Chun-Te Chu
Distilling Vision-Language Models on Millions of Videos
Jan 11, 2024



Abstract:The recent advance in vision-language models is largely attributed to the abundance of image-text data. We aim to replicate this success for video-language models, but there simply is not enough human-curated video-text data available. We thus resort to fine-tuning a video-language model from a strong image-language baseline with synthesized instructional data. The resulting video-language model is then used to auto-label millions of videos to generate high-quality captions. We show the adapted video-language model performs well on a wide range of video-language benchmarks. For instance, it surpasses the best prior result on open-ended NExT-QA by 2.8%. Besides, our model generates detailed descriptions for previously unseen videos, which provide better textual supervision than existing methods. Experiments show that a video-language dual-encoder model contrastively trained on these auto-generated captions is 3.8% better than the strongest baseline that also leverages vision-language models. Our best model outperforms state-of-the-art methods on MSR-VTT zero-shot text-to-video retrieval by 6%.
BasisNet: Two-stage Model Synthesis for Efficient Inference
May 07, 2021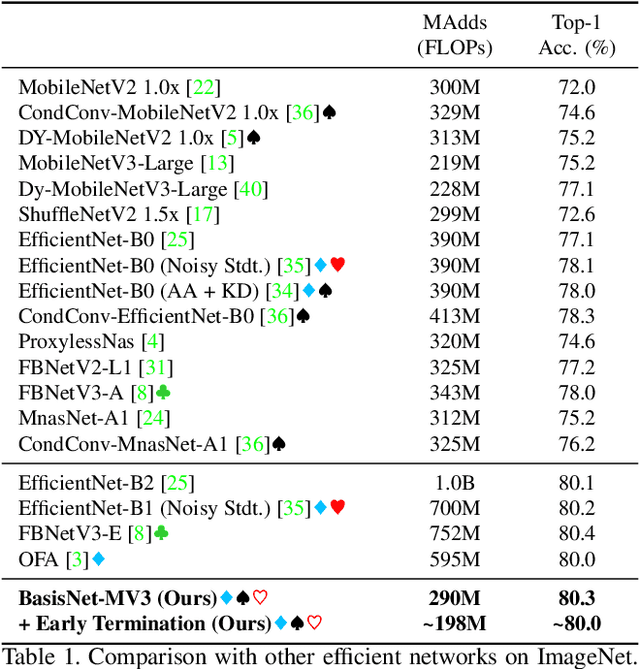
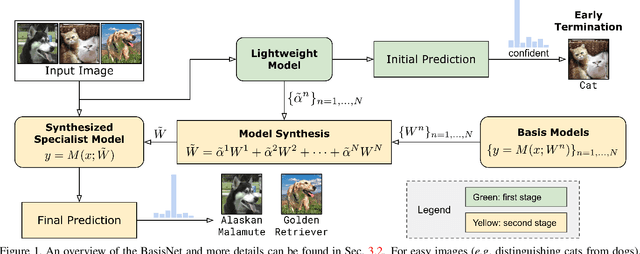
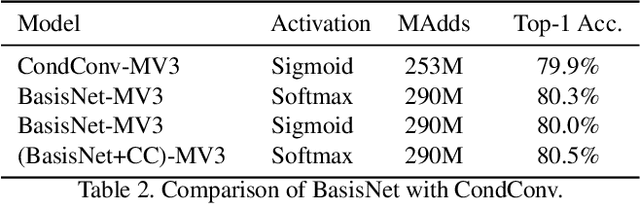
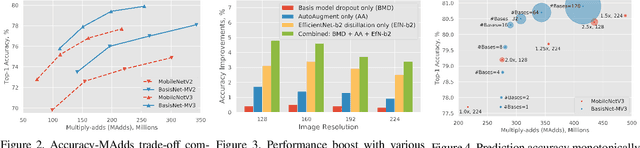
Abstract:In this work, we present BasisNet which combines recent advancements in efficient neural network architectures, conditional computation, and early termination in a simple new form. Our approach incorporates a lightweight model to preview the input and generate input-dependent combination coefficients, which later controls the synthesis of a more accurate specialist model to make final prediction. The two-stage model synthesis strategy can be applied to any network architectures and both stages are jointly trained. We also show that proper training recipes are critical for increasing generalizability for such high capacity neural networks. On ImageNet classification benchmark, our BasisNet with MobileNets as backbone demonstrated clear advantage on accuracy-efficiency trade-off over several strong baselines. Specifically, BasisNet-MobileNetV3 obtained 80.3% top-1 accuracy with only 290M Multiply-Add operations, halving the computational cost of previous state-of-the-art without sacrificing accuracy. With early termination, the average cost can be further reduced to 198M MAdds while maintaining accuracy of 80.0% on ImageNet.
Camera View Adjustment Prediction for Improving Image Composition
Apr 15, 2021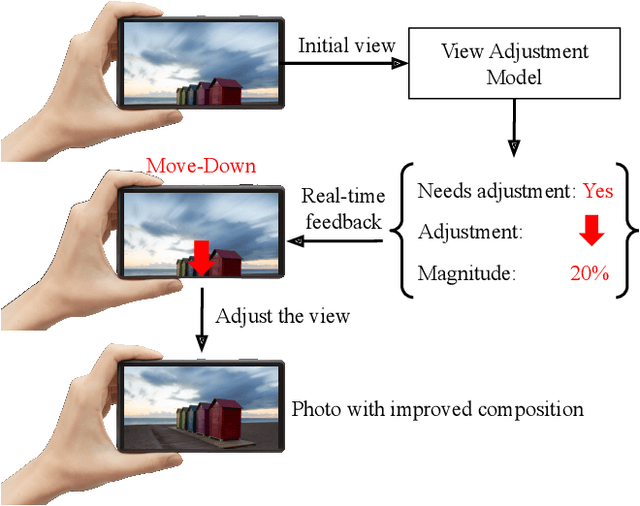
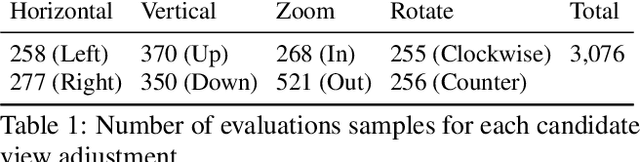

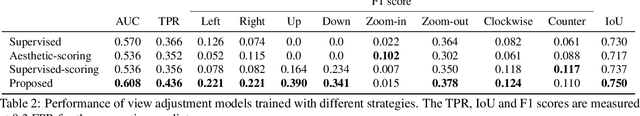
Abstract:Image composition plays an important role in the quality of a photo. However, not every camera user possesses the knowledge and expertise required for capturing well-composed photos. While post-capture cropping can improve the composition sometimes, it does not work in many common scenarios in which the photographer needs to adjust the camera view to capture the best shot. To address this issue, we propose a deep learning-based approach that provides suggestions to the photographer on how to adjust the camera view before capturing. By optimizing the composition before a photo is captured, our system helps photographers to capture better photos. As there is no publicly-available dataset for this task, we create a view adjustment dataset by repurposing existing image cropping datasets. Furthermore, we propose a two-stage semi-supervised approach that utilizes both labeled and unlabeled images for training a view adjustment model. Experiment results show that the proposed semi-supervised approach outperforms the corresponding supervised alternatives, and our user study results show that the suggested view adjustment improves image composition 79% of the time.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge