Chaewon Park
GenCLIP: Generalizing CLIP Prompts for Zero-shot Anomaly Detection
Apr 21, 2025Abstract:Zero-shot anomaly detection (ZSAD) aims to identify anomalies in unseen categories by leveraging CLIP's zero-shot capabilities to match text prompts with visual features. A key challenge in ZSAD is learning general prompts stably and utilizing them effectively, while maintaining both generalizability and category specificity. Although general prompts have been explored in prior works, achieving their stable optimization and effective deployment remains a significant challenge. In this work, we propose GenCLIP, a novel framework that learns and leverages general prompts more effectively through multi-layer prompting and dual-branch inference. Multi-layer prompting integrates category-specific visual cues from different CLIP layers, enriching general prompts with more comprehensive and robust feature representations. By combining general prompts with multi-layer visual features, our method further enhances its generalization capability. To balance specificity and generalization, we introduce a dual-branch inference strategy, where a vision-enhanced branch captures fine-grained category-specific features, while a query-only branch prioritizes generalization. The complementary outputs from both branches improve the stability and reliability of anomaly detection across unseen categories. Additionally, we propose an adaptive text prompt filtering mechanism, which removes irrelevant or atypical class names not encountered during CLIP's training, ensuring that only meaningful textual inputs contribute to the final vision-language alignment.
K-HATERS: A Hate Speech Detection Corpus in Korean with Target-Specific Ratings
Oct 24, 2023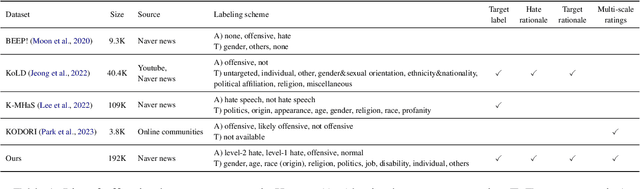

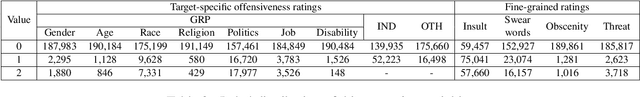
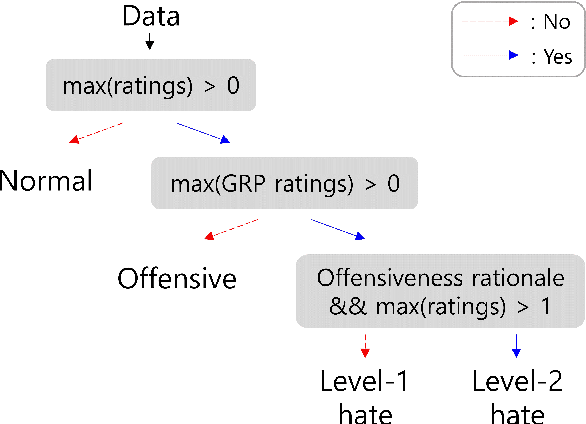
Abstract:Numerous datasets have been proposed to combat the spread of online hate. Despite these efforts, a majority of these resources are English-centric, primarily focusing on overt forms of hate. This research gap calls for developing high-quality corpora in diverse languages that also encapsulate more subtle hate expressions. This study introduces K-HATERS, a new corpus for hate speech detection in Korean, comprising approximately 192K news comments with target-specific offensiveness ratings. This resource is the largest offensive language corpus in Korean and is the first to offer target-specific ratings on a three-point Likert scale, enabling the detection of hate expressions in Korean across varying degrees of offensiveness. We conduct experiments showing the effectiveness of the proposed corpus, including a comparison with existing datasets. Additionally, to address potential noise and bias in human annotations, we explore a novel idea of adopting the Cognitive Reflection Test, which is widely used in social science for assessing an individual's cognitive ability, as a proxy of labeling quality. Findings indicate that annotations from individuals with the lowest test scores tend to yield detection models that make biased predictions toward specific target groups and are less accurate. This study contributes to the NLP research on hate speech detection and resource construction. The code and dataset can be accessed at https://github.com/ssu-humane/K-HATERS.
Guided Slot Attention for Unsupervised Video Object Segmentation
Mar 15, 2023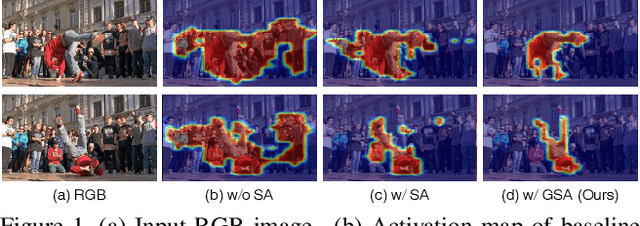
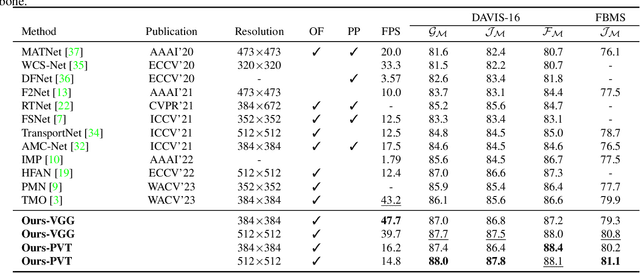
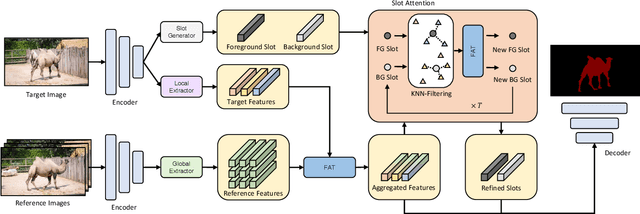
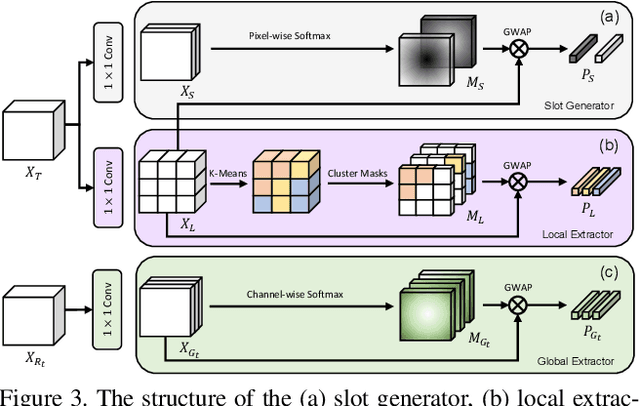
Abstract:Unsupervised video object segmentation aims to segment the most prominent object in a video sequence. However, the existence of complex backgrounds and multiple foreground objects make this task challenging. To address this issue, we propose a guided slot attention network to reinforce spatial structural information and obtain better foreground--background separation. The foreground and background slots, which are initialized with query guidance, are iteratively refined based on interactions with template information. Furthermore, to improve slot--template interaction and effectively fuse global and local features in the target and reference frames, K-nearest neighbors filtering and a feature aggregation transformer are introduced. The proposed model achieves state-of-the-art performance on two popular datasets. Additionally, we demonstrate the robustness of the proposed model in challenging scenes through various comparative experiments.
Two-stream Decoder Feature Normality Estimating Network for Industrial Anomaly Detection
Feb 20, 2023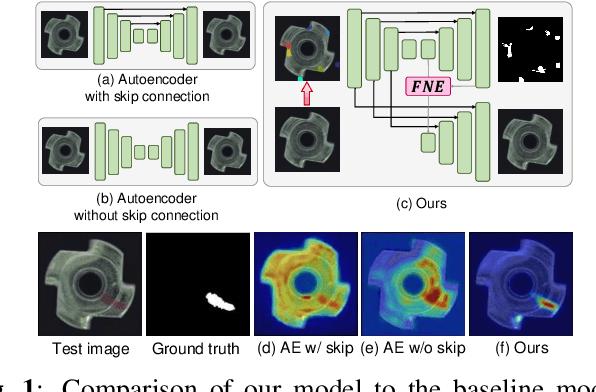
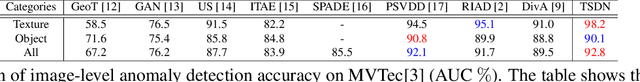
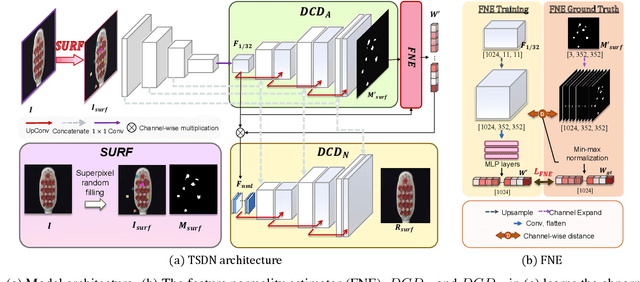
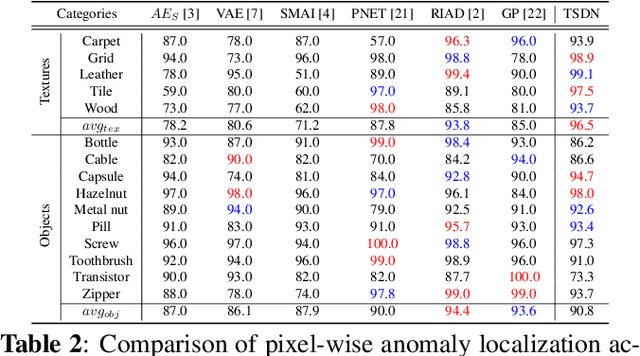
Abstract:Image reconstruction-based anomaly detection has recently been in the spotlight because of the difficulty of constructing anomaly datasets. These approaches work by learning to model normal features without seeing abnormal samples during training and then discriminating anomalies at test time based on the reconstructive errors. However, these models have limitations in reconstructing the abnormal samples due to their indiscriminate conveyance of features. Moreover, these approaches are not explicitly optimized for distinguishable anomalies. To address these problems, we propose a two-stream decoder network (TSDN), designed to learn both normal and abnormal features. Additionally, we propose a feature normality estimator (FNE) to eliminate abnormal features and prevent high-quality reconstruction of abnormal regions. Evaluation on a standard benchmark demonstrated performance better than state-of-the-art models.
Global-Local Aggregation with Deformable Point Sampling for Camouflaged Object Detection
Nov 22, 2022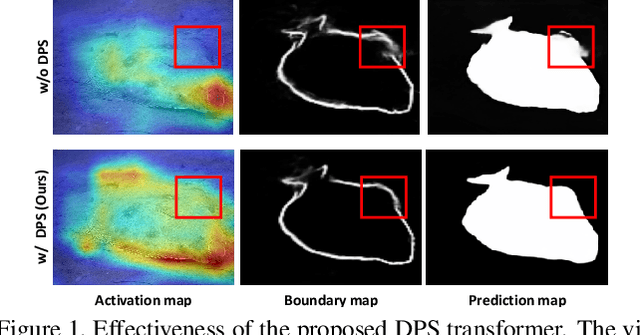
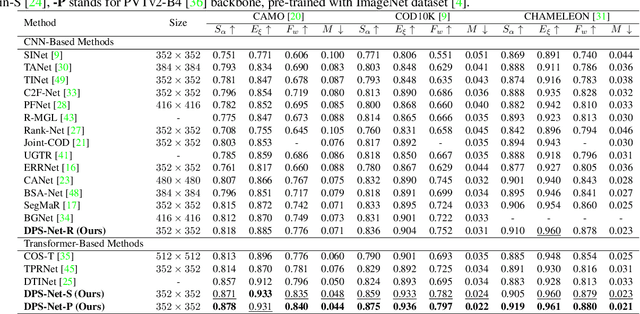
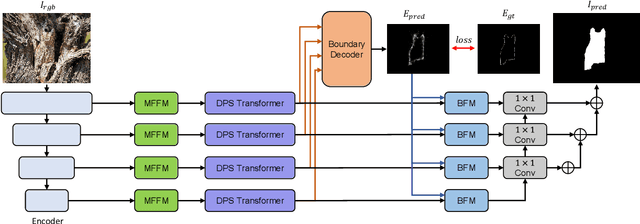
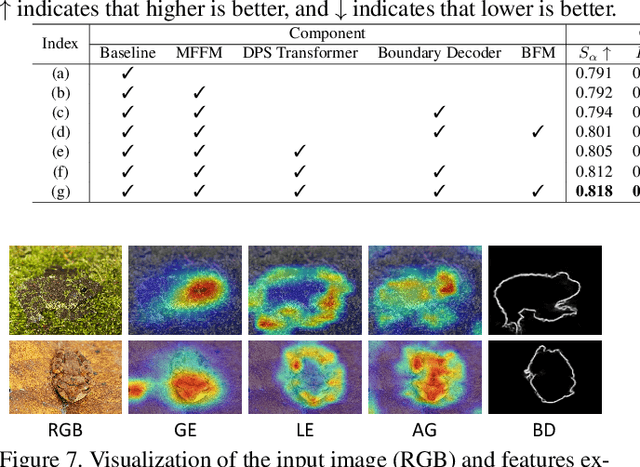
Abstract:The camouflaged object detection (COD) task aims to find and segment objects that have a color or texture that is very similar to that of the background. Despite the difficulties of the task, COD is attracting attention in medical, lifesaving, and anti-military fields. To overcome the difficulties of COD, we propose a novel global-local aggregation architecture with a deformable point sampling method. Further, we propose a global-local aggregation transformer that integrates an object's global information, background, and boundary local information, which is important in COD tasks. The proposed transformer obtains global information from feature channels and effectively extracts important local information from the subdivided patch using the deformable point sampling method. Accordingly, the model effectively integrates global and local information for camouflaged objects and also shows that important boundary information in COD can be efficiently utilized. Our method is evaluated on three popular datasets and achieves state-of-the-art performance. We prove the effectiveness of the proposed method through comparative experiments.
FAPM: Fast Adaptive Patch Memory for Real-time Industrial Anomaly Detection
Nov 14, 2022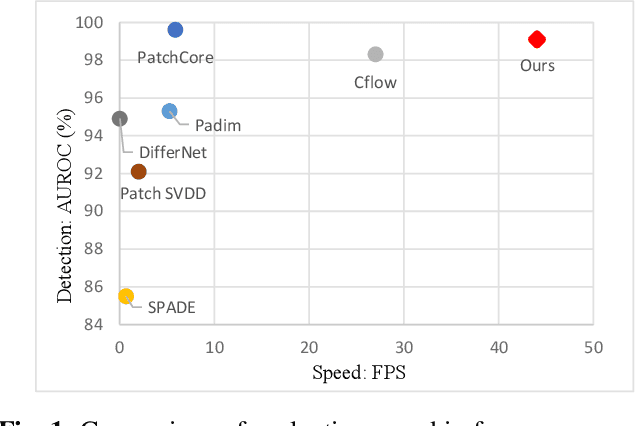
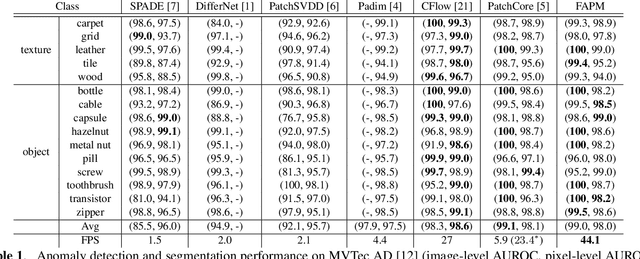
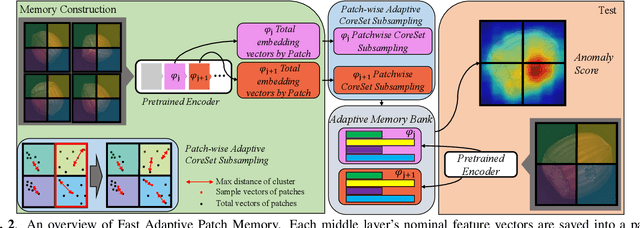
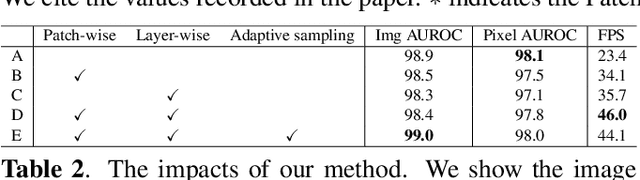
Abstract:Feature embedding-based methods have performed exceptionally well in detecting industrial anomalies by comparing the features of the target image and the normal image. However, such approaches do not consider the inference speed, which is as important as accuracy in real-world applications. To relieve this issue, we propose a method called fast adaptive patch memory (FAPM) for real-time industrial anomaly detection. FAPM consists of patch-wise and layer-wise memory banks that save the embedding features of images in patch-level and layer-level, eliminating unnecessary repeated calculations. We also propose patch-wise adaptive coreset sampling for fast and accurate detection. FAPM performs well for both accuracy and speed compared to other state-of-the-art methods.
Unsupervised Video Object Segmentation via Prototype Memory Network
Sep 08, 2022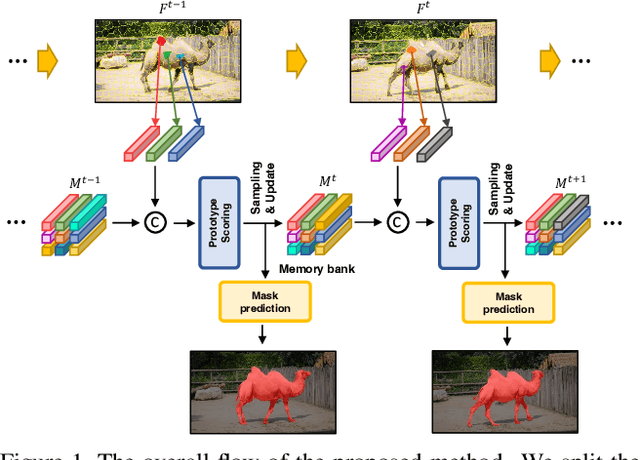
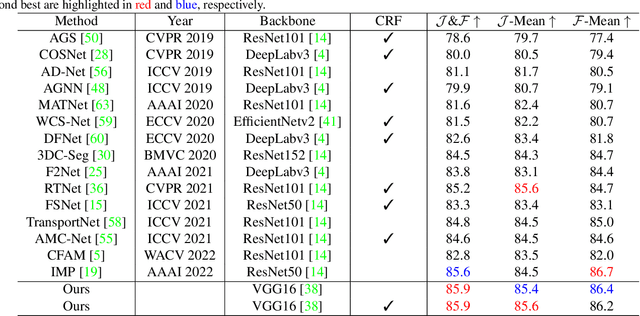
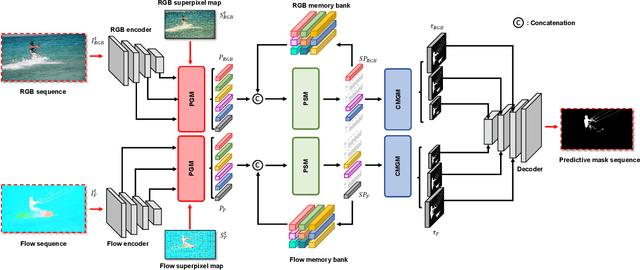
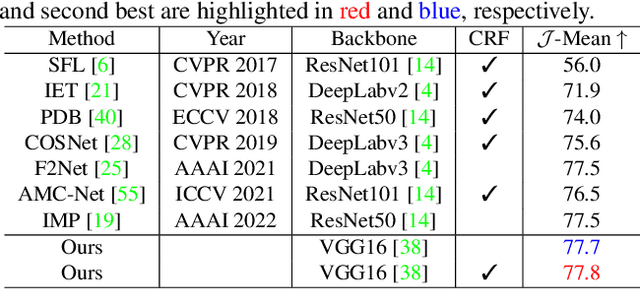
Abstract:Unsupervised video object segmentation aims to segment a target object in the video without a ground truth mask in the initial frame. This challenging task requires extracting features for the most salient common objects within a video sequence. This difficulty can be solved by using motion information such as optical flow, but using only the information between adjacent frames results in poor connectivity between distant frames and poor performance. To solve this problem, we propose a novel prototype memory network architecture. The proposed model effectively extracts the RGB and motion information by extracting superpixel-based component prototypes from the input RGB images and optical flow maps. In addition, the model scores the usefulness of the component prototypes in each frame based on a self-learning algorithm and adaptively stores the most useful prototypes in memory and discards obsolete prototypes. We use the prototypes in the memory bank to predict the next query frames mask, which enhances the association between distant frames to help with accurate mask prediction. Our method is evaluated on three datasets, achieving state-of-the-art performance. We prove the effectiveness of the proposed model with various ablation studies.
Treating Motion as Option to Reduce Motion Dependency in Unsupervised Video Object Segmentation
Sep 04, 2022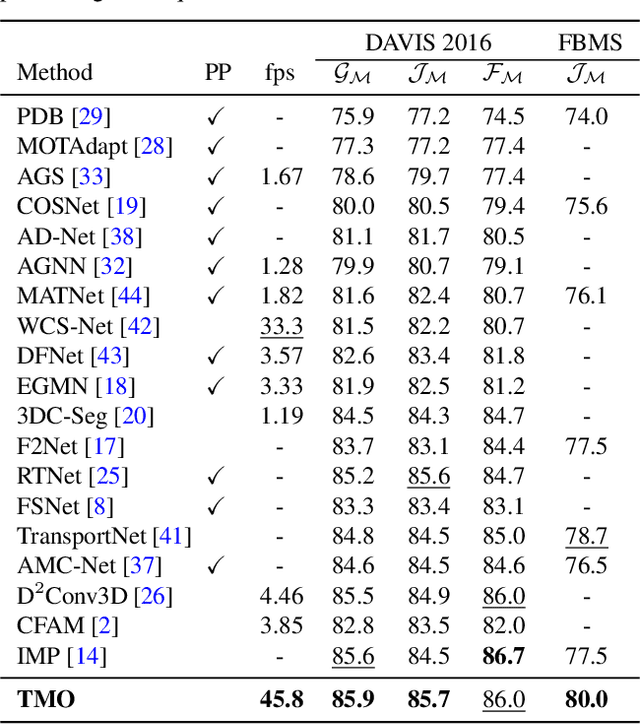
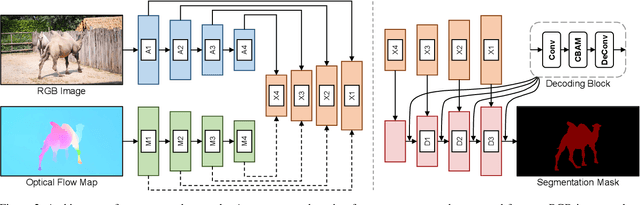
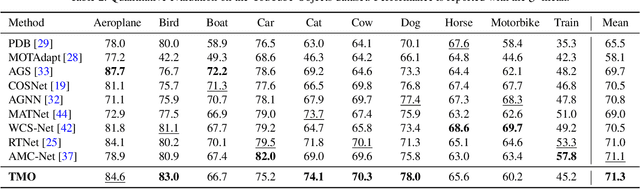

Abstract:Unsupervised video object segmentation (VOS) aims to detect the most salient object in a video sequence at the pixel level. In unsupervised VOS, most state-of-the-art methods leverage motion cues obtained from optical flow maps in addition to appearance cues to exploit the property that salient objects usually have distinctive movements compared to the background. However, as they are overly dependent on motion cues, which may be unreliable in some cases, they cannot achieve stable prediction. To reduce this motion dependency of existing two-stream VOS methods, we propose a novel motion-as-option network that optionally utilizes motion cues. Additionally, to fully exploit the property of the proposed network that motion is not always required, we introduce a collaborative network learning strategy. On all the public benchmark datasets, our proposed network affords state-of-the-art performance with real-time inference speed.
Pixel-Level Equalized Matching for Video Object Segmentation
Sep 04, 2022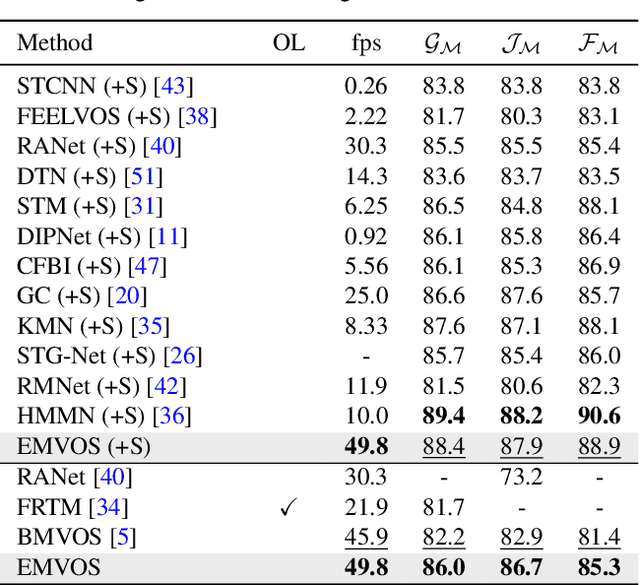
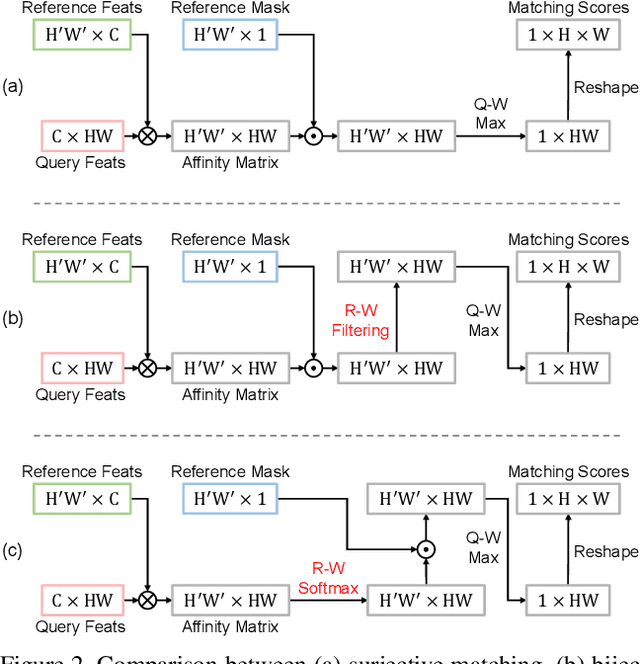
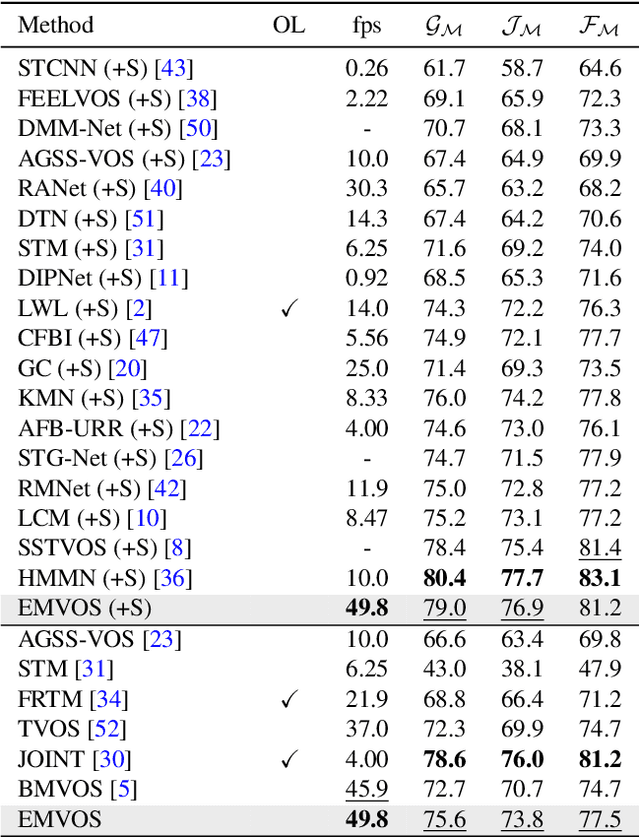
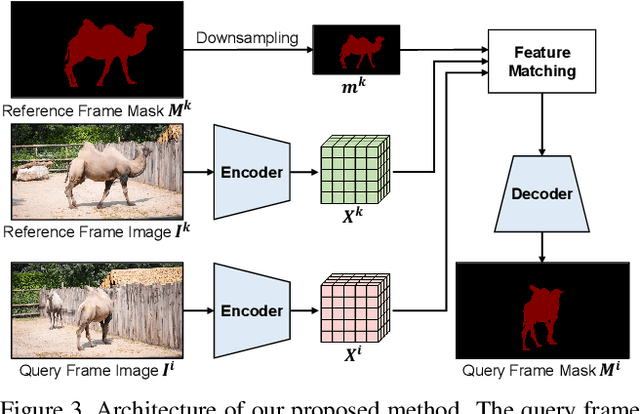
Abstract:Feature similarity matching, which transfers the information of the reference frame to the query frame, is a key component in semi-supervised video object segmentation. If surjective matching is adopted, background distractors can easily occur and degrade the performance. Bijective matching mechanisms try to prevent this by restricting the amount of information being transferred to the query frame, but have two limitations: 1) surjective matching cannot be fully leveraged as it is transformed to bijective matching at test time; and 2) test-time manual tuning is required for searching the optimal hyper-parameters. To overcome these limitations while ensuring reliable information transfer, we introduce an equalized matching mechanism. To prevent the reference frame information from being overly referenced, the potential contribution to the query frame is equalized by simply applying a softmax operation along with the query. On public benchmark datasets, our proposed approach achieves a comparable performance to state-of-the-art methods.
SPSN: Superpixel Prototype Sampling Network for RGB-D Salient Object Detection
Jul 16, 2022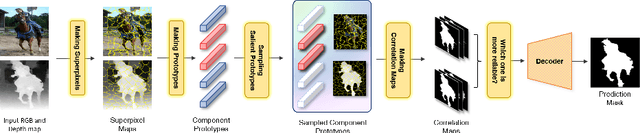
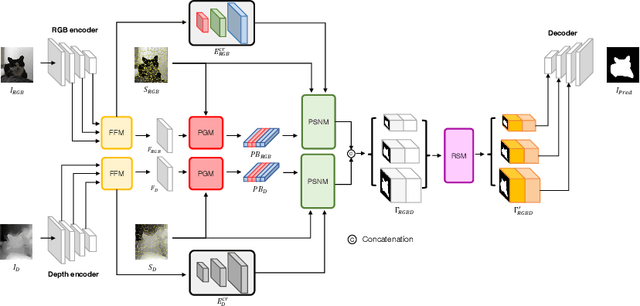
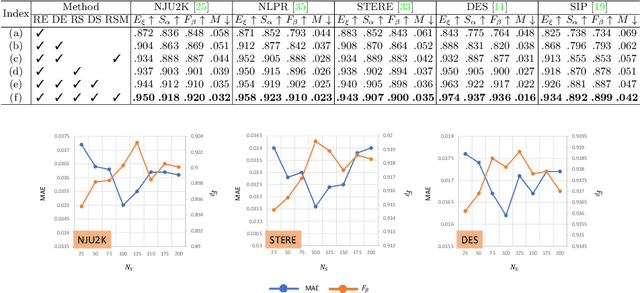
Abstract:RGB-D salient object detection (SOD) has been in the spotlight recently because it is an important preprocessing operation for various vision tasks. However, despite advances in deep learning-based methods, RGB-D SOD is still challenging due to the large domain gap between an RGB image and the depth map and low-quality depth maps. To solve this problem, we propose a novel superpixel prototype sampling network (SPSN) architecture. The proposed model splits the input RGB image and depth map into component superpixels to generate component prototypes. We design a prototype sampling network so that the network only samples prototypes corresponding to salient objects. In addition, we propose a reliance selection module to recognize the quality of each RGB and depth feature map and adaptively weight them in proportion to their reliability. The proposed method makes the model robust to inconsistencies between RGB images and depth maps and eliminates the influence of non-salient objects. Our method is evaluated on five popular datasets, achieving state-of-the-art performance. We prove the effectiveness of the proposed method through comparative experiments.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge