Edoardo Barba
Optimizing LLMs for Italian: Reducing Token Fertility and Enhancing Efficiency Through Vocabulary Adaptation
Apr 23, 2025Abstract:The number of pretrained Large Language Models (LLMs) is increasing steadily, though the majority are designed predominantly for the English language. While state-of-the-art LLMs can handle other languages, due to language contamination or some degree of multilingual pretraining data, they are not optimized for non-English languages, leading to inefficient encoding (high token "fertility") and slower inference speed. In this work, we thoroughly compare a variety of vocabulary adaptation techniques for optimizing English LLMs for the Italian language, and put forward Semantic Alignment Vocabulary Adaptation (SAVA), a novel method that leverages neural mapping for vocabulary substitution. SAVA achieves competitive performance across multiple downstream tasks, enhancing grounded alignment strategies. We adapt two LLMs: Mistral-7b-v0.1, reducing token fertility by 25\%, and Llama-3.1-8B, optimizing the vocabulary and reducing the number of parameters by 1 billion. We show that, following the adaptation of the vocabulary, these models can recover their performance with a relatively limited stage of continual training on the target language. Finally, we test the capabilities of the adapted models on various multi-choice and generative tasks.
Word Sense Linking: Disambiguating Outside the Sandbox
Dec 12, 2024



Abstract:Word Sense Disambiguation (WSD) is the task of associating a word in a given context with its most suitable meaning among a set of possible candidates. While the task has recently witnessed renewed interest, with systems achieving performances above the estimated inter-annotator agreement, at the time of writing it still struggles to find downstream applications. We argue that one of the reasons behind this is the difficulty of applying WSD to plain text. Indeed, in the standard formulation, models work under the assumptions that a) all the spans to disambiguate have already been identified, and b) all the possible candidate senses of each span are provided, both of which are requirements that are far from trivial. In this work, we present a new task called Word Sense Linking (WSL) where, given an input text and a reference sense inventory, systems have to both identify which spans to disambiguate and then link them to their most suitable meaning.We put forward a transformer-based architecture for the task and thoroughly evaluate both its performance and those of state-of-the-art WSD systems scaled to WSL, iteratively relaxing the assumptions of WSD. We hope that our work will foster easier integration of lexical semantics into downstream applications.
Beyond Correlation: Interpretable Evaluation of Machine Translation Metrics
Oct 07, 2024



Abstract:Machine Translation (MT) evaluation metrics assess translation quality automatically. Recently, researchers have employed MT metrics for various new use cases, such as data filtering and translation re-ranking. However, most MT metrics return assessments as scalar scores that are difficult to interpret, posing a challenge to making informed design choices. Moreover, MT metrics' capabilities have historically been evaluated using correlation with human judgment, which, despite its efficacy, falls short of providing intuitive insights into metric performance, especially in terms of new metric use cases. To address these issues, we introduce an interpretable evaluation framework for MT metrics. Within this framework, we evaluate metrics in two scenarios that serve as proxies for the data filtering and translation re-ranking use cases. Furthermore, by measuring the performance of MT metrics using Precision, Recall, and F-score, we offer clearer insights into their capabilities than correlation with human judgments. Finally, we raise concerns regarding the reliability of manually curated data following the Direct Assessments+Scalar Quality Metrics (DA+SQM) guidelines, reporting a notably low agreement with Multidimensional Quality Metrics (MQM) annotations.
Guardians of the Machine Translation Meta-Evaluation: Sentinel Metrics Fall In!
Aug 25, 2024



Abstract:Annually, at the Conference of Machine Translation (WMT), the Metrics Shared Task organizers conduct the meta-evaluation of Machine Translation (MT) metrics, ranking them according to their correlation with human judgments. Their results guide researchers toward enhancing the next generation of metrics and MT systems. With the recent introduction of neural metrics, the field has witnessed notable advancements. Nevertheless, the inherent opacity of these metrics has posed substantial challenges to the meta-evaluation process. This work highlights two issues with the meta-evaluation framework currently employed in WMT, and assesses their impact on the metrics rankings. To do this, we introduce the concept of sentinel metrics, which are designed explicitly to scrutinize the meta-evaluation process's accuracy, robustness, and fairness. By employing sentinel metrics, we aim to validate our findings, and shed light on and monitor the potential biases or inconsistencies in the rankings. We discover that the present meta-evaluation framework favors two categories of metrics: i) those explicitly trained to mimic human quality assessments, and ii) continuous metrics. Finally, we raise concerns regarding the evaluation capabilities of state-of-the-art metrics, emphasizing that they might be basing their assessments on spurious correlations found in their training data.
Maverick: Efficient and Accurate Coreference Resolution Defying Recent Trends
Jul 31, 2024



Abstract:Large autoregressive generative models have emerged as the cornerstone for achieving the highest performance across several Natural Language Processing tasks. However, the urge to attain superior results has, at times, led to the premature replacement of carefully designed task-specific approaches without exhaustive experimentation. The Coreference Resolution task is no exception; all recent state-of-the-art solutions adopt large generative autoregressive models that outperform encoder-based discriminative systems. In this work,we challenge this recent trend by introducing Maverick, a carefully designed - yet simple - pipeline, which enables running a state-of-the-art Coreference Resolution system within the constraints of an academic budget, outperforming models with up to 13 billion parameters with as few as 500 million parameters. Maverick achieves state-of-the-art performance on the CoNLL-2012 benchmark, training with up to 0.006x the memory resources and obtaining a 170x faster inference compared to previous state-of-the-art systems. We extensively validate the robustness of the Maverick framework with an array of diverse experiments, reporting improvements over prior systems in data-scarce, long-document, and out-of-domain settings. We release our code and models for research purposes at https://github.com/SapienzaNLP/maverick-coref.
ReLiK: Retrieve and LinK, Fast and Accurate Entity Linking and Relation Extraction on an Academic Budget
Jul 31, 2024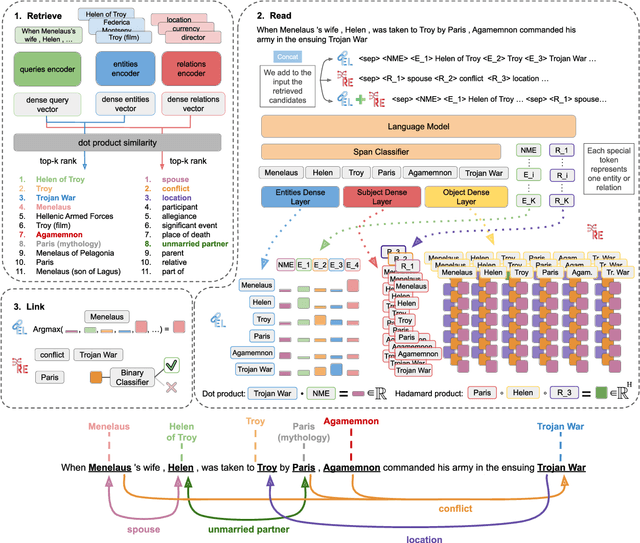
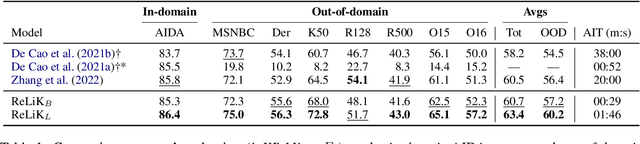
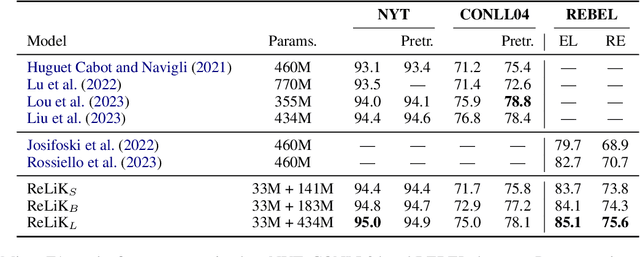
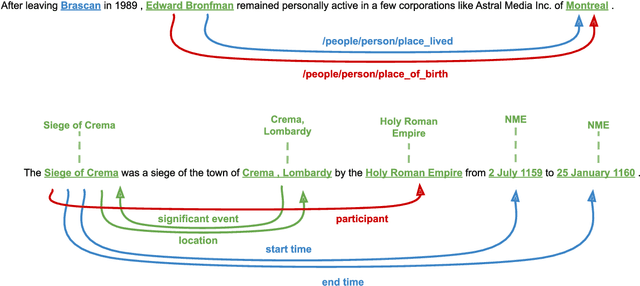
Abstract:Entity Linking (EL) and Relation Extraction (RE) are fundamental tasks in Natural Language Processing, serving as critical components in a wide range of applications. In this paper, we propose ReLiK, a Retriever-Reader architecture for both EL and RE, where, given an input text, the Retriever module undertakes the identification of candidate entities or relations that could potentially appear within the text. Subsequently, the Reader module is tasked to discern the pertinent retrieved entities or relations and establish their alignment with the corresponding textual spans. Notably, we put forward an innovative input representation that incorporates the candidate entities or relations alongside the text, making it possible to link entities or extract relations in a single forward pass and to fully leverage pre-trained language models contextualization capabilities, in contrast with previous Retriever-Reader-based methods, which require a forward pass for each candidate. Our formulation of EL and RE achieves state-of-the-art performance in both in-domain and out-of-domain benchmarks while using academic budget training and with up to 40x inference speed compared to competitors. Finally, we show how our architecture can be used seamlessly for Information Extraction (cIE), i.e. EL + RE, and setting a new state of the art by employing a shared Reader that simultaneously extracts entities and relations.
The Effect of Training Schedules on Morphological Robustness and Generalization
Jul 19, 2024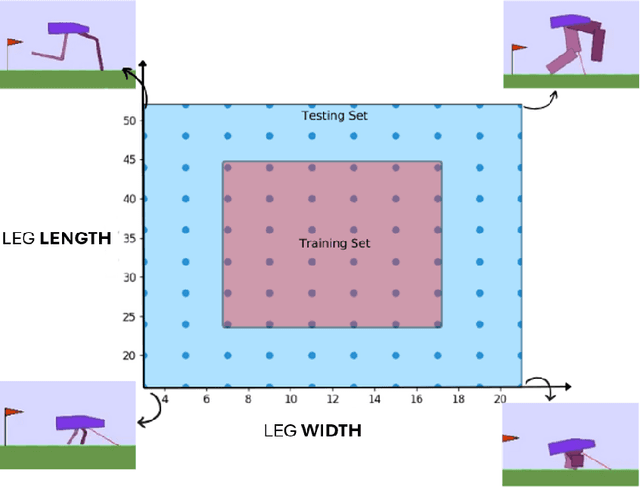
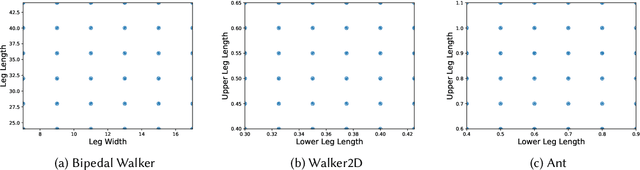
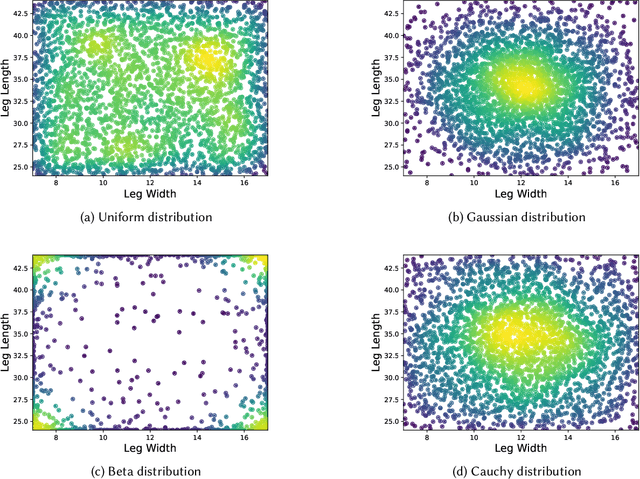
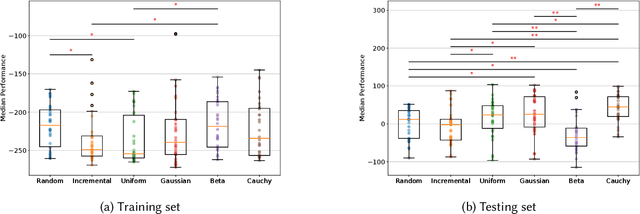
Abstract:Robustness and generalizability are the key properties of artificial neural network (ANN)-based controllers for maintaining a reliable performance in case of changes. It is demonstrated that exposing the ANNs to variations during training processes can improve their robustness and generalization capabilities. However, the way in which this variation is introduced can have a significant impact. In this paper, we define various training schedules to specify how these variations are introduced during an evolutionary learning process. In particular, we focus on morphological robustness and generalizability concerned with finding an ANN-based controller that can provide sufficient performance on a range of physical variations. Then, we perform an extensive analysis of the effect of these training schedules on morphological generalization. Furthermore, we formalize the process of training sample selection (i.e., morphological variations) to improve generalization as a reinforcement learning problem. Overall, our results provide deeper insights into the role of variability and the ways of enhancing the generalization property of evolved ANN-based controllers.
Code-Switching with Word Senses for Pretraining in Neural Machine Translation
Oct 21, 2023Abstract:Lexical ambiguity is a significant and pervasive challenge in Neural Machine Translation (NMT), with many state-of-the-art (SOTA) NMT systems struggling to handle polysemous words (Campolungo et al., 2022). The same holds for the NMT pretraining paradigm of denoising synthetic "code-switched" text (Pan et al., 2021; Iyer et al., 2023), where word senses are ignored in the noising stage -- leading to harmful sense biases in the pretraining data that are subsequently inherited by the resulting models. In this work, we introduce Word Sense Pretraining for Neural Machine Translation (WSP-NMT) - an end-to-end approach for pretraining multilingual NMT models leveraging word sense-specific information from Knowledge Bases. Our experiments show significant improvements in overall translation quality. Then, we show the robustness of our approach to scale to various challenging data and resource-scarce scenarios and, finally, report fine-grained accuracy improvements on the DiBiMT disambiguation benchmark. Our studies yield interesting and novel insights into the merits and challenges of integrating word sense information and structured knowledge in multilingual pretraining for NMT.
Semantic Role Labeling Meets Definition Modeling: Using Natural Language to Describe Predicate-Argument Structures
Dec 02, 2022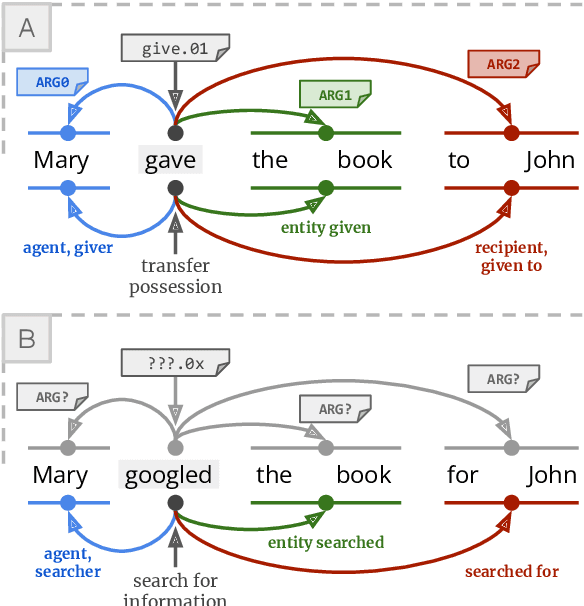
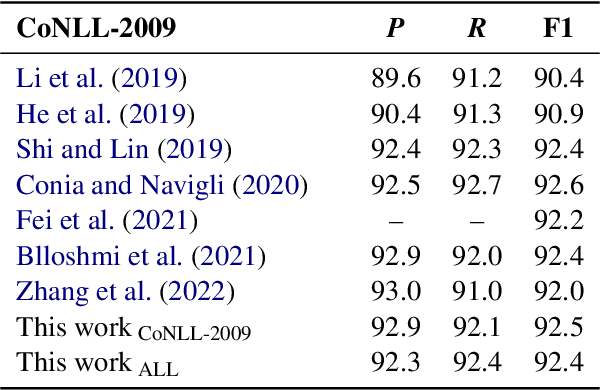
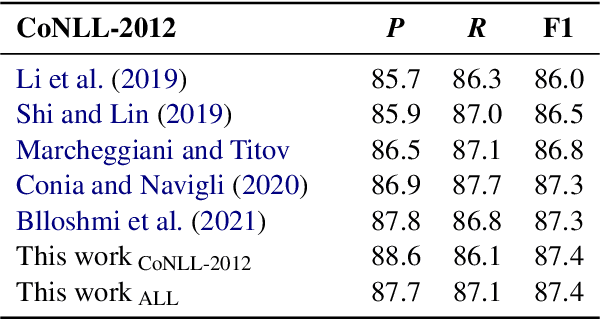
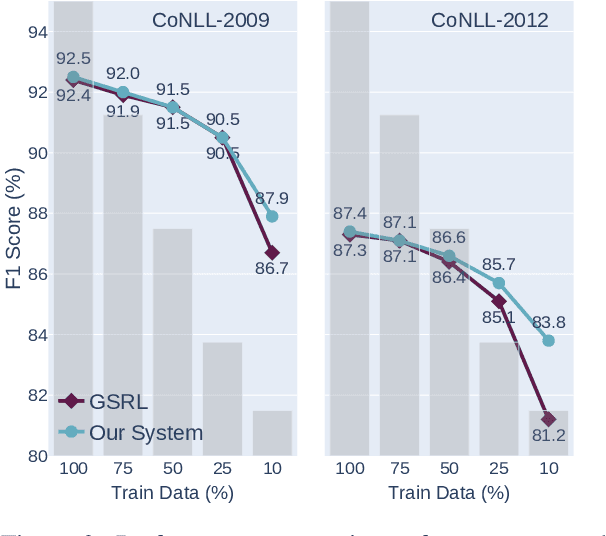
Abstract:One of the common traits of past and present approaches for Semantic Role Labeling (SRL) is that they rely upon discrete labels drawn from a predefined linguistic inventory to classify predicate senses and their arguments. However, we argue this need not be the case. In this paper, we present an approach that leverages Definition Modeling to introduce a generalized formulation of SRL as the task of describing predicate-argument structures using natural language definitions instead of discrete labels. Our novel formulation takes a first step towards placing interpretability and flexibility foremost, and yet our experiments and analyses on PropBank-style and FrameNet-style, dependency-based and span-based SRL also demonstrate that a flexible model with an interpretable output does not necessarily come at the expense of performance. We release our software for research purposes at https://github.com/SapienzaNLP/dsrl.
Entity Disambiguation with Entity Definitions
Oct 11, 2022


Abstract:Local models have recently attained astounding performances in Entity Disambiguation (ED), with generative and extractive formulations being the most promising research directions. However, previous works limited their studies to using, as the textual representation of each candidate, only its Wikipedia title. Although certainly effective, this strategy presents a few critical issues, especially when titles are not sufficiently informative or distinguishable from one another. In this paper, we address this limitation and investigate to what extent more expressive textual representations can mitigate it. We thoroughly evaluate our approach against standard benchmarks in ED and find extractive formulations to be particularly well-suited to these representations: we report a new state of the art on 2 out of 6 benchmarks we consider and strongly improve the generalization capability over unseen patterns. We release our code, data and model checkpoints at https://github.com/SapienzaNLP/extend.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge