Ernst Th. Scholten
Nodule detection and generation on chest X-rays: NODE21 Challenge
Jan 04, 2024



Abstract:Pulmonary nodules may be an early manifestation of lung cancer, the leading cause of cancer-related deaths among both men and women. Numerous studies have established that deep learning methods can yield high-performance levels in the detection of lung nodules in chest X-rays. However, the lack of gold-standard public datasets slows down the progression of the research and prevents benchmarking of methods for this task. To address this, we organized a public research challenge, NODE21, aimed at the detection and generation of lung nodules in chest X-rays. While the detection track assesses state-of-the-art nodule detection systems, the generation track determines the utility of nodule generation algorithms to augment training data and hence improve the performance of the detection systems. This paper summarizes the results of the NODE21 challenge and performs extensive additional experiments to examine the impact of the synthetically generated nodule training images on the detection algorithm performance.
Kidney abnormality segmentation in thorax-abdomen CT scans
Sep 06, 2023
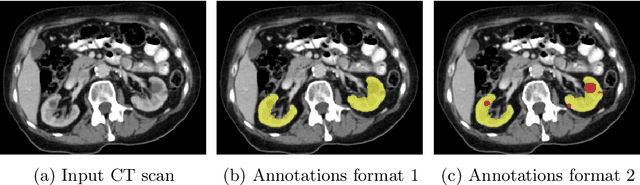


Abstract:In this study, we introduce a deep learning approach for segmenting kidney parenchyma and kidney abnormalities to support clinicians in identifying and quantifying renal abnormalities such as cysts, lesions, masses, metastases, and primary tumors. Our end-to-end segmentation method was trained on 215 contrast-enhanced thoracic-abdominal CT scans, with half of these scans containing one or more abnormalities. We began by implementing our own version of the original 3D U-Net network and incorporated four additional components: an end-to-end multi-resolution approach, a set of task-specific data augmentations, a modified loss function using top-$k$, and spatial dropout. Furthermore, we devised a tailored post-processing strategy. Ablation studies demonstrated that each of the four modifications enhanced kidney abnormality segmentation performance, while three out of four improved kidney parenchyma segmentation. Subsequently, we trained the nnUNet framework on our dataset. By ensembling the optimized 3D U-Net and the nnUNet with our specialized post-processing, we achieved marginally superior results. Our best-performing model attained Dice scores of 0.965 and 0.947 for segmenting kidney parenchyma in two test sets (20 scans without abnormalities and 30 with abnormalities), outperforming an independent human observer who scored 0.944 and 0.925, respectively. In segmenting kidney abnormalities within the 30 test scans containing them, the top-performing method achieved a Dice score of 0.585, while an independent second human observer reached a score of 0.664, suggesting potential for further improvement in computerized methods. All training data is available to the research community under a CC-BY 4.0 license on https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.8014289
Automated Estimation of Total Lung Volume using Chest Radiographs and Deep Learning
May 03, 2021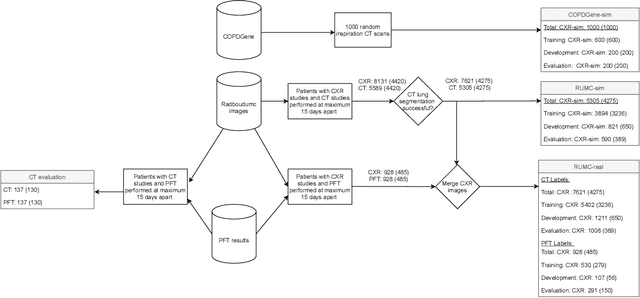
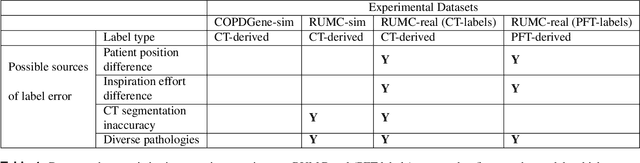
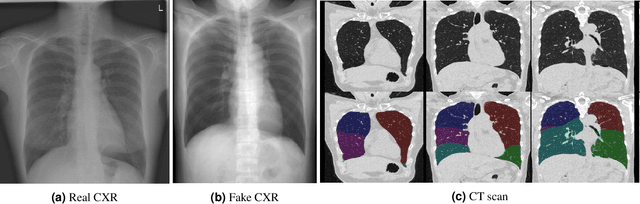
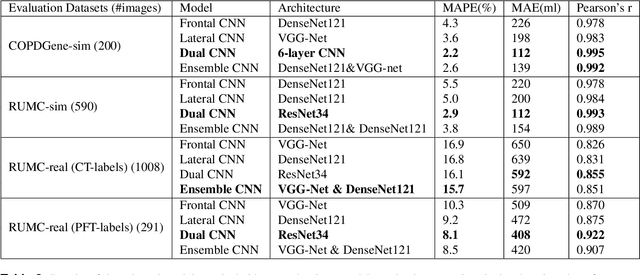
Abstract:Total lung volume is an important quantitative biomarker and is used for the assessment of restrictive lung diseases. In this study, we investigate the performance of several deep-learning approaches for automated measurement of total lung volume from chest radiographs. 7621 posteroanterior and lateral view chest radiographs (CXR) were collected from patients with chest CT available. Similarly, 928 CXR studies were chosen from patients with pulmonary function test (PFT) results. The reference total lung volume was calculated from lung segmentation on CT or PFT data, respectively. This dataset was used to train deep-learning architectures to predict total lung volume from chest radiographs. The experiments were constructed in a step-wise fashion with increasing complexity to demonstrate the effect of training with CT-derived labels only and the sources of error. The optimal models were tested on 291 CXR studies with reference lung volume obtained from PFT. The optimal deep-learning regression model showed an MAE of 408 ml and a MAPE of 8.1\% and Pearson's r = 0.92 using both frontal and lateral chest radiographs as input. CT-derived labels were useful for pre-training but the optimal performance was obtained by fine-tuning the network with PFT-derived labels. We demonstrate, for the first time, that state-of-the-art deep learning solutions can accurately measure total lung volume from plain chest radiographs. The proposed model can be used to obtain total lung volume from routinely acquired chest radiographs at no additional cost and could be a useful tool to identify trends over time in patients referred regularly for chest x-rays.
Towards automatic pulmonary nodule management in lung cancer screening with deep learning
May 23, 2017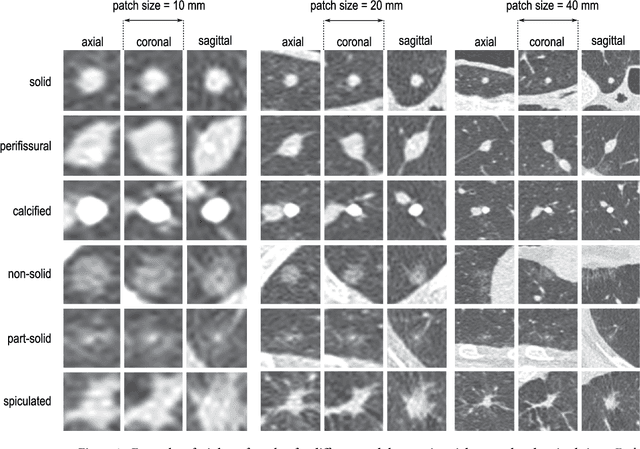
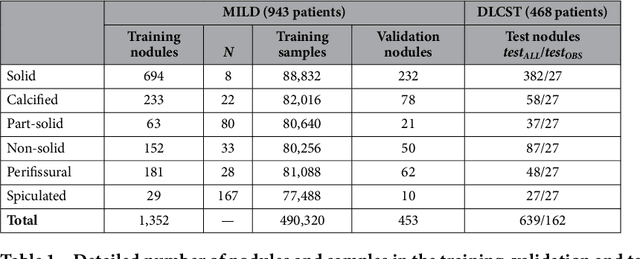
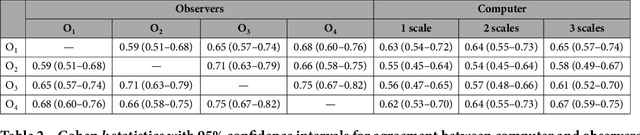
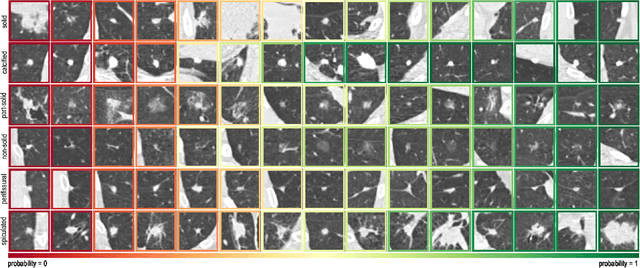
Abstract:The introduction of lung cancer screening programs will produce an unprecedented amount of chest CT scans in the near future, which radiologists will have to read in order to decide on a patient follow-up strategy. According to the current guidelines, the workup of screen-detected nodules strongly relies on nodule size and nodule type. In this paper, we present a deep learning system based on multi-stream multi-scale convolutional networks, which automatically classifies all nodule types relevant for nodule workup. The system processes raw CT data containing a nodule without the need for any additional information such as nodule segmentation or nodule size and learns a representation of 3D data by analyzing an arbitrary number of 2D views of a given nodule. The deep learning system was trained with data from the Italian MILD screening trial and validated on an independent set of data from the Danish DLCST screening trial. We analyze the advantage of processing nodules at multiple scales with a multi-stream convolutional network architecture, and we show that the proposed deep learning system achieves performance at classifying nodule type that surpasses the one of classical machine learning approaches and is within the inter-observer variability among four experienced human observers.
* Published on Scientific Reports
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge