Eike Schneiders
Tangles: Unpacking Extended Collision Experiences with Soma Trajectories
Mar 20, 2025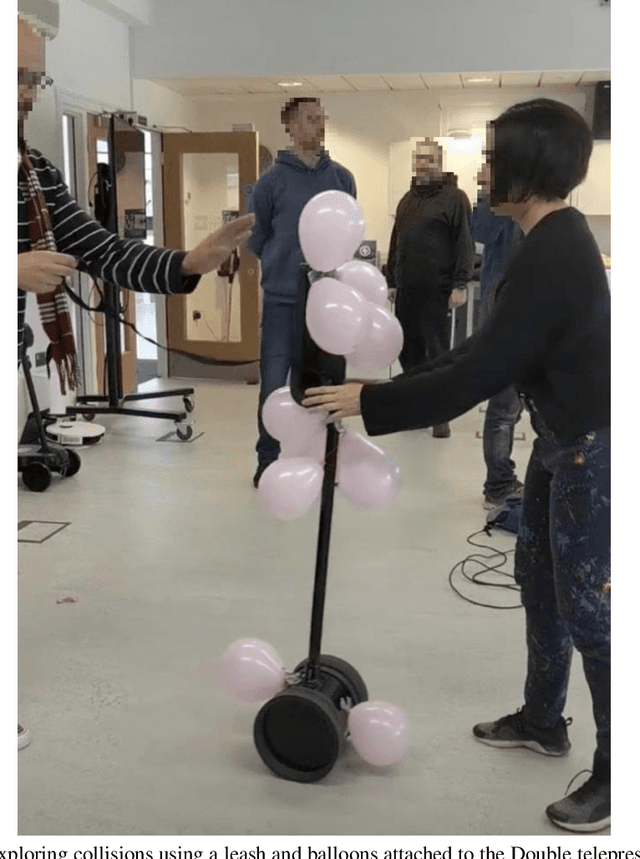
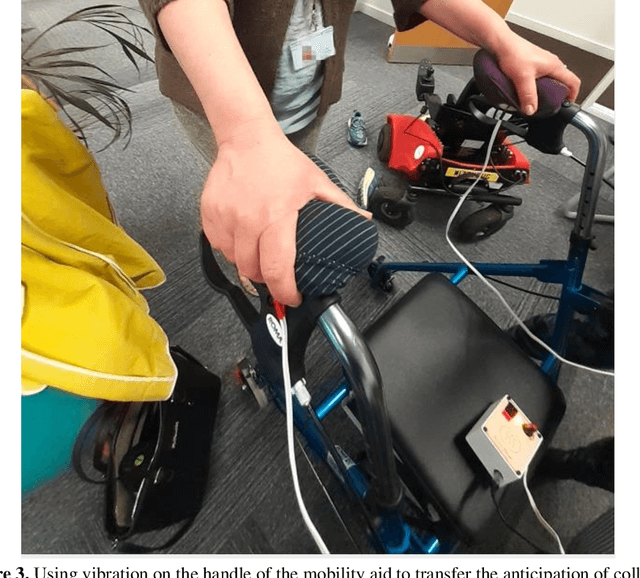


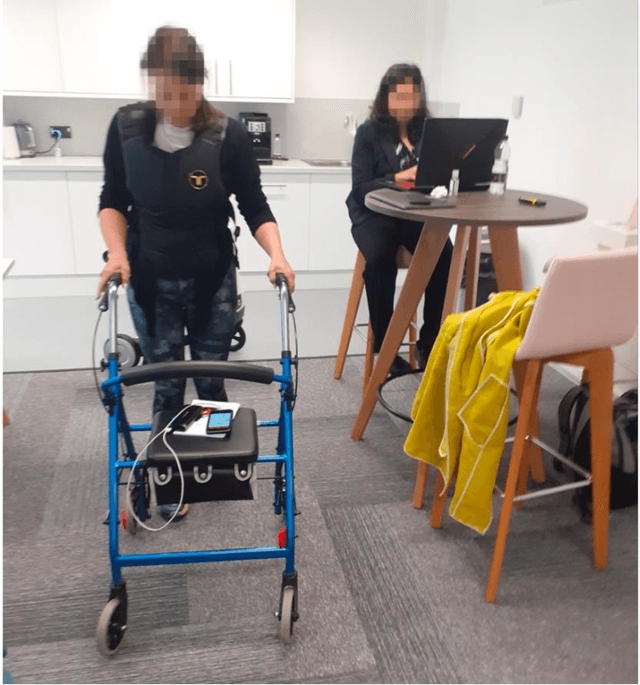
Abstract:We reappraise the idea of colliding with robots, moving from a position that tries to avoid or mitigate collisions to one that considers them an important facet of human interaction. We report on a soma design workshop that explored how our bodies could collide with telepresence robots, mobility aids, and a quadruped robot. Based on our findings, we employed soma trajectories to analyse collisions as extended experiences that negotiate key transitions of consent, preparation, launch, contact, ripple, sting, untangle, debris and reflect. We then employed these ideas to analyse two collision experiences, an accidental collision between a person and a drone, and the deliberate design of a robot to play with cats, revealing how real-world collisions involve the complex and ongoing entanglement of soma trajectories. We discuss how viewing collisions as entangled trajectories, or tangles, can be used analytically, as a design approach, and as a lens to broach ethical complexity.
How Artists Improvise and Provoke Robotics
Oct 29, 2024Abstract:We explore transdisciplinary collaborations between artists and roboticists across a portfolio of artworks. Brendan Walker's Broncomatic was a breath controlled mechanical rodeo bull ride. Blast Theory's Cat Royale deployed a robot arm to play with a family of three cats for twelve days. Different Bodies is a prototype improvised dance performance in which dancers with disabilities physically manipulate two mirrored robot arms. We reflect on these to explore how artists shape robotics research through the two key strategies of improvisation and provocation. Artists are skilled at improvising extended robot experiences that surface opportunities for technology-focused design, but which also require researchers to improvise their research processes. Artists may provoke audiences into reflecting on the societal implications of robots, but at the same time challenge the established techno-centric concepts, methods and underlying epistemology of robotics research.
Understanding Entrainment in Human Groups: Optimising Human-Robot Collaboration from Lessons Learned during Human-Human Collaboration
Feb 23, 2024



Abstract:Successful entrainment during collaboration positively affects trust, willingness to collaborate, and likeability towards collaborators. In this paper, we present a mixed-method study to investigate characteristics of successful entrainment leading to pair and group-based synchronisation. Drawing inspiration from industrial settings, we designed a fast-paced, short-cycle repetitive task. Using motion tracking, we investigated entrainment in both dyadic and triadic task completion. Furthermore, we utilise audio-video recordings and semi-structured interviews to contextualise participants' experiences. This paper contributes to the Human-Computer/Robot Interaction (HCI/HRI) literature using a human-centred approach to identify characteristics of entrainment during pair- and group-based collaboration. We present five characteristics related to successful entrainment. These are related to the occurrence of entrainment, leader-follower patterns, interpersonal communication, the importance of the point-of-assembly, and the value of acoustic feedback. Finally, we present three design considerations for future research and design on collaboration with robots.
Charting Ethical Tensions in Multispecies Technology Research through Beneficiary-Epistemology Space
Feb 23, 2024Abstract:While ethical challenges are widely discussed in HCI, far less is reported about the ethical processes that researchers routinely navigate. We reflect on a multispecies project that negotiated an especially complex ethical approval process. Cat Royale was an artist-led exploration of creating an artwork to engage audiences in exploring trust in autonomous systems. The artwork took the form of a robot that played with three cats. Gaining ethical approval required an extensive dialogue with three Institutional Review Boards (IRBs) covering computer science, veterinary science and animal welfare, raising tensions around the welfare of the cats, perceived benefits and appropriate methods, and reputational risk to the University. To reveal these tensions we introduce beneficiary-epistemology space, that makes explicit who benefits from research (humans or animals) and underlying epistemologies. Positioning projects and IRBs in this space can help clarify tensions and highlight opportunities to recruit additional expertise.
Designing Multispecies Worlds for Robots, Cats, and Humans
Feb 23, 2024



Abstract:We reflect on the design of a multispecies world centred around a bespoke enclosure in which three cats and a robot arm coexist for six hours a day during a twelve-day installation as part of an artist-led project. In this paper, we present the project's design process, encompassing various interconnected components, including the cats, the robot and its autonomous systems, the custom end-effectors and robot attachments, the diverse roles of the humans-in-the-loop, and the custom-designed enclosure. Subsequently, we provide a detailed account of key moments during the deployment and discuss the design implications for future multispecies systems. Specifically, we argue that designing the technology and its interactions is not sufficient, but that it is equally important to consider the design of the `world' in which the technology operates. Finally, we highlight the necessity of human involvement in areas such as breakdown recovery, animal welfare, and their role as audience.
The Effect of Predictive Formal Modelling at Runtime on Performance in Human-Swarm Interaction
Jan 22, 2024Abstract:Formal Modelling is often used as part of the design and testing process of software development to ensure that components operate within suitable bounds even in unexpected circumstances. In this paper, we use predictive formal modelling (PFM) at runtime in a human-swarm mission and show that this integration can be used to improve the performance of human-swarm teams. We recruited 60 participants to operate a simulated aerial swarm to deliver parcels to target locations. In the PFM condition, operators were informed of the estimated completion times given the number of drones deployed, whereas in the No-PFM condition, operators did not have this information. The operators could control the mission by adding or removing drones from the mission and thereby, increasing or decreasing the overall mission cost. The evaluation of human-swarm performance relied on four key metrics: the time taken to complete tasks, the number of agents involved, the total number of tasks accomplished, and the overall cost associated with the human-swarm task. Our results show that PFM modelling at runtime improves mission performance without significantly affecting the operator's workload or the system's usability.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge