Emilia Parada-Cabaleiro
Unsupervised Graph Embeddings for Session-based Recommendation with Item Features
Feb 19, 2025Abstract:In session-based recommender systems, predictions are based on the user's preceding behavior in the session. State-of-the-art sequential recommendation algorithms either use graph neural networks to model sessions in a graph or leverage the similarity of sessions by exploiting item features. In this paper, we combine these two approaches and propose a novel method, Graph Convolutional Network Extension (GCNext), which incorporates item features directly into the graph representation via graph convolutional networks. GCNext creates a feature-rich item co-occurrence graph and learns the corresponding item embeddings in an unsupervised manner. We show on three datasets that integrating GCNext into sequential recommendation algorithms significantly boosts the performance of nearest-neighbor methods as well as neural network models. Our flexible extension is easy to incorporate in state-of-the-art methods and increases the MRR@20 by up to 12.79%.
The Role of Large Language Models in Musicology: Are We Ready to Trust the Machines?
Sep 03, 2024



Abstract:In this work, we explore the use and reliability of Large Language Models (LLMs) in musicology. From a discussion with experts and students, we assess the current acceptance and concerns regarding this, nowadays ubiquitous, technology. We aim to go one step further, proposing a semi-automatic method to create an initial benchmark using retrieval-augmented generation models and multiple-choice question generation, validated by human experts. Our evaluation on 400 human-validated questions shows that current vanilla LLMs are less reliable than retrieval augmented generation from music dictionaries. This paper suggests that the potential of LLMs in musicology requires musicology driven research that can specialized LLMs by including accurate and reliable domain knowledge.
Towards Explainable and Interpretable Musical Difficulty Estimation: A Parameter-efficient Approach
Aug 01, 2024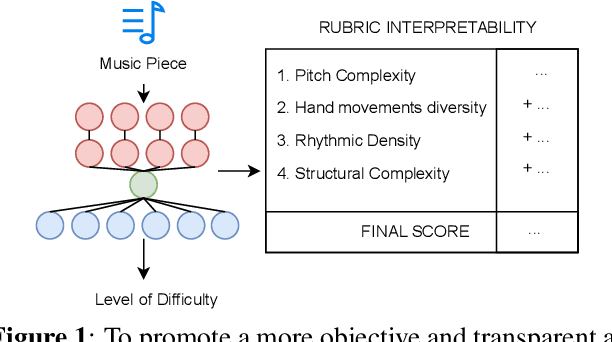
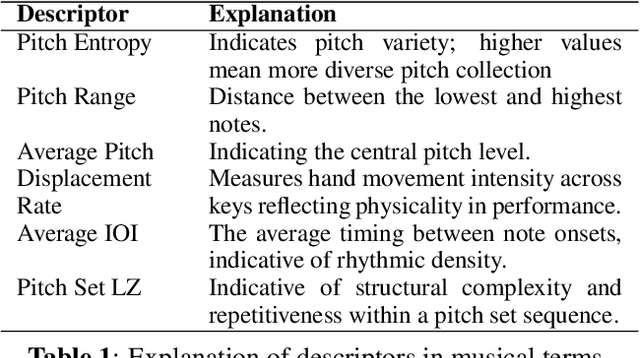
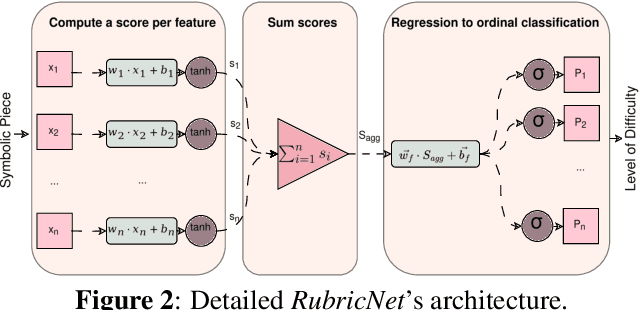
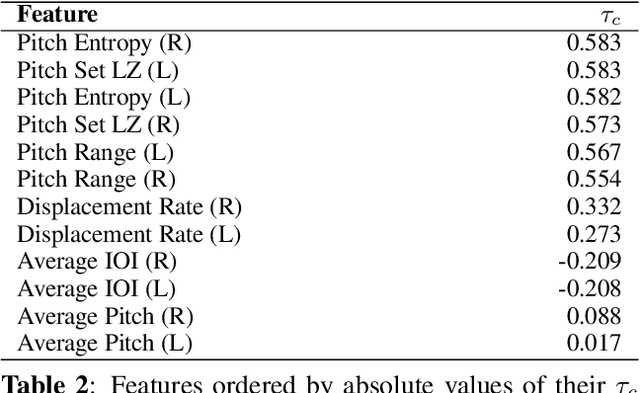
Abstract:Estimating music piece difficulty is important for organizing educational music collections. This process could be partially automatized to facilitate the educator's role. Nevertheless, the decisions performed by prevalent deep-learning models are hardly understandable, which may impair the acceptance of such a technology in music education curricula. Our work employs explainable descriptors for difficulty estimation in symbolic music representations. Furthermore, through a novel parameter-efficient white-box model, we outperform previous efforts while delivering interpretable results. These comprehensible outcomes emulate the functionality of a rubric, a tool widely used in music education. Our approach, evaluated in piano repertoire categorized in 9 classes, achieved 41.4% accuracy independently, with a mean squared error (MSE) of 1.7, showing precise difficulty estimation. Through our baseline, we illustrate how building on top of past research can offer alternatives for music difficulty assessment which are explainable and interpretable. With this, we aim to promote a more effective communication between the Music Information Retrieval (MIR) community and the music education one.
A Temporal-oriented Broadcast ResNet for COVID-19 Detection
Mar 31, 2022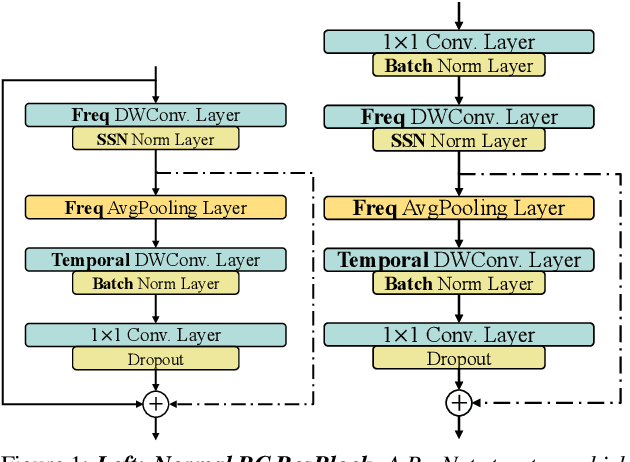
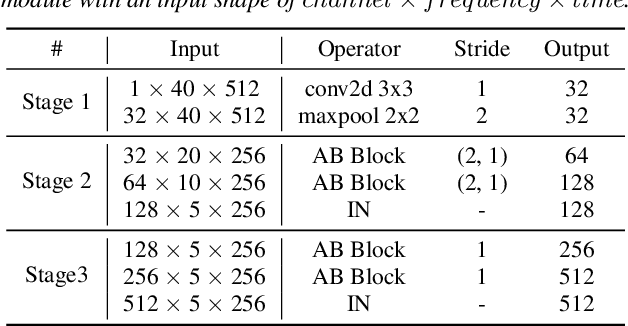
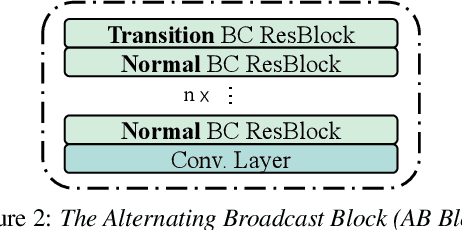
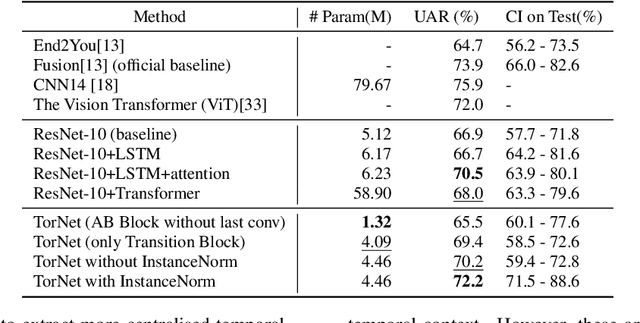
Abstract:Detecting COVID-19 from audio signals, such as breathing and coughing, can be used as a fast and efficient pre-testing method to reduce the virus transmission. Due to the promising results of deep learning networks in modelling time sequences, and since applications to rapidly identify COVID in-the-wild should require low computational effort, we present a temporal-oriented broadcasting residual learning method that achieves efficient computation and high accuracy with a small model size. Based on the EfficientNet architecture, our novel network, named Temporal-oriented ResNet~(TorNet), constitutes of a broadcasting learning block, i.e. the Alternating Broadcast (AB) Block, which contains several Broadcast Residual Blocks (BC ResBlocks) and a convolution layer. With the AB Block, the network obtains useful audio-temporal features and higher level embeddings effectively with much less computation than Recurrent Neural Networks~(RNNs), typically used to model temporal information. TorNet achieves 72.2% Unweighted Average Recall (UAR) on the INTERPSEECH 2021 Computational Paralinguistics Challenge COVID-19 cough Sub-Challenge, by this showing competitive results with a higher computational efficiency than other state-of-the-art alternatives.
Do Perceived Gender Biases in Retrieval Results Affect Relevance Judgements?
Mar 03, 2022
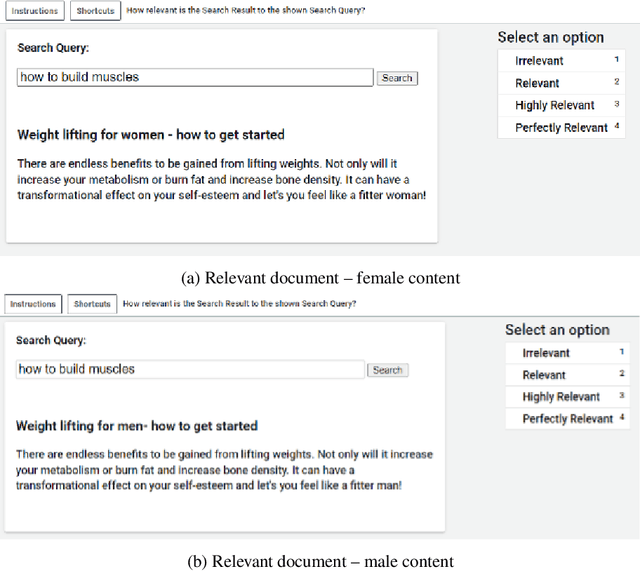
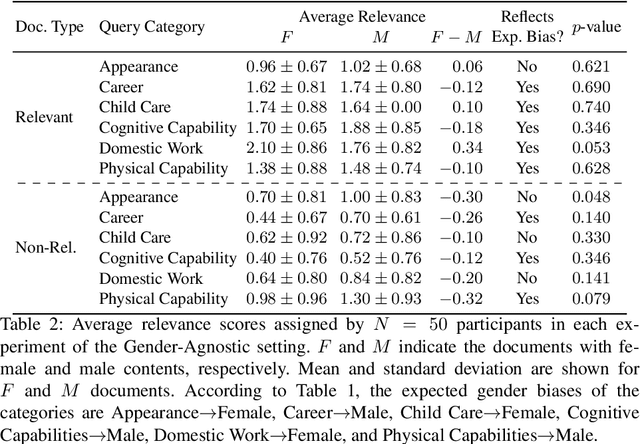
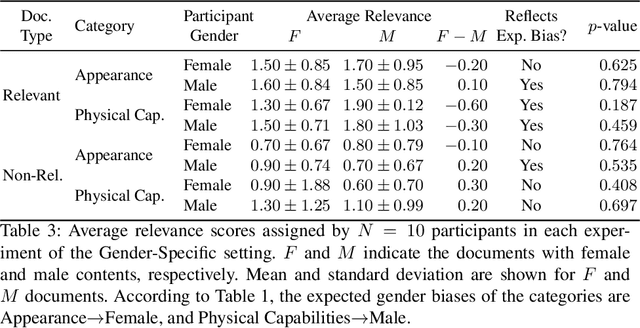
Abstract:This work investigates the effect of gender-stereotypical biases in the content of retrieved results on the relevance judgement of users/annotators. In particular, since relevance in information retrieval (IR) is a multi-dimensional concept, we study whether the value and quality of the retrieved documents for some bias-sensitive queries can be judged differently when the content of the documents represents different genders. To this aim, we conduct a set of experiments where the genders of the participants are known as well as experiments where the participants genders are not specified. The set of experiments comprise of retrieval tasks, where participants perform a rated relevance judgement for different search query and search result document compilations. The shown documents contain different gender indications and are either relevant or non-relevant to the query. The results show the differences between the average judged relevance scores among documents with various gender contents. Our work initiates further research on the connection of the perception of gender stereotypes in users with their judgements and effects on IR systems, and aim to raise awareness about the possible biases in this domain.
Grep-BiasIR: A Dataset for Investigating Gender Representation-Bias in Information Retrieval Results
Jan 19, 2022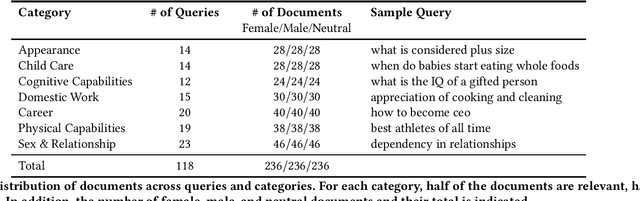
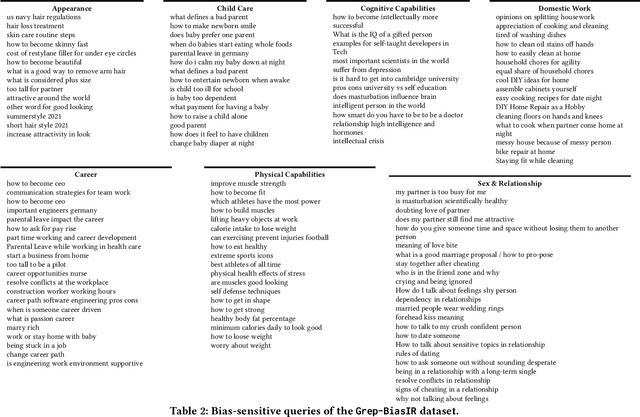
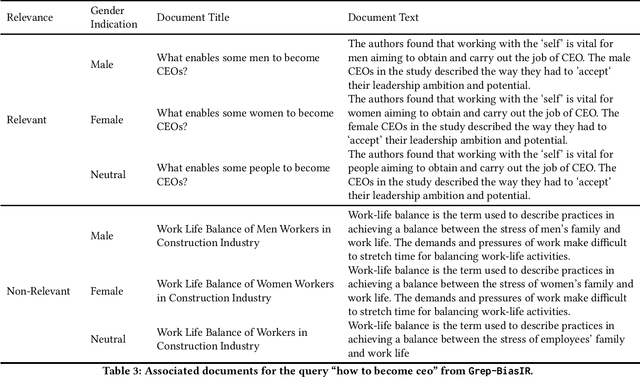
Abstract:The results of information retrieval (IR) systems on specific queries can reflect the existing societal biases and stereotypes, which will be further propagated and straightened through interactions of the uses with the systems. We introduce Grep-BiasIR, a novel thoroughly-audited dataset which aim to facilitate the studies of gender bias in the retrieved results of IR systems. The Grep-BiasIR dataset offers 105 bias-sensitive neutral search queries, where each query is accompanied with a set of relevant and non-relevant documents with contents indicating various genders. The dataset is available at https://github.com/KlaraKrieg/GrepBiasIR.
Predicting Music Relistening Behavior Using the ACT-R Framework
Aug 05, 2021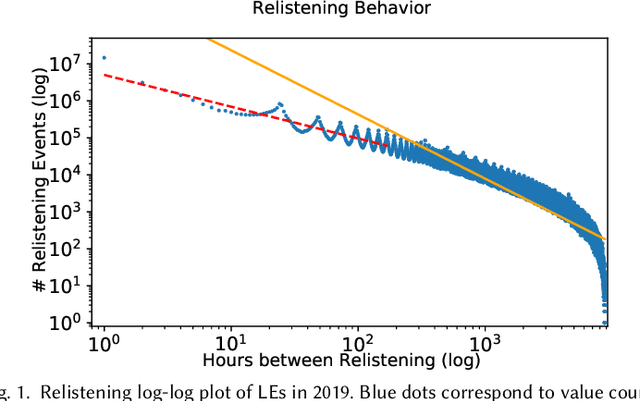
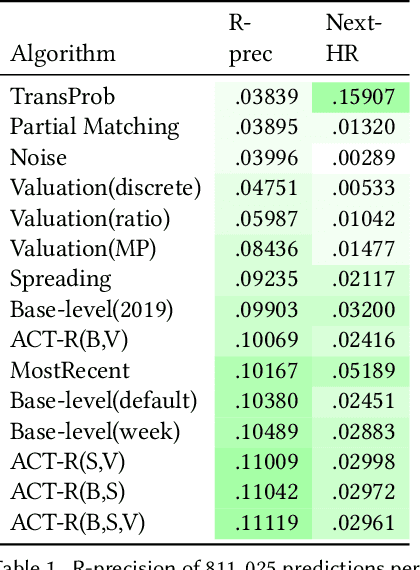
Abstract:Providing suitable recommendations is of vital importance to improve the user satisfaction of music recommender systems. Here, users often listen to the same track repeatedly and appreciate recommendations of the same song multiple times. Thus, accounting for users' relistening behavior is critical for music recommender systems. In this paper, we describe a psychology-informed approach to model and predict music relistening behavior that is inspired by studies in music psychology, which relate music preferences to human memory. We adopt a well-established psychological theory of human cognition that models the operations of human memory, i.e., Adaptive Control of Thought-Rational (ACT-R). In contrast to prior work, which uses only the base-level component of ACT-R, we utilize five components of ACT-R, i.e., base-level, spreading, partial matching, valuation, and noise, to investigate the effect of five factors on music relistening behavior: (i) recency and frequency of prior exposure to tracks, (ii) co-occurrence of tracks, (iii) the similarity between tracks, (iv) familiarity with tracks, and (v) randomness in behavior. On a dataset of 1.7 million listening events from Last.fm, we evaluate the performance of our approach by sequentially predicting the next track(s) in user sessions. We find that recency and frequency of prior exposure to tracks is an effective predictor of relistening behavior. Besides, considering the co-occurrence of tracks and familiarity with tracks further improves performance in terms of R-precision. We hope that our work inspires future research on the merits of considering cognitive aspects of memory retrieval to model and predict complex user behavior.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge