Dogyoon Lee
CoMoGaussian: Continuous Motion-Aware Gaussian Splatting from Motion-Blurred Images
Mar 07, 2025Abstract:3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) has gained significant attention for their high-quality novel view rendering, motivating research to address real-world challenges. A critical issue is the camera motion blur caused by movement during exposure, which hinders accurate 3D scene reconstruction. In this study, we propose CoMoGaussian, a Continuous Motion-Aware Gaussian Splatting that reconstructs precise 3D scenes from motion-blurred images while maintaining real-time rendering speed. Considering the complex motion patterns inherent in real-world camera movements, we predict continuous camera trajectories using neural ordinary differential equations (ODEs). To ensure accurate modeling, we employ rigid body transformations, preserving the shape and size of the object but rely on the discrete integration of sampled frames. To better approximate the continuous nature of motion blur, we introduce a continuous motion refinement (CMR) transformation that refines rigid transformations by incorporating additional learnable parameters. By revisiting fundamental camera theory and leveraging advanced neural ODE techniques, we achieve precise modeling of continuous camera trajectories, leading to improved reconstruction accuracy. Extensive experiments demonstrate state-of-the-art performance both quantitatively and qualitatively on benchmark datasets, which include a wide range of motion blur scenarios, from moderate to extreme blur.
CoCoGaussian: Leveraging Circle of Confusion for Gaussian Splatting from Defocused Images
Dec 20, 2024



Abstract:3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) has attracted significant attention for its high-quality novel view rendering, inspiring research to address real-world challenges. While conventional methods depend on sharp images for accurate scene reconstruction, real-world scenarios are often affected by defocus blur due to finite depth of field, making it essential to account for realistic 3D scene representation. In this study, we propose CoCoGaussian, a Circle of Confusion-aware Gaussian Splatting that enables precise 3D scene representation using only defocused images. CoCoGaussian addresses the challenge of defocus blur by modeling the Circle of Confusion (CoC) through a physically grounded approach based on the principles of photographic defocus. Exploiting 3D Gaussians, we compute the CoC diameter from depth and learnable aperture information, generating multiple Gaussians to precisely capture the CoC shape. Furthermore, we introduce a learnable scaling factor to enhance robustness and provide more flexibility in handling unreliable depth in scenes with reflective or refractive surfaces. Experiments on both synthetic and real-world datasets demonstrate that CoCoGaussian achieves state-of-the-art performance across multiple benchmarks.
ProDepth: Boosting Self-Supervised Multi-Frame Monocular Depth with Probabilistic Fusion
Jul 12, 2024



Abstract:Self-supervised multi-frame monocular depth estimation relies on the geometric consistency between successive frames under the assumption of a static scene. However, the presence of moving objects in dynamic scenes introduces inevitable inconsistencies, causing misaligned multi-frame feature matching and misleading self-supervision during training. In this paper, we propose a novel framework called ProDepth, which effectively addresses the mismatch problem caused by dynamic objects using a probabilistic approach. We initially deduce the uncertainty associated with static scene assumption by adopting an auxiliary decoder. This decoder analyzes inconsistencies embedded in the cost volume, inferring the probability of areas being dynamic. We then directly rectify the erroneous cost volume for dynamic areas through a Probabilistic Cost Volume Modulation (PCVM) module. Specifically, we derive probability distributions of depth candidates from both single-frame and multi-frame cues, modulating the cost volume by adaptively fusing those distributions based on the inferred uncertainty. Additionally, we present a self-supervision loss reweighting strategy that not only masks out incorrect supervision with high uncertainty but also mitigates the risks in remaining possible dynamic areas in accordance with the probability. Our proposed method excels over state-of-the-art approaches in all metrics on both Cityscapes and KITTI datasets, and demonstrates superior generalization ability on the Waymo Open dataset.
Sparse-DeRF: Deblurred Neural Radiance Fields from Sparse View
Jul 09, 2024



Abstract:Recent studies construct deblurred neural radiance fields (DeRF) using dozens of blurry images, which are not practical scenarios if only a limited number of blurry images are available. This paper focuses on constructing DeRF from sparse-view for more pragmatic real-world scenarios. As observed in our experiments, establishing DeRF from sparse views proves to be a more challenging problem due to the inherent complexity arising from the simultaneous optimization of blur kernels and NeRF from sparse view. Sparse-DeRF successfully regularizes the complicated joint optimization, presenting alleviated overfitting artifacts and enhanced quality on radiance fields. The regularization consists of three key components: Surface smoothness, helps the model accurately predict the scene structure utilizing unseen and additional hidden rays derived from the blur kernel based on statistical tendencies of real-world; Modulated gradient scaling, helps the model adjust the amount of the backpropagated gradient according to the arrangements of scene objects; Perceptual distillation improves the perceptual quality by overcoming the ill-posed multi-view inconsistency of image deblurring and distilling the pre-filtered information, compensating for the lack of clean information in blurry images. We demonstrate the effectiveness of the Sparse-DeRF with extensive quantitative and qualitative experimental results by training DeRF from 2-view, 4-view, and 6-view blurry images.
CRiM-GS: Continuous Rigid Motion-Aware Gaussian Splatting from Motion Blur Images
Jul 04, 2024



Abstract:Neural radiance fields (NeRFs) have received significant attention due to their high-quality novel view rendering ability, prompting research to address various real-world cases. One critical challenge is the camera motion blur caused by camera movement during exposure time, which prevents accurate 3D scene reconstruction. In this study, we propose continuous rigid motion-aware gaussian splatting (CRiM-GS) to reconstruct accurate 3D scene from blurry images with real-time rendering speed. Considering the actual camera motion blurring process, which consists of complex motion patterns, we predict the continuous movement of the camera based on neural ordinary differential equations (ODEs). Specifically, we leverage rigid body transformations to model the camera motion with proper regularization, preserving the shape and size of the object. Furthermore, we introduce a continuous deformable 3D transformation in the \textit{SE(3)} field to adapt the rigid body transformation to real-world problems by ensuring a higher degree of freedom. By revisiting fundamental camera theory and employing advanced neural network training techniques, we achieve accurate modeling of continuous camera trajectories. We conduct extensive experiments, demonstrating state-of-the-art performance both quantitatively and qualitatively on benchmark datasets.
SMURF: Continuous Dynamics for Motion-Deblurring Radiance Fields
Mar 12, 2024Abstract:Neural radiance fields (NeRF) has attracted considerable attention for their exceptional ability in synthesizing novel views with high fidelity. However, the presence of motion blur, resulting from slight camera movements during extended shutter exposures, poses a significant challenge, potentially compromising the quality of the reconstructed 3D scenes. While recent studies have addressed this issue, they do not consider the continuous dynamics of camera movements during image acquisition, leading to inaccurate scene reconstruction. Additionally, these methods are plagued by slow training and rendering speed. To effectively handle these issues, we propose sequential motion understanding radiance fields (SMURF), a novel approach that employs neural ordinary differential equation (Neural-ODE) to model continuous camera motion and leverages the explicit volumetric representation method for faster training and robustness to motion-blurred input images. The core idea of the SMURF is continuous motion blurring kernel (CMBK), a unique module designed to model a continuous camera movements for processing blurry inputs. Our model, rigorously evaluated against benchmark datasets, demonstrates state-of-the-art performance both quantitatively and qualitatively.
Synchronizing Vision and Language: Bidirectional Token-Masking AutoEncoder for Referring Image Segmentation
Nov 29, 2023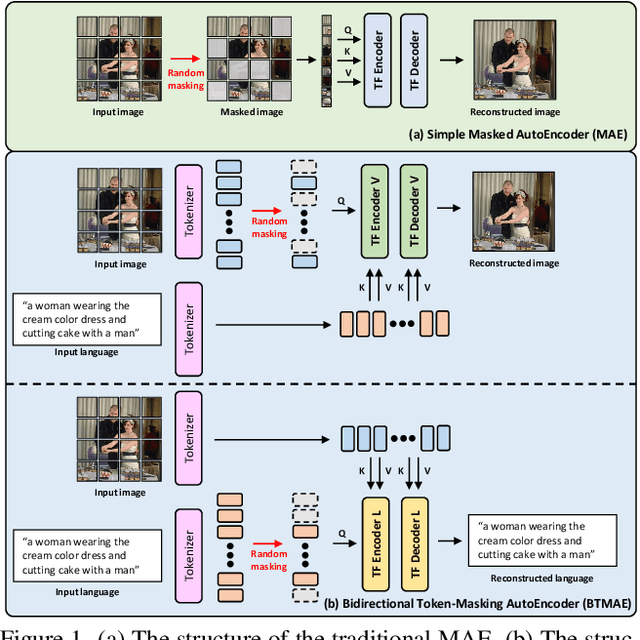
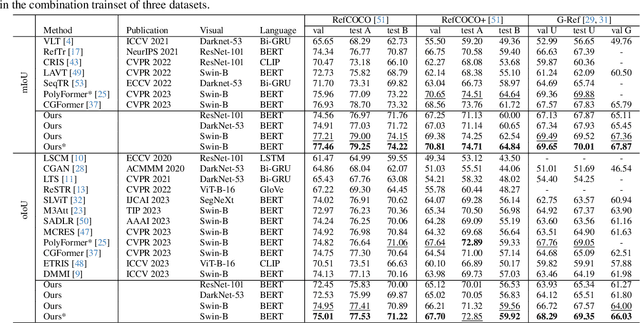
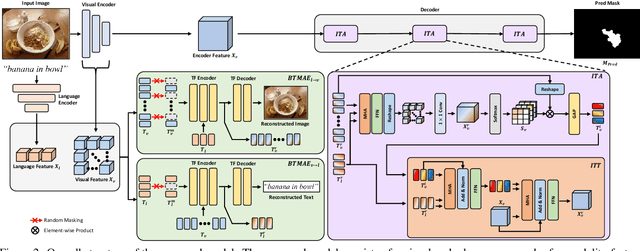
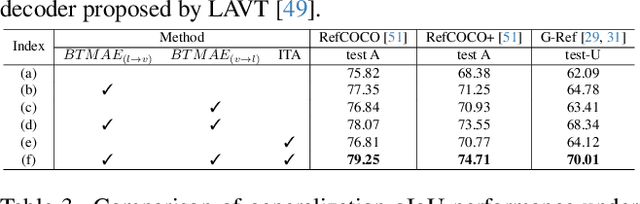
Abstract:Referring Image Segmentation (RIS) aims to segment target objects expressed in natural language within a scene at the pixel level. Various recent RIS models have achieved state-of-the-art performance by generating contextual tokens to model multimodal features from pretrained encoders and effectively fusing them using transformer-based cross-modal attention. While these methods match language features with image features to effectively identify likely target objects, they often struggle to correctly understand contextual information in complex and ambiguous sentences and scenes. To address this issue, we propose a novel bidirectional token-masking autoencoder (BTMAE) inspired by the masked autoencoder (MAE). The proposed model learns the context of image-to-language and language-to-image by reconstructing missing features in both image and language features at the token level. In other words, this approach involves mutually complementing across the features of images and language, with a focus on enabling the network to understand interconnected deep contextual information between the two modalities. This learning method enhances the robustness of RIS performance in complex sentences and scenes. Our BTMAE achieves state-of-the-art performance on three popular datasets, and we demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed method through various ablation studies.
Guided Slot Attention for Unsupervised Video Object Segmentation
Mar 15, 2023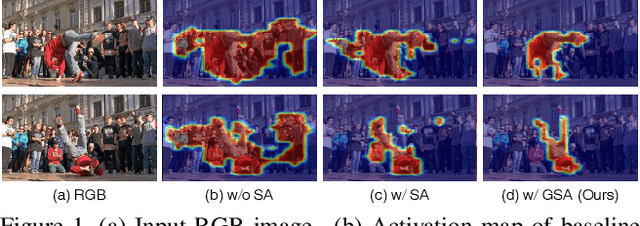
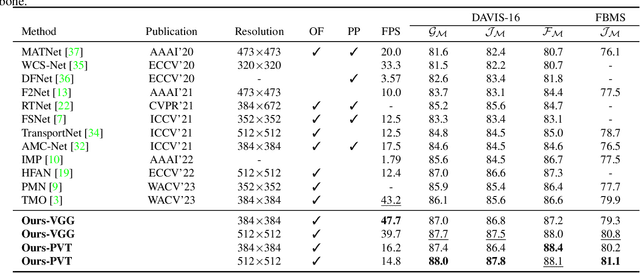
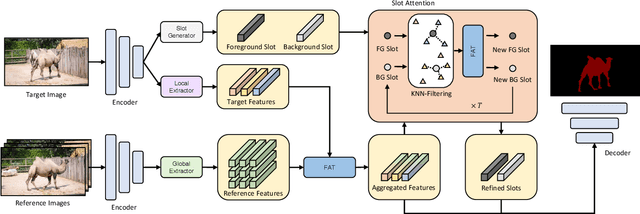
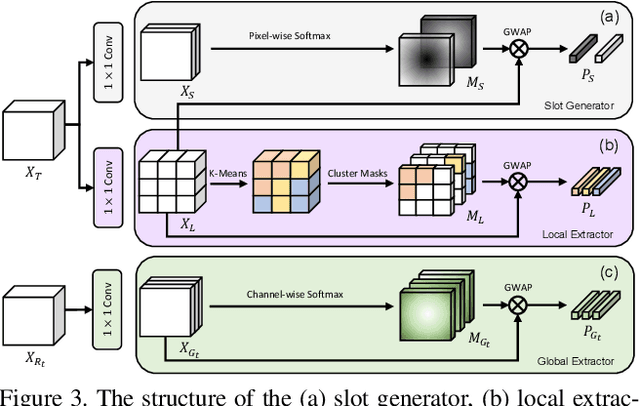
Abstract:Unsupervised video object segmentation aims to segment the most prominent object in a video sequence. However, the existence of complex backgrounds and multiple foreground objects make this task challenging. To address this issue, we propose a guided slot attention network to reinforce spatial structural information and obtain better foreground--background separation. The foreground and background slots, which are initialized with query guidance, are iteratively refined based on interactions with template information. Furthermore, to improve slot--template interaction and effectively fuse global and local features in the target and reference frames, K-nearest neighbors filtering and a feature aggregation transformer are introduced. The proposed model achieves state-of-the-art performance on two popular datasets. Additionally, we demonstrate the robustness of the proposed model in challenging scenes through various comparative experiments.
TSANET: Temporal and Scale Alignment for Unsupervised Video Object Segmentation
Mar 08, 2023



Abstract:Unsupervised Video Object Segmentation (UVOS) refers to the challenging task of segmenting the prominent object in videos without manual guidance. In other words, the network detects the accurate region of the target object in a sequence of RGB frames without prior knowledge. In recent works, two approaches for UVOS have been discussed that can be divided into: appearance and appearance-motion based methods. Appearance based methods utilize the correlation information of inter-frames to capture target object that commonly appears in a sequence. However, these methods does not consider the motion of target object due to exploit the correlation information between randomly paired frames. Appearance-motion based methods, on the other hand, fuse the appearance features from RGB frames with the motion features from optical flow. Motion cue provides useful information since salient objects typically show distinctive motion in a sequence. However, these approaches have the limitation that the dependency on optical flow is dominant. In this paper, we propose a novel framework for UVOS that can address aforementioned limitations of two approaches in terms of both time and scale. Temporal Alignment Fusion aligns the saliency information of adjacent frames with the target frame to leverage the information of adjacent frames. Scale Alignment Decoder predicts the target object mask precisely by aggregating differently scaled feature maps via continuous mapping with implicit neural representation. We present experimental results on public benchmark datasets, DAVIS 2016 and FBMS, which demonstrate the effectiveness of our method. Furthermore, we outperform the state-of-the-art methods on DAVIS 2016.
DP-NeRF: Deblurred Neural Radiance Field with Physical Scene Priors
Dec 02, 2022



Abstract:Neural Radiance Field(NeRF) has exhibited outstanding three-dimensional(3D) reconstruction quality via the novel view synthesis from multi-view images and paired calibrated camera parameters. However, previous NeRF-based systems have been demonstrated under strictly controlled settings, with little attention paid to less ideal scenarios, including with the presence of noise such as exposure, illumination changes, and blur. In particular, though blur frequently occurs in real situations, NeRF that can handle blurred images has received little attention. The few studies that have investigated NeRF for blurred images have not considered geometric and appearance consistency in 3D space, which is one of the most important factors in 3D reconstruction. This leads to inconsistency and the degradation of the perceptual quality of the constructed scene. Hence, this paper proposes a DP-NeRF, a novel clean NeRF framework for blurred images, which is constrained with two physical priors. These priors are derived from the actual blurring process during image acquisition by the camera. DP-NeRF proposes rigid blurring kernel to impose 3D consistency utilizing the physical priors and adaptive weight proposal to refine the color composition error in consideration of the relationship between depth and blur. We present extensive experimental results for synthetic and real scenes with two types of blur: camera motion blur and defocus blur. The results demonstrate that DP-NeRF successfully improves the perceptual quality of the constructed NeRF ensuring 3D geometric and appearance consistency. We further demonstrate the effectiveness of our model with comprehensive ablation analysis.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge