Eleni Miltsakaki
NAVCON: A Cognitively Inspired and Linguistically Grounded Corpus for Vision and Language Navigation
Dec 17, 2024Abstract:We present NAVCON, a large-scale annotated Vision-Language Navigation (VLN) corpus built on top of two popular datasets (R2R and RxR). The paper introduces four core, cognitively motivated and linguistically grounded, navigation concepts and an algorithm for generating large-scale silver annotations of naturally occurring linguistic realizations of these concepts in navigation instructions. We pair the annotated instructions with video clips of an agent acting on these instructions. NAVCON contains 236, 316 concept annotations for approximately 30, 0000 instructions and 2.7 million aligned images (from approximately 19, 000 instructions) showing what the agent sees when executing an instruction. To our knowledge, this is the first comprehensive resource of navigation concepts. We evaluated the quality of the silver annotations by conducting human evaluation studies on NAVCON samples. As further validation of the quality and usefulness of the resource, we trained a model for detecting navigation concepts and their linguistic realizations in unseen instructions. Additionally, we show that few-shot learning with GPT-4o performs well on this task using large-scale silver annotations of NAVCON.
A Feasibility Study of Answer-Agnostic Question Generation for Education
Mar 29, 2022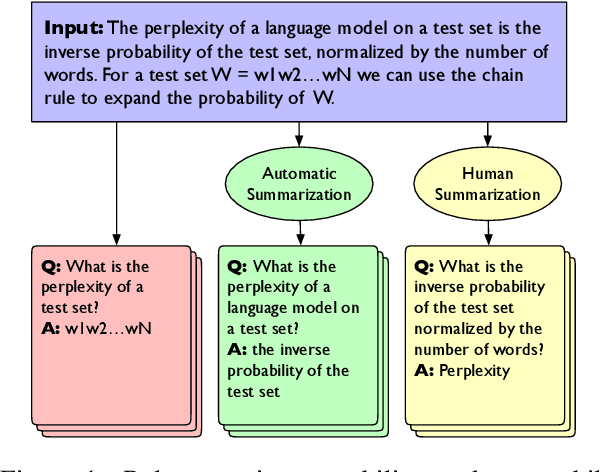
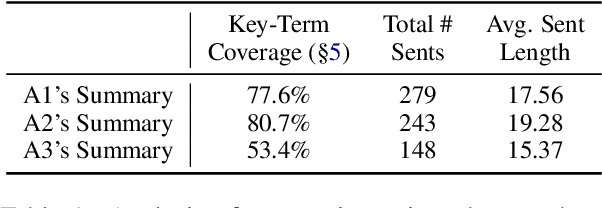
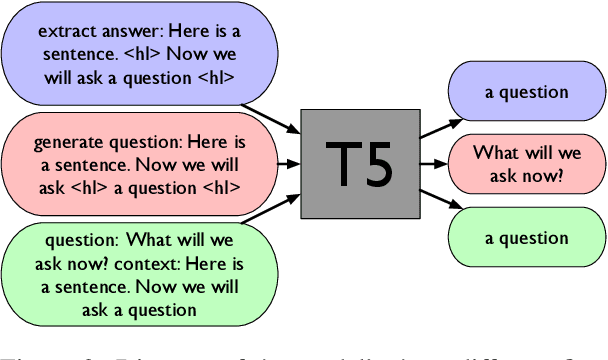
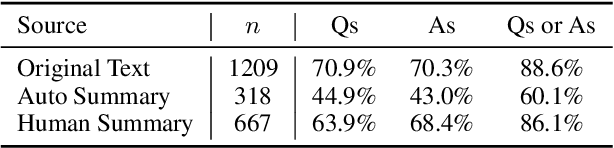
Abstract:We conduct a feasibility study into the applicability of answer-agnostic question generation models to textbook passages. We show that a significant portion of errors in such systems arise from asking irrelevant or uninterpretable questions and that such errors can be ameliorated by providing summarized input. We find that giving these models human-written summaries instead of the original text results in a significant increase in acceptability of generated questions (33% $\rightarrow$ 83%) as determined by expert annotators. We also find that, in the absence of human-written summaries, automatic summarization can serve as a good middle ground.
Cross-modal Map Learning for Vision and Language Navigation
Mar 21, 2022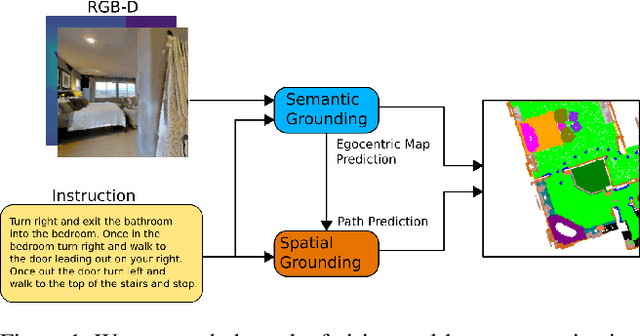
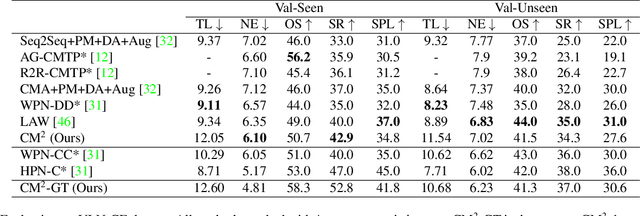
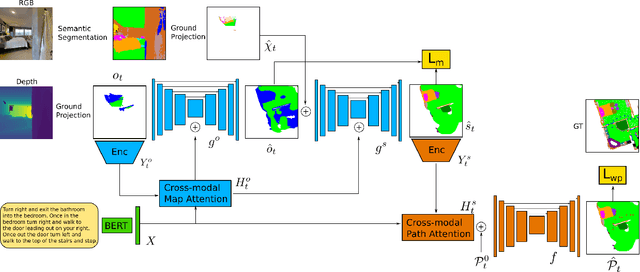
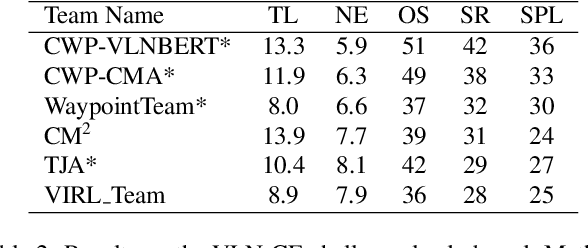
Abstract:We consider the problem of Vision-and-Language Navigation (VLN). The majority of current methods for VLN are trained end-to-end using either unstructured memory such as LSTM, or using cross-modal attention over the egocentric observations of the agent. In contrast to other works, our key insight is that the association between language and vision is stronger when it occurs in explicit spatial representations. In this work, we propose a cross-modal map learning model for vision-and-language navigation that first learns to predict the top-down semantics on an egocentric map for both observed and unobserved regions, and then predicts a path towards the goal as a set of waypoints. In both cases, the prediction is informed by the language through cross-modal attention mechanisms. We experimentally test the basic hypothesis that language-driven navigation can be solved given a map, and then show competitive results on the full VLN-CE benchmark.
Complexity-Weighted Loss and Diverse Reranking for Sentence Simplification
Apr 04, 2019
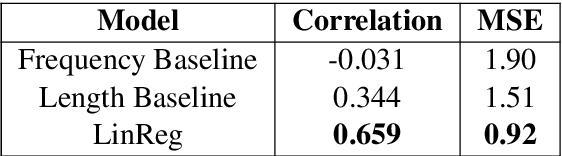
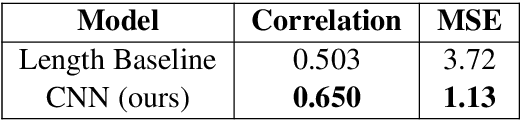
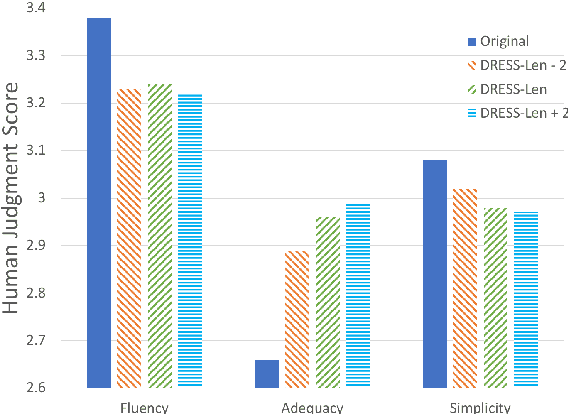
Abstract:Sentence simplification is the task of rewriting texts so they are easier to understand. Recent research has applied sequence-to-sequence (Seq2Seq) models to this task, focusing largely on training-time improvements via reinforcement learning and memory augmentation. One of the main problems with applying generic Seq2Seq models for simplification is that these models tend to copy directly from the original sentence, resulting in outputs that are relatively long and complex. We aim to alleviate this issue through the use of two main techniques. First, we incorporate content word complexities, as predicted with a leveled word complexity model, into our loss function during training. Second, we generate a large set of diverse candidate simplifications at test time, and rerank these to promote fluency, adequacy, and simplicity. Here, we measure simplicity through a novel sentence complexity model. These extensions allow our models to perform competitively with state-of-the-art systems while generating simpler sentences. We report standard automatic and human evaluation metrics.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge