Federico Malato
Search-Based Adversarial Estimates for Improving Sample Efficiency in Off-Policy Reinforcement Learning
Feb 03, 2025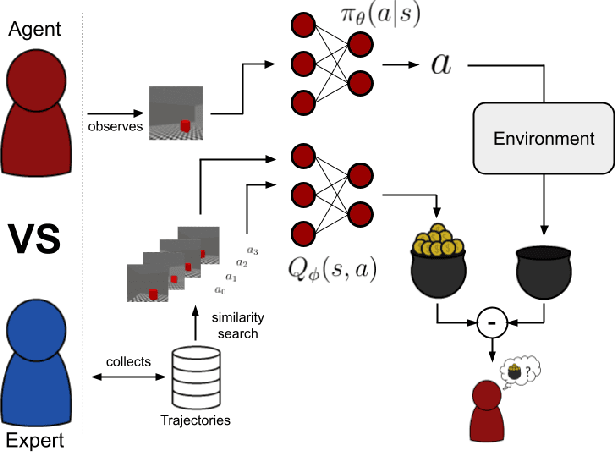
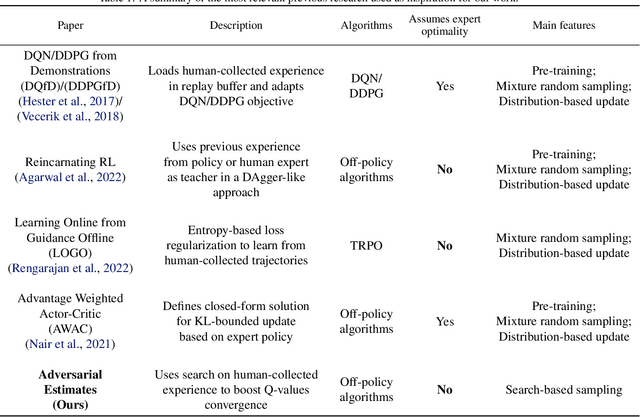
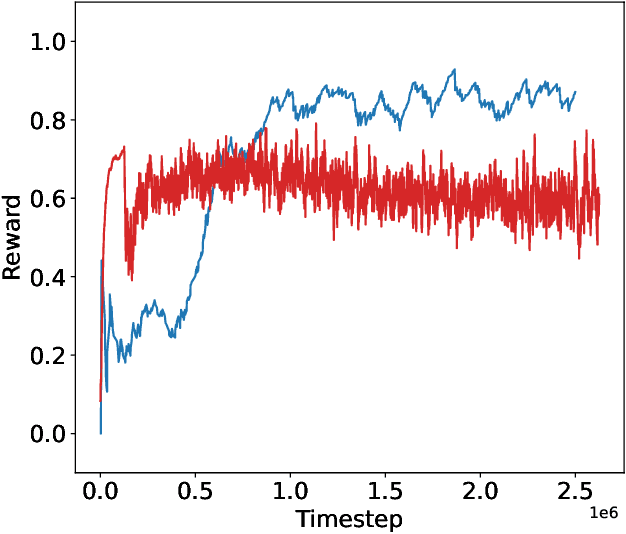
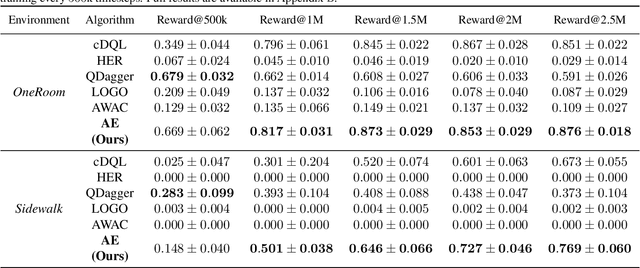
Abstract:Sample inefficiency is a long-lasting challenge in deep reinforcement learning (DRL). Despite dramatic improvements have been made, the problem is far from being solved and is especially challenging in environments with sparse or delayed rewards. In our work, we propose to use Adversarial Estimates as a new, simple and efficient approach to mitigate this problem for a class of feedback-based DRL algorithms. Our approach leverages latent similarity search from a small set of human-collected trajectories to boost learning, using only five minutes of human-recorded experience. The results of our study show algorithms trained with Adversarial Estimates converge faster than their original version. Moreover, we discuss how our approach could enable learning in feedback-based algorithms in extreme scenarios with very sparse rewards.
ROAR: Reinforcing Original to Augmented Data Ratio Dynamics for Wav2Vec2.0 Based ASR
Jun 14, 2024Abstract:While automatic speech recognition (ASR) greatly benefits from data augmentation, the augmentation recipes themselves tend to be heuristic. In this paper, we address one of the heuristic approach associated with balancing the right amount of augmented data in ASR training by introducing a reinforcement learning (RL) based dynamic adjustment of original-to-augmented data ratio (OAR). Unlike the fixed OAR approach in conventional data augmentation, our proposed method employs a deep Q-network (DQN) as the RL mechanism to learn the optimal dynamics of OAR throughout the wav2vec2.0 based ASR training. We conduct experiments using the LibriSpeech dataset with varying amounts of training data, specifically, the 10Min, 1H, 10H, and 100H splits to evaluate the efficacy of the proposed method under different data conditions. Our proposed method, on average, achieves a relative improvement of 4.96% over the open-source wav2vec2.0 base model on standard LibriSpeech test sets.
* Accepted: Interspeech 2024
Online Adaptation for Enhancing Imitation Learning Policies
Jun 07, 2024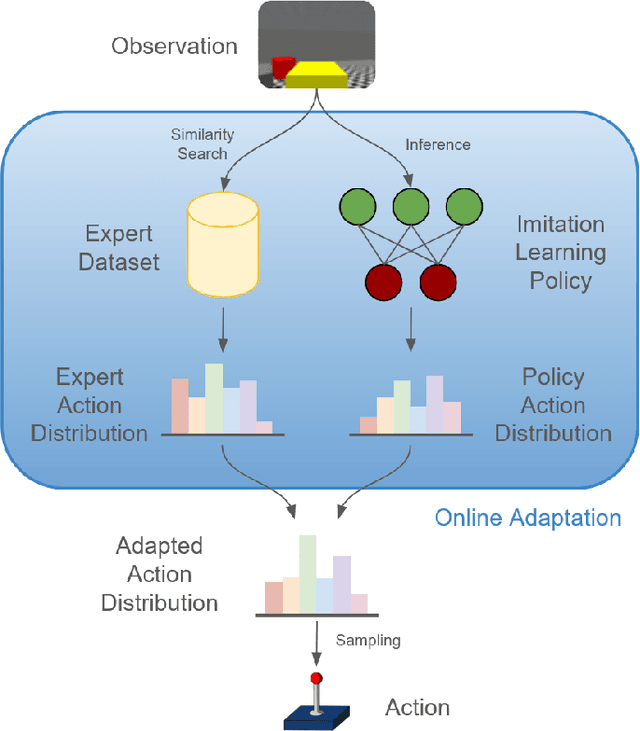
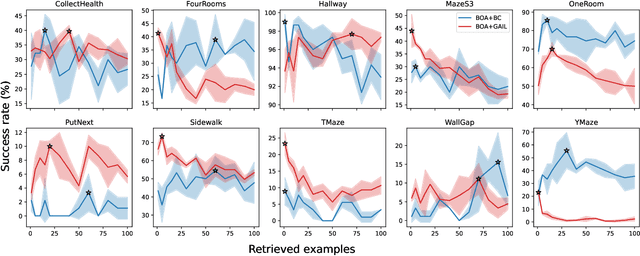
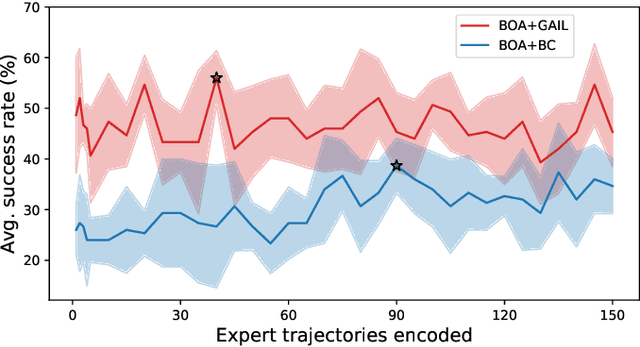
Abstract:Imitation learning enables autonomous agents to learn from human examples, without the need for a reward signal. Still, if the provided dataset does not encapsulate the task correctly, or when the task is too complex to be modeled, such agents fail to reproduce the expert policy. We propose to recover from these failures through online adaptation. Our approach combines the action proposal coming from a pre-trained policy with relevant experience recorded by an expert. The combination results in an adapted action that closely follows the expert. Our experiments show that an adapted agent performs better than its pure imitation learning counterpart. Notably, adapted agents can achieve reasonable performance even when the base, non-adapted policy catastrophically fails.
Behavioral Cloning via Search in Embedded Demonstration Dataset
Jun 15, 2023Abstract:Behavioural cloning uses a dataset of demonstrations to learn a behavioural policy. To overcome various learning and policy adaptation problems, we propose to use latent space to index a demonstration dataset, instantly access similar relevant experiences, and copy behavior from these situations. Actions from a selected similar situation can be performed by the agent until representations of the agent's current situation and the selected experience diverge in the latent space. Thus, we formulate our control problem as a search problem over a dataset of experts' demonstrations. We test our approach on BASALT MineRL-dataset in the latent representation of a Video PreTraining model. We compare our model to state-of-the-art Minecraft agents. Our approach can effectively recover meaningful demonstrations and show human-like behavior of an agent in the Minecraft environment in a wide variety of scenarios. Experimental results reveal that performance of our search-based approach is comparable to trained models, while allowing zero-shot task adaptation by changing the demonstration examples.
Towards Solving Fuzzy Tasks with Human Feedback: A Retrospective of the MineRL BASALT 2022 Competition
Mar 23, 2023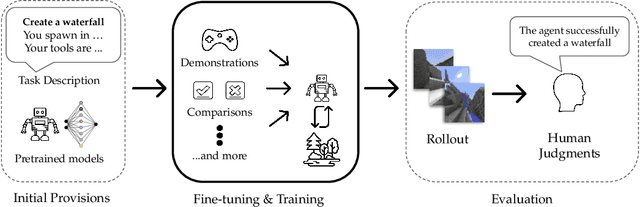

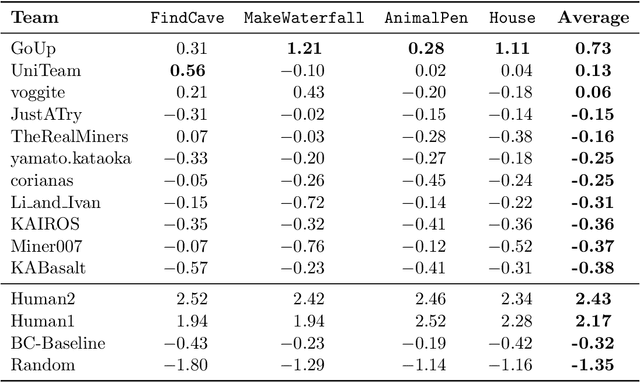
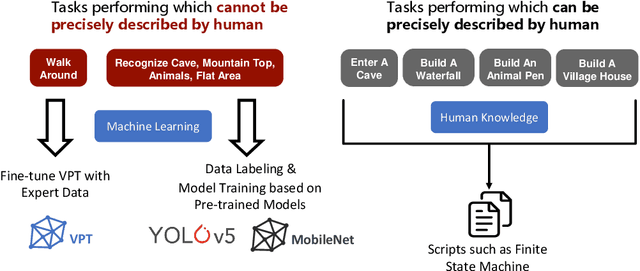
Abstract:To facilitate research in the direction of fine-tuning foundation models from human feedback, we held the MineRL BASALT Competition on Fine-Tuning from Human Feedback at NeurIPS 2022. The BASALT challenge asks teams to compete to develop algorithms to solve tasks with hard-to-specify reward functions in Minecraft. Through this competition, we aimed to promote the development of algorithms that use human feedback as channels to learn the desired behavior. We describe the competition and provide an overview of the top solutions. We conclude by discussing the impact of the competition and future directions for improvement.
Behavioral Cloning via Search in Video PreTraining Latent Space
Dec 27, 2022Abstract:Our aim is to build autonomous agents that can solve tasks in environments like Minecraft. To do so, we used an imitation learning-based approach. We formulate our control problem as a search problem over a dataset of experts' demonstrations, where the agent copies actions from a similar demonstration trajectory of image-action pairs. We perform a proximity search over the BASALT MineRL-dataset in the latent representation of a Video PreTraining model. The agent copies the actions from the expert trajectory as long as the distance between the state representations of the agent and the selected expert trajectory from the dataset do not diverge. Then the proximity search is repeated. Our approach can effectively recover meaningful demonstration trajectories and show human-like behavior of an agent in the Minecraft environment.
Improving Behavioural Cloning with Human-Driven Dynamic Dataset Augmentation
Jan 19, 2022Abstract:Behavioural cloning has been extensively used to train agents and is recognized as a fast and solid approach to teach general behaviours based on expert trajectories. Such method follows the supervised learning paradigm and it strongly depends on the distribution of the data. In our paper, we show how combining behavioural cloning with human-in-the-loop training solves some of its flaws and provides an agent task-specific corrections to overcome tricky situations while speeding up the training time and lowering the required resources. To do this, we introduce a novel approach that allows an expert to take control of the agent at any moment during a simulation and provide optimal solutions to its problematic situations. Our experiments show that this approach leads to better policies both in terms of quantitative evaluation and in human-likeliness.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge