Eni Halilaj
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Carnegie Mellon University, Pennsylvania, USA
Optimizing Locomotor Task Sets in Biological Joint Moment Estimation for Hip Exoskeleton Applications
Dec 10, 2024Abstract:Accurate estimation of a user's biological joint moment from wearable sensor data is vital for improving exoskeleton control during real-world locomotor tasks. However, most state-of-the-art methods rely on deep learning techniques that necessitate extensive in-lab data collection, posing challenges in acquiring sufficient data to develop robust models. To address this challenge, we introduce a locomotor task set optimization strategy designed to identify a minimal, yet representative, set of tasks that preserves model performance while significantly reducing the data collection burden. In this optimization, we performed a cluster analysis on the dimensionally reduced biomechanical features of various cyclic and non-cyclic tasks. We identified the minimal viable clusters (i.e., tasks) to train a neural network for estimating hip joint moments and evaluated its performance. Our cross-validation analysis across subjects showed that the optimized task set-based model achieved a root mean squared error of 0.30$\pm$0.05 Nm/kg. This performance was significantly better than using only cyclic tasks (p<0.05) and was comparable to using the full set of tasks. Our results demonstrate the ability to maintain model accuracy while significantly reducing the cost associated with data collection and model training. This highlights the potential for future exoskeleton designers to leverage this strategy to minimize the data requirements for deep learning-based models in wearable robot control.
WHAM: Reconstructing World-grounded Humans with Accurate 3D Motion
Dec 12, 2023Abstract:The estimation of 3D human motion from video has progressed rapidly but current methods still have several key limitations. First, most methods estimate the human in camera coordinates. Second, prior work on estimating humans in global coordinates often assumes a flat ground plane and produces foot sliding. Third, the most accurate methods rely on computationally expensive optimization pipelines, limiting their use to offline applications. Finally, existing video-based methods are surprisingly less accurate than single-frame methods. We address these limitations with WHAM (World-grounded Humans with Accurate Motion), which accurately and efficiently reconstructs 3D human motion in a global coordinate system from video. WHAM learns to lift 2D keypoint sequences to 3D using motion capture data and fuses this with video features, integrating motion context and visual information. WHAM exploits camera angular velocity estimated from a SLAM method together with human motion to estimate the body's global trajectory. We combine this with a contact-aware trajectory refinement method that lets WHAM capture human motion in diverse conditions, such as climbing stairs. WHAM outperforms all existing 3D human motion recovery methods across multiple in-the-wild benchmarks. Code will be available for research purposes at http://wham.is.tue.mpg.de/
SRL-Assisted AFM: Generating Planar Unstructured Quadrilateral Meshes with Supervised and Reinforcement Learning-Assisted Advancing Front Method
Apr 30, 2023



Abstract:High-quality mesh generation is the foundation of accurate finite element analysis. Due to the vast interior vertices search space and complex initial boundaries, mesh generation for complicated domains requires substantial manual processing and has long been considered the most challenging and time-consuming bottleneck of the entire modeling and analysis process. In this paper, we present a novel computational framework named ``SRL-assisted AFM" for meshing planar geometries by combining the advancing front method with neural networks that select reference vertices and update the front boundary using ``policy networks." These deep neural networks are trained using a unique pipeline that combines supervised learning with reinforcement learning to iteratively improve mesh quality. First, we generate different initial boundaries by randomly sampling points in a square domain and connecting them sequentially. These boundaries are used for obtaining input meshes and extracting training datasets in the supervised learning module. We then iteratively improve the reinforcement learning model performance with reward functions designed for special requirements, such as improving the mesh quality and controlling the number and distribution of extraordinary points. Our proposed supervised learning neural networks achieve an accuracy higher than 98% on predicting commercial software. The final reinforcement learning neural networks automatically generate high-quality quadrilateral meshes for complex planar domains with sharp features and boundary layers.
Open source software for automatic subregional assessment of knee cartilage degradation using quantitative T2 relaxometry and deep learning
Dec 22, 2020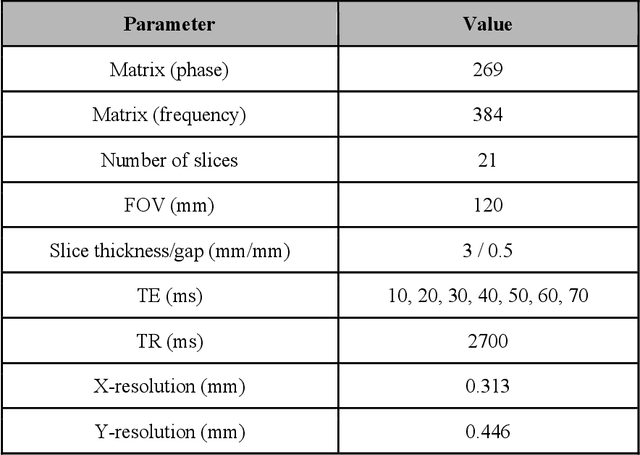
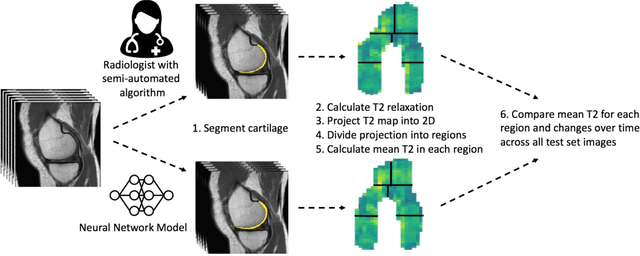
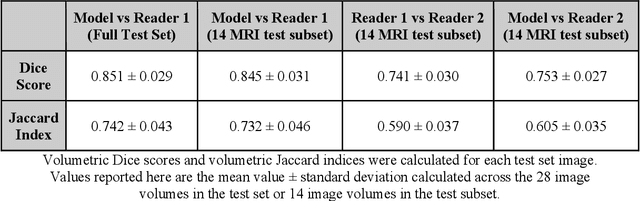
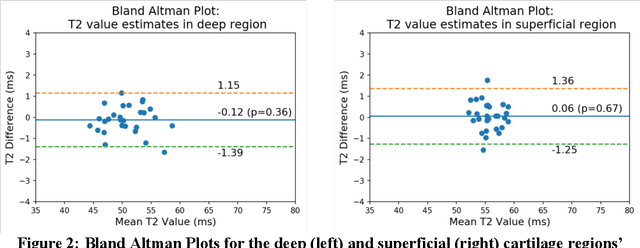
Abstract:Objective: We evaluate a fully-automated femoral cartilage segmentation model for measuring T2 relaxation values and longitudinal changes using multi-echo spin echo (MESE) MRI. We have open sourced this model and corresponding segmentations. Methods: We trained a neural network to segment femoral cartilage from MESE MRIs. Cartilage was divided into 12 subregions along medial-lateral, superficial-deep, and anterior-central-posterior boundaries. Subregional T2 values and four-year changes were calculated using a musculoskeletal radiologist's segmentations (Reader 1) and the model's segmentations. These were compared using 28 held out images. A subset of 14 images were also evaluated by a second expert (Reader 2) for comparison. Results: Model segmentations agreed with Reader 1 segmentations with a Dice score of 0.85 +/- 0.03. The model's estimated T2 values for individual subregions agreed with those of Reader 1 with an average Spearman correlation of 0.89 and average mean absolute error (MAE) of 1.34 ms. The model's estimated four-year change in T2 for individual regions agreed with Reader 1 with an average correlation of 0.80 and average MAE of 1.72 ms. The model agreed with Reader 1 at least as closely as Reader 2 agreed with Reader 1 in terms of Dice score (0.85 vs 0.75) and subregional T2 values. Conclusions: We present a fast, fully-automated model for segmentation of MESE MRIs. Assessments of cartilage health using its segmentations agree with those of an expert as closely as experts agree with one another. This has the potential to accelerate osteoarthritis research.
Multi-view Human Pose and Shape Estimation Using Learnable Volumetric Aggregation
Nov 26, 2020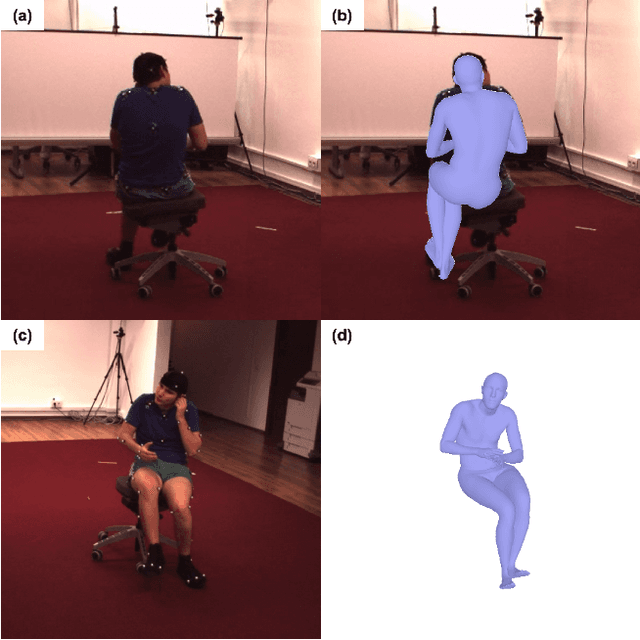
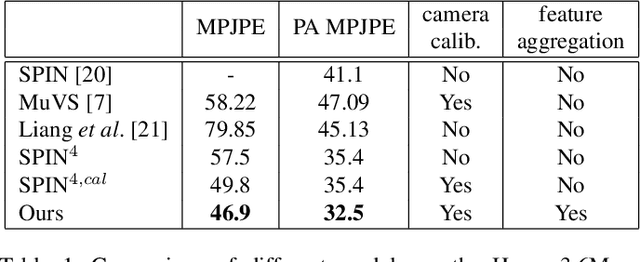
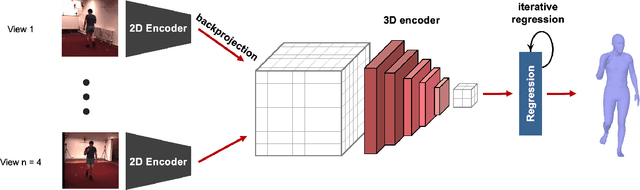
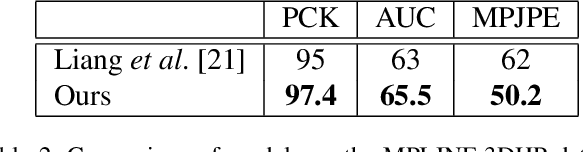
Abstract:Human pose and shape estimation from RGB images is a highly sought after alternative to marker-based motion capture, which is laborious, requires expensive equipment, and constrains capture to laboratory environments. Monocular vision-based algorithms, however, still suffer from rotational ambiguities and are not ready for translation in healthcare applications, where high accuracy is paramount. While fusion of data from multiple viewpoints could overcome these challenges, current algorithms require further improvement to obtain clinically acceptable accuracies. In this paper, we propose a learnable volumetric aggregation approach to reconstruct 3D human body pose and shape from calibrated multi-view images. We use a parametric representation of the human body, which makes our approach directly applicable to medical applications. Compared to previous approaches, our framework shows higher accuracy and greater promise for real-time prediction, given its cost efficiency.
ShortFuse: Biomedical Time Series Representations in the Presence of Structured Information
May 16, 2017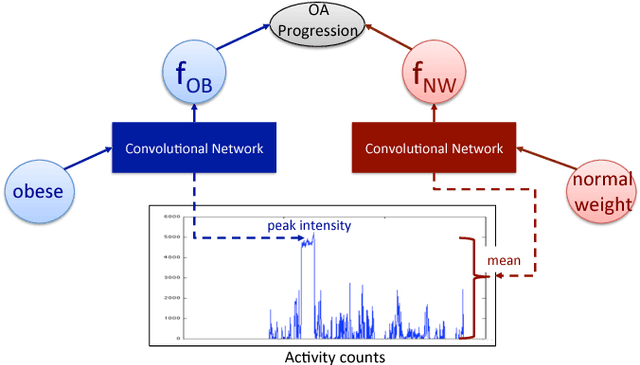
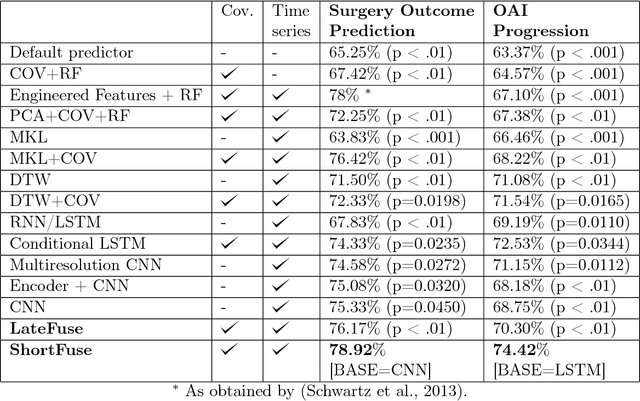
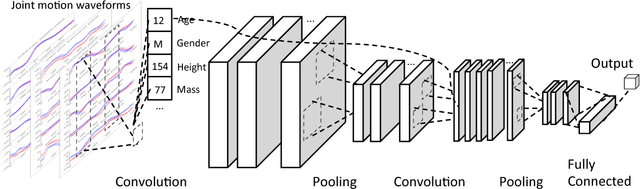
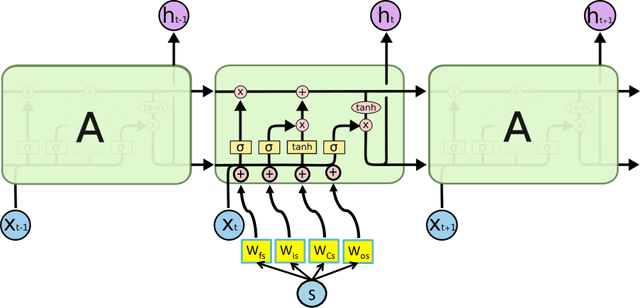
Abstract:In healthcare applications, temporal variables that encode movement, health status and longitudinal patient evolution are often accompanied by rich structured information such as demographics, diagnostics and medical exam data. However, current methods do not jointly optimize over structured covariates and time series in the feature extraction process. We present ShortFuse, a method that boosts the accuracy of deep learning models for time series by explicitly modeling temporal interactions and dependencies with structured covariates. ShortFuse introduces hybrid convolutional and LSTM cells that incorporate the covariates via weights that are shared across the temporal domain. ShortFuse outperforms competing models by 3% on two biomedical applications, forecasting osteoarthritis-related cartilage degeneration and predicting surgical outcomes for cerebral palsy patients, matching or exceeding the accuracy of models that use features engineered by domain experts.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge