Steve Benford
Tangles: Unpacking Extended Collision Experiences with Soma Trajectories
Mar 20, 2025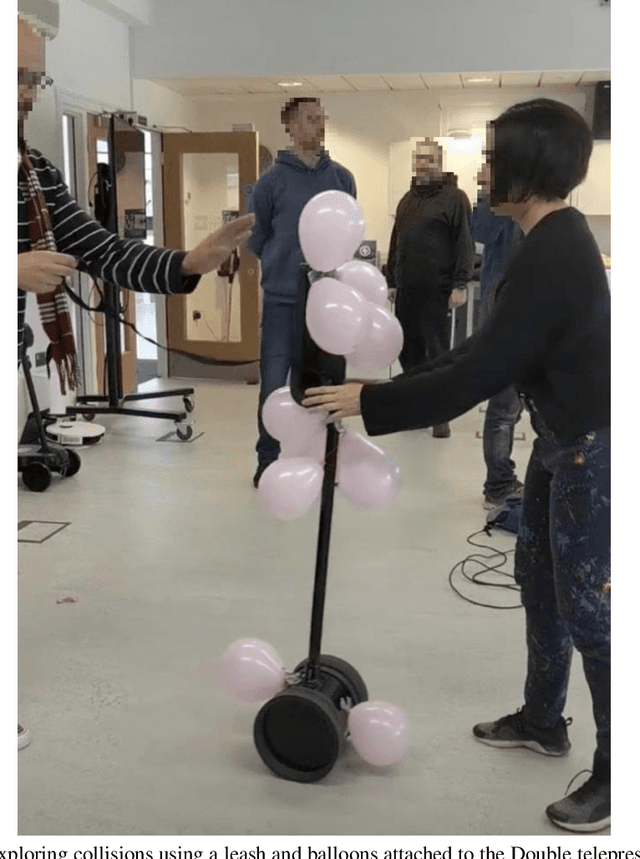
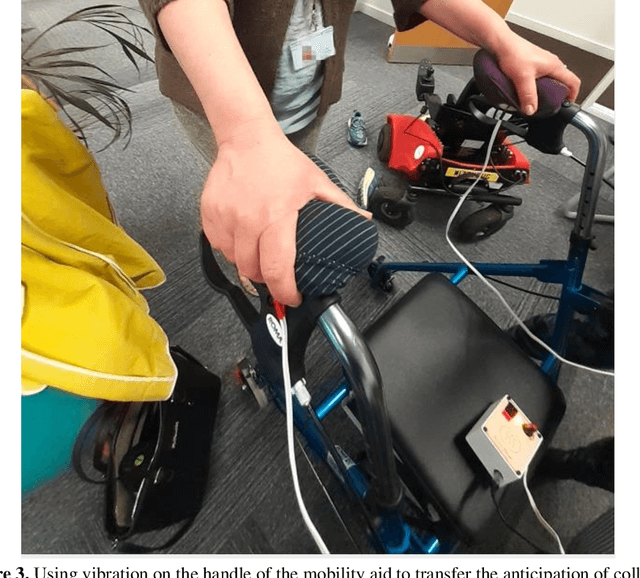


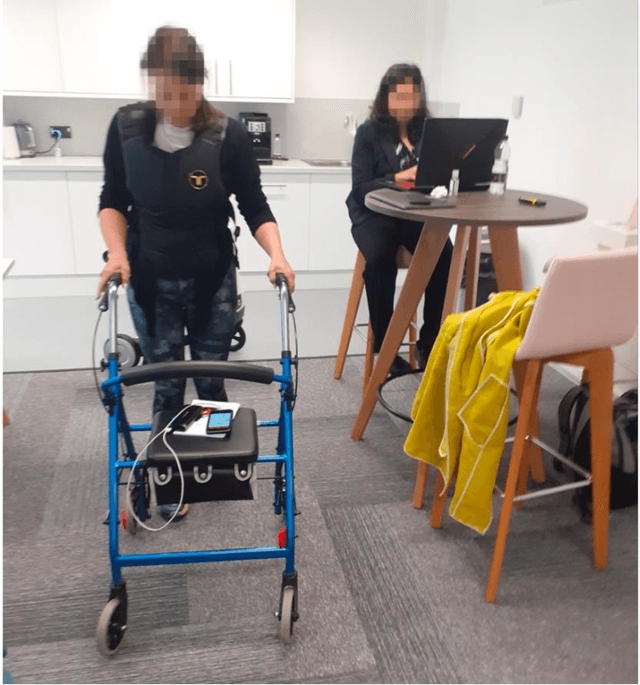
Abstract:We reappraise the idea of colliding with robots, moving from a position that tries to avoid or mitigate collisions to one that considers them an important facet of human interaction. We report on a soma design workshop that explored how our bodies could collide with telepresence robots, mobility aids, and a quadruped robot. Based on our findings, we employed soma trajectories to analyse collisions as extended experiences that negotiate key transitions of consent, preparation, launch, contact, ripple, sting, untangle, debris and reflect. We then employed these ideas to analyse two collision experiences, an accidental collision between a person and a drone, and the deliberate design of a robot to play with cats, revealing how real-world collisions involve the complex and ongoing entanglement of soma trajectories. We discuss how viewing collisions as entangled trajectories, or tangles, can be used analytically, as a design approach, and as a lens to broach ethical complexity.
How Artists Improvise and Provoke Robotics
Oct 29, 2024Abstract:We explore transdisciplinary collaborations between artists and roboticists across a portfolio of artworks. Brendan Walker's Broncomatic was a breath controlled mechanical rodeo bull ride. Blast Theory's Cat Royale deployed a robot arm to play with a family of three cats for twelve days. Different Bodies is a prototype improvised dance performance in which dancers with disabilities physically manipulate two mirrored robot arms. We reflect on these to explore how artists shape robotics research through the two key strategies of improvisation and provocation. Artists are skilled at improvising extended robot experiences that surface opportunities for technology-focused design, but which also require researchers to improvise their research processes. Artists may provoke audiences into reflecting on the societal implications of robots, but at the same time challenge the established techno-centric concepts, methods and underlying epistemology of robotics research.
Uncovering the Metaverse within Everyday Environments: a Coarse-to-Fine Approach
Apr 11, 2024



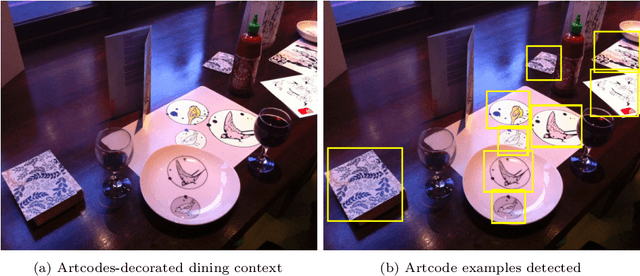
Abstract:The recent release of the Apple Vision Pro has reignited interest in the metaverse, showcasing the intensified efforts of technology giants in developing platforms and devices to facilitate its growth. As the metaverse continues to proliferate, it is foreseeable that everyday environments will become increasingly saturated with its presence. Consequently, uncovering links to these metaverse items will be a crucial first step to interacting with this new augmented world. In this paper, we address the problem of establishing connections with virtual worlds within everyday environments, especially those that are not readily discernible through direct visual inspection. We introduce a vision-based approach leveraging Artcode visual markers to uncover hidden metaverse links embedded in our ambient surroundings. This approach progressively localises the access points to the metaverse, transitioning from coarse to fine localisation, thus facilitating an exploratory interaction process. Detailed experiments are conducted to study the performance of the proposed approach, demonstrating its effectiveness in Artcode localisation and enabling new interaction opportunities.
Charting Ethical Tensions in Multispecies Technology Research through Beneficiary-Epistemology Space
Feb 23, 2024Abstract:While ethical challenges are widely discussed in HCI, far less is reported about the ethical processes that researchers routinely navigate. We reflect on a multispecies project that negotiated an especially complex ethical approval process. Cat Royale was an artist-led exploration of creating an artwork to engage audiences in exploring trust in autonomous systems. The artwork took the form of a robot that played with three cats. Gaining ethical approval required an extensive dialogue with three Institutional Review Boards (IRBs) covering computer science, veterinary science and animal welfare, raising tensions around the welfare of the cats, perceived benefits and appropriate methods, and reputational risk to the University. To reveal these tensions we introduce beneficiary-epistemology space, that makes explicit who benefits from research (humans or animals) and underlying epistemologies. Positioning projects and IRBs in this space can help clarify tensions and highlight opportunities to recruit additional expertise.
Designing Multispecies Worlds for Robots, Cats, and Humans
Feb 23, 2024



Abstract:We reflect on the design of a multispecies world centred around a bespoke enclosure in which three cats and a robot arm coexist for six hours a day during a twelve-day installation as part of an artist-led project. In this paper, we present the project's design process, encompassing various interconnected components, including the cats, the robot and its autonomous systems, the custom end-effectors and robot attachments, the diverse roles of the humans-in-the-loop, and the custom-designed enclosure. Subsequently, we provide a detailed account of key moments during the deployment and discuss the design implications for future multispecies systems. Specifically, we argue that designing the technology and its interactions is not sufficient, but that it is equally important to consider the design of the `world' in which the technology operates. Finally, we highlight the necessity of human involvement in areas such as breakdown recovery, animal welfare, and their role as audience.
Using Metamorphic Relations to Verify and Enhance Artcode Classification
Aug 05, 2021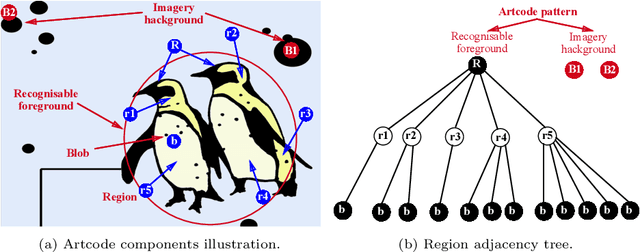
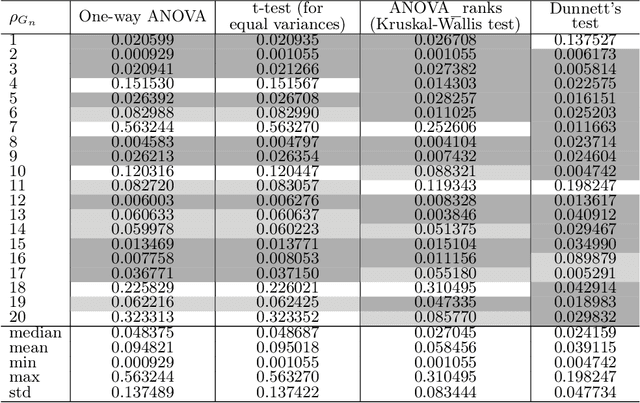
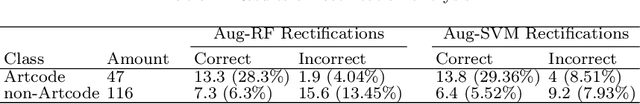
Abstract:Software testing is often hindered where it is impossible or impractical to determine the correctness of the behaviour or output of the software under test (SUT), a situation known as the oracle problem. An example of an area facing the oracle problem is automatic image classification, using machine learning to classify an input image as one of a set of predefined classes. An approach to software testing that alleviates the oracle problem is metamorphic testing (MT). While traditional software testing examines the correctness of individual test cases, MT instead examines the relations amongst multiple executions of test cases and their outputs. These relations are called metamorphic relations (MRs): if an MR is found to be violated, then a fault must exist in the SUT. This paper examines the problem of classifying images containing visually hidden markers called Artcodes, and applies MT to verify and enhance the trained classifiers. This paper further examines two MRs, Separation and Occlusion, and reports on their capability in verifying the image classification using one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) in conjunction with three other statistical analysis methods: t-test (for unequal variances), Kruskal-Wallis test, and Dunnett's test. In addition to our previously-studied classifier, that used Random Forests, we introduce a new classifier that uses a support vector machine, and present its MR-augmented version. Experimental evaluations across a number of performance metrics show that the augmented classifiers can achieve better performance than non-augmented classifiers. This paper also analyses how the enhanced performance is obtained.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge