussian. We hypothesize that adding noise to the latent space of an INN can enable differentially private image modification. Manipulation of the latent space leads to a modified image while preserving important details. Further, by conditioning the INN on meta-data provided with the dataset we aim at leaving dimensions important for downstream tasks like classification untouched while altering other parts that potentially contain identifying information. We term our method content-aware differential privacy (CADP). We conduct experiments on publicly available benchmarking datasets as well as dedicated medical ones. In addition, we show the generalizability of our method to categorical data. The source code is publicly available at https://github.com/Cardio-AI/CADP.
CAD-RADS Scoring using Deep Learning and Task-Specific Centerline Labeling
Feb 08, 2022



Abstract:With coronary artery disease (CAD) persisting to be one of the leading causes of death worldwide, interest in supporting physicians with algorithms to speed up and improve diagnosis is high. In clinical practice, the severeness of CAD is often assessed with a coronary CT angiography (CCTA) scan and manually graded with the CAD-Reporting and Data System (CAD-RADS) score. The clinical questions this score assesses are whether patients have CAD or not (rule-out) and whether they have severe CAD or not (hold-out). In this work, we reach new state-of-the-art performance for automatic CAD-RADS scoring. We propose using severity-based label encoding, test time augmentation (TTA) and model ensembling for a task-specific deep learning architecture. Furthermore, we introduce a novel task- and model-specific, heuristic coronary segment labeling, which subdivides coronary trees into consistent parts across patients. It is fast, robust, and easy to implement. We were able to raise the previously reported area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC) from 0.914 to 0.942 in the rule-out and from 0.921 to 0.950 in the hold-out task respectively.
Comparison of Evaluation Metrics for Landmark Detection in CMR Images
Jan 28, 2022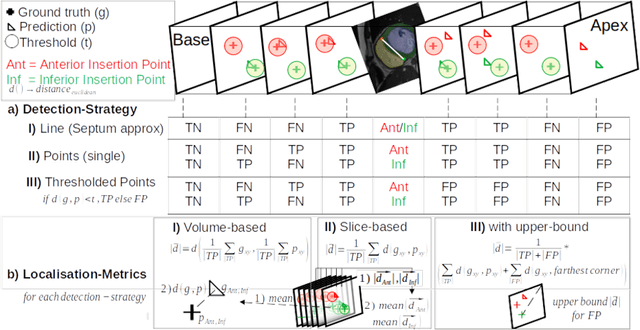

Abstract:Cardiac Magnetic Resonance (CMR) images are widely used for cardiac diagnosis and ventricular assessment. Extracting specific landmarks like the right ventricular insertion points is of importance for spatial alignment and 3D modeling. The automatic detection of such landmarks has been tackled by multiple groups using Deep Learning, but relatively little attention has been paid to the failure cases of evaluation metrics in this field. In this work, we extended the public ACDC dataset with additional labels of the right ventricular insertion points and compare different variants of a heatmap-based landmark detection pipeline. In this comparison, we demonstrate very likely pitfalls of apparently simple detection and localisation metrics which highlights the importance of a clear detection strategy and the definition of an upper limit for localisation-based metrics. Our preliminary results indicate that a combination of different metrics is necessary, as they yield different winners for method comparison. Additionally, they highlight the need of a comprehensive metric description and evaluation standardisation, especially for the error cases where no metrics could be computed or where no lower/upper boundary of a metric exists. Code and labels: https://github.com/Cardio-AI/rvip_landmark_detection
Automatic CAD-RADS Scoring Using Deep Learning
Oct 05, 2020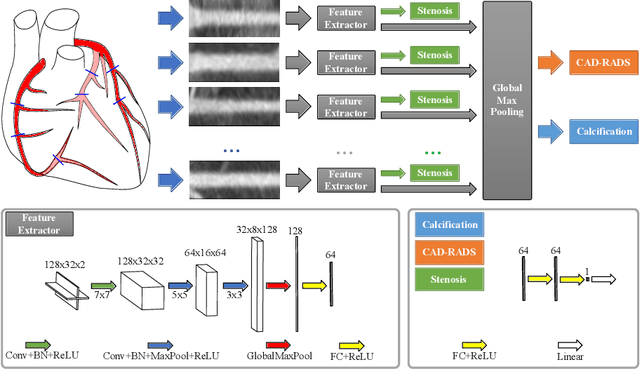

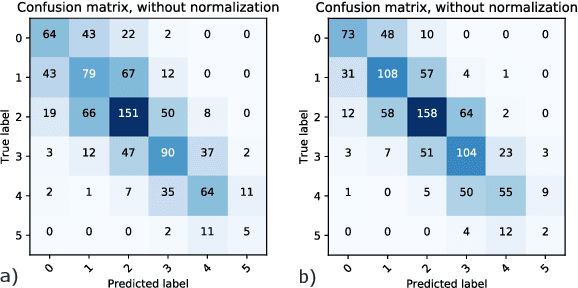
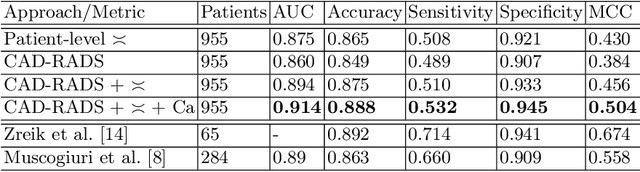
Abstract:Coronary CT angiography (CCTA) has established its role as a non-invasive modality for the diagnosis of coronary artery disease (CAD). The CAD-Reporting and Data System (CAD-RADS) has been developed to standardize communication and aid in decision making based on CCTA findings. The CAD-RADS score is determined by manual assessment of all coronary vessels and the grading of lesions within the coronary artery tree. We propose a bottom-up approach for fully-automated prediction of this score using deep-learning operating on a segment-wise representation of the coronary arteries. The method relies solely on a prior fully-automated centerline extraction and segment labeling and predicts the segment-wise stenosis degree and the overall calcification grade as auxiliary tasks in a multi-task learning setup. We evaluate our approach on a data collection consisting of 2,867 patients. On the task of identifying patients with a CAD-RADS score indicating the need for further invasive investigation our approach reaches an area under curve (AUC) of 0.923 and an AUC of 0.914 for determining whether the patient suffers from CAD. This level of performance enables our approach to be used in a fully-automated screening setup or to assist diagnostic CCTA reading, especially due to its neural architecture design -- which allows comprehensive predictions.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge