Christina Luong
Point Tracking as a Temporal Cue for Robust Myocardial Segmentation in Echocardiography Videos
Jan 14, 2026Abstract:Purpose: Myocardium segmentation in echocardiography videos is a challenging task due to low contrast, noise, and anatomical variability. Traditional deep learning models either process frames independently, ignoring temporal information, or rely on memory-based feature propagation, which accumulates error over time. Methods: We propose Point-Seg, a transformer-based segmentation framework that integrates point tracking as a temporal cue to ensure stable and consistent segmentation of myocardium across frames. Our method leverages a point-tracking module trained on a synthetic echocardiography dataset to track key anatomical landmarks across video sequences. These tracked trajectories provide an explicit motion-aware signal that guides segmentation, reducing drift and eliminating the need for memory-based feature accumulation. Additionally, we incorporate a temporal smoothing loss to further enhance temporal consistency across frames. Results: We evaluate our approach on both public and private echocardiography datasets. Experimental results demonstrate that Point-Seg has statistically similar accuracy in terms of Dice to state-of-the-art segmentation models in high quality echo data, while it achieves better segmentation accuracy in lower quality echo with improved temporal stability. Furthermore, Point-Seg has the key advantage of pixel-level myocardium motion information as opposed to other segmentation methods. Such information is essential in the computation of other downstream tasks such as myocardial strain measurement and regional wall motion abnormality detection. Conclusion: Point-Seg demonstrates that point tracking can serve as an effective temporal cue for consistent video segmentation, offering a reliable and generalizable approach for myocardium segmentation in echocardiography videos. The code is available at https://github.com/DeepRCL/PointSeg.
EchoAgent: Guideline-Centric Reasoning Agent for Echocardiography Measurement and Interpretation
Nov 17, 2025Abstract:Purpose: Echocardiographic interpretation requires video-level reasoning and guideline-based measurement analysis, which current deep learning models for cardiac ultrasound do not support. We present EchoAgent, a framework that enables structured, interpretable automation for this domain. Methods: EchoAgent orchestrates specialized vision tools under Large Language Model (LLM) control to perform temporal localization, spatial measurement, and clinical interpretation. A key contribution is a measurement-feasibility prediction model that determines whether anatomical structures are reliably measurable in each frame, enabling autonomous tool selection. We curated a benchmark of diverse, clinically validated video-query pairs for evaluation. Results: EchoAgent achieves accurate, interpretable results despite added complexity of spatiotemporal video analysis. Outputs are grounded in visual evidence and clinical guidelines, supporting transparency and traceability. Conclusion: This work demonstrates the feasibility of agentic, guideline-aligned reasoning for echocardiographic video analysis, enabled by task-specific tools and full video-level automation. EchoAgent sets a new direction for trustworthy AI in cardiac ultrasound.
ControlEchoSynth: Boosting Ejection Fraction Estimation Models via Controlled Video Diffusion
Aug 25, 2025



Abstract:Synthetic data generation represents a significant advancement in boosting the performance of machine learning (ML) models, particularly in fields where data acquisition is challenging, such as echocardiography. The acquisition and labeling of echocardiograms (echo) for heart assessment, crucial in point-of-care ultrasound (POCUS) settings, often encounter limitations due to the restricted number of echo views available, typically captured by operators with varying levels of experience. This study proposes a novel approach for enhancing clinical diagnosis accuracy by synthetically generating echo views. These views are conditioned on existing, real views of the heart, focusing specifically on the estimation of ejection fraction (EF), a critical parameter traditionally measured from biplane apical views. By integrating a conditional generative model, we demonstrate an improvement in EF estimation accuracy, providing a comparative analysis with traditional methods. Preliminary results indicate that our synthetic echoes, when used to augment existing datasets, not only enhance EF estimation but also show potential in advancing the development of more robust, accurate, and clinically relevant ML models. This approach is anticipated to catalyze further research in synthetic data applications, paving the way for innovative solutions in medical imaging diagnostics.
EchoGLAD: Hierarchical Graph Neural Networks for Left Ventricle Landmark Detection on Echocardiograms
Jul 23, 2023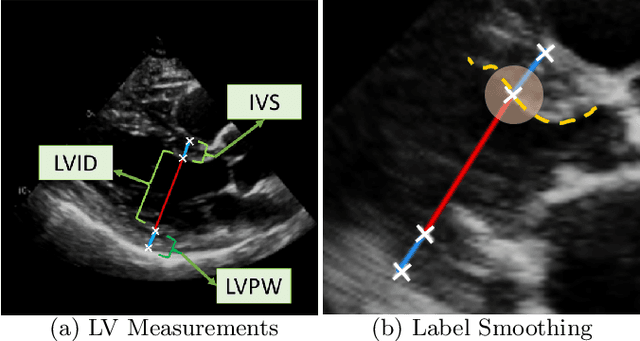
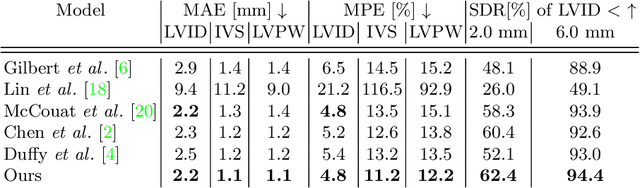
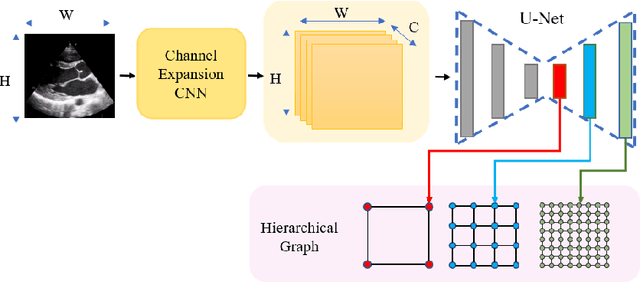
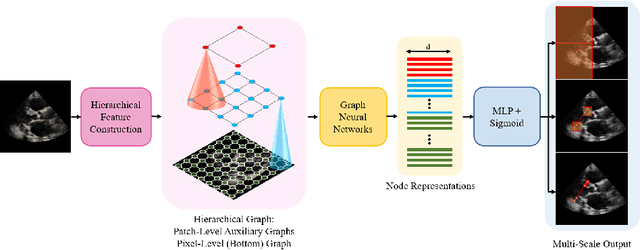
Abstract:The functional assessment of the left ventricle chamber of the heart requires detecting four landmark locations and measuring the internal dimension of the left ventricle and the approximate mass of the surrounding muscle. The key challenge of automating this task with machine learning is the sparsity of clinical labels, i.e., only a few landmark pixels in a high-dimensional image are annotated, leading many prior works to heavily rely on isotropic label smoothing. However, such a label smoothing strategy ignores the anatomical information of the image and induces some bias. To address this challenge, we introduce an echocardiogram-based, hierarchical graph neural network (GNN) for left ventricle landmark detection (EchoGLAD). Our main contributions are: 1) a hierarchical graph representation learning framework for multi-resolution landmark detection via GNNs; 2) induced hierarchical supervision at different levels of granularity using a multi-level loss. We evaluate our model on a public and a private dataset under the in-distribution (ID) and out-of-distribution (OOD) settings. For the ID setting, we achieve the state-of-the-art mean absolute errors (MAEs) of 1.46 mm and 1.86 mm on the two datasets. Our model also shows better OOD generalization than prior works with a testing MAE of 4.3 mm.
Echo-SyncNet: Self-supervised Cardiac View Synchronization in Echocardiography
Feb 03, 2021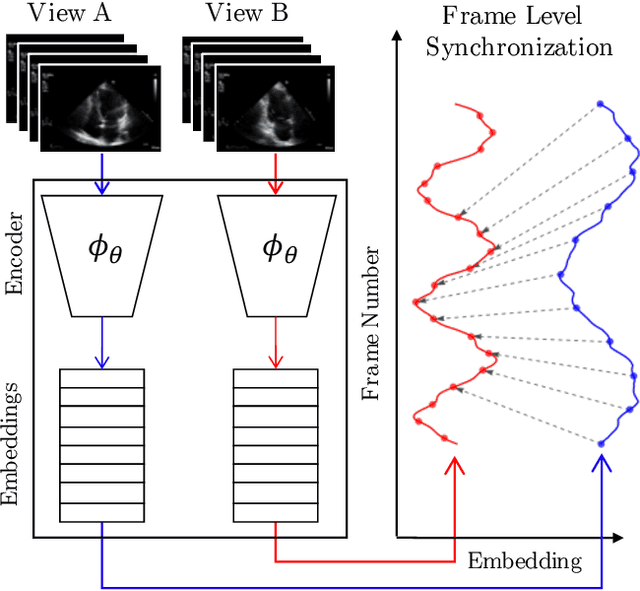
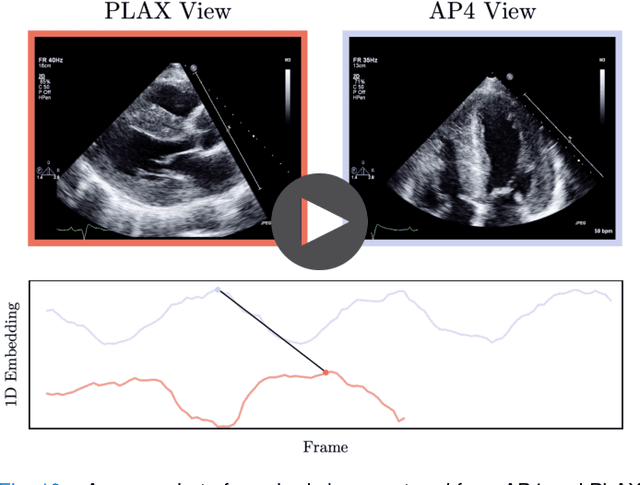
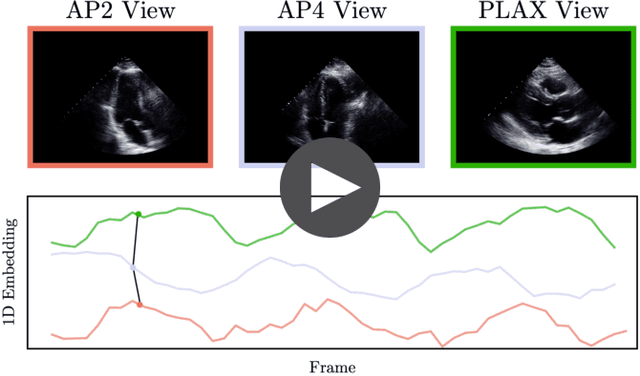
Abstract:In echocardiography (echo), an electrocardiogram (ECG) is conventionally used to temporally align different cardiac views for assessing critical measurements. However, in emergencies or point-of-care situations, acquiring an ECG is often not an option, hence motivating the need for alternative temporal synchronization methods. Here, we propose Echo-SyncNet, a self-supervised learning framework to synchronize various cross-sectional 2D echo series without any external input. The proposed framework takes advantage of both intra-view and inter-view self supervisions. The former relies on spatiotemporal patterns found between the frames of a single echo cine and the latter on the interdependencies between multiple cines. The combined supervisions are used to learn a feature-rich embedding space where multiple echo cines can be temporally synchronized. We evaluate the framework with multiple experiments: 1) Using data from 998 patients, Echo-SyncNet shows promising results for synchronizing Apical 2 chamber and Apical 4 chamber cardiac views; 2) Using data from 3070 patients, our experiments reveal that the learned representations of Echo-SyncNet outperform a supervised deep learning method that is optimized for automatic detection of fine-grained cardiac phase; 3) We show the usefulness of the learned representations in a one-shot learning scenario of cardiac keyframe detection. Without any fine-tuning, keyframes in 1188 validation patient studies are identified by synchronizing them with only one labeled reference study. We do not make any prior assumption about what specific cardiac views are used for training and show that Echo-SyncNet can accurately generalize to views not present in its training set. Project repository: github.com/fatemehtd/Echo-SyncNet.
U-LanD: Uncertainty-Driven Video Landmark Detection
Feb 02, 2021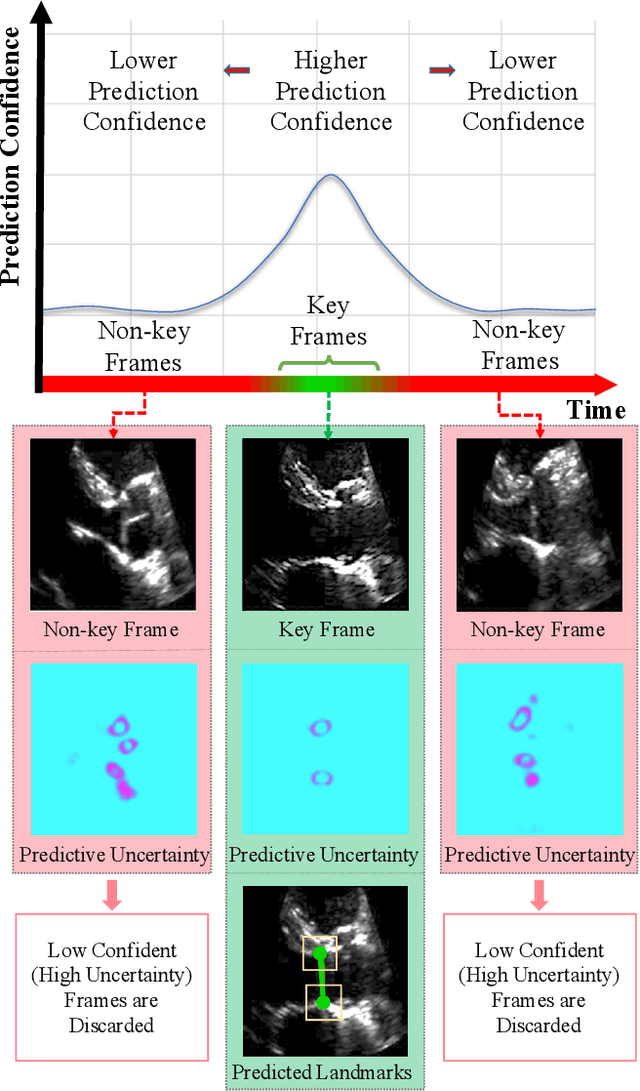
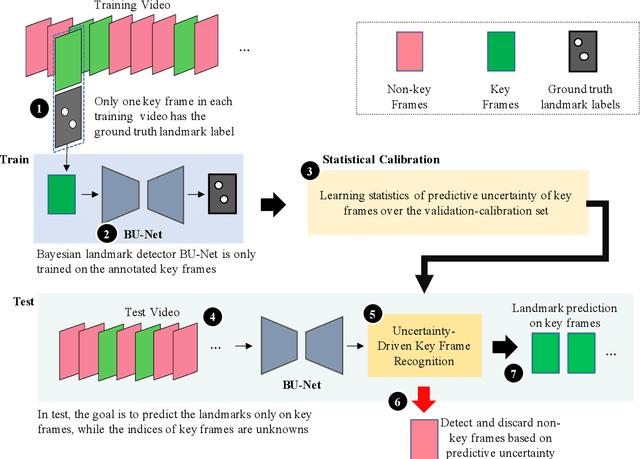
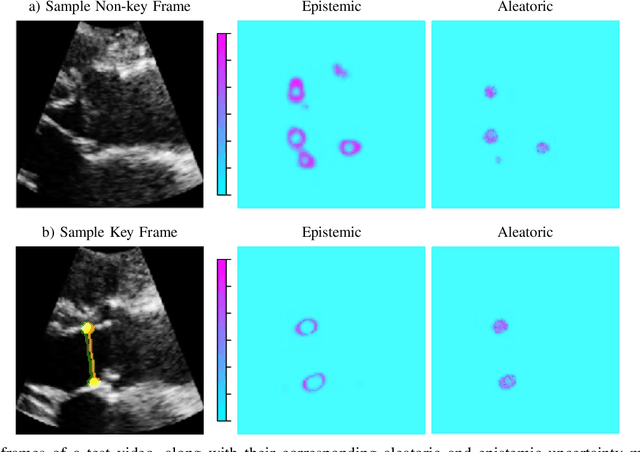
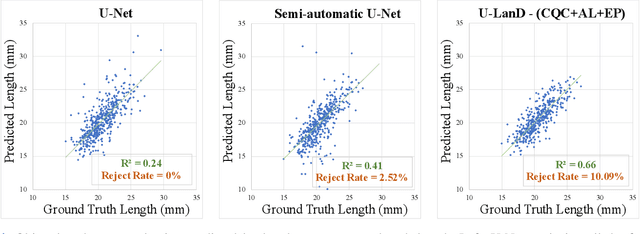
Abstract:This paper presents U-LanD, a framework for joint detection of key frames and landmarks in videos. We tackle a specifically challenging problem, where training labels are noisy and highly sparse. U-LanD builds upon a pivotal observation: a deep Bayesian landmark detector solely trained on key video frames, has significantly lower predictive uncertainty on those frames vs. other frames in videos. We use this observation as an unsupervised signal to automatically recognize key frames on which we detect landmarks. As a test-bed for our framework, we use ultrasound imaging videos of the heart, where sparse and noisy clinical labels are only available for a single frame in each video. Using data from 4,493 patients, we demonstrate that U-LanD can exceedingly outperform the state-of-the-art non-Bayesian counterpart by a noticeable absolute margin of 42% in R2 score, with almost no overhead imposed on the model size. Our approach is generic and can be potentially applied to other challenging data with noisy and sparse training labels.
Reciprocal Landmark Detection and Tracking with Extremely Few Annotations
Jan 27, 2021



Abstract:Localization of anatomical landmarks to perform two-dimensional measurements in echocardiography is part of routine clinical workflow in cardiac disease diagnosis. Automatic localization of those landmarks is highly desirable to improve workflow and reduce interobserver variability. Training a machine learning framework to perform such localization is hindered given the sparse nature of gold standard labels; only few percent of cardiac cine series frames are normally manually labeled for clinical use. In this paper, we propose a new end-to-end reciprocal detection and tracking model that is specifically designed to handle the sparse nature of echocardiography labels. The model is trained using few annotated frames across the entire cardiac cine sequence to generate consistent detection and tracking of landmarks, and an adversarial training for the model is proposed to take advantage of these annotated frames. The superiority of the proposed reciprocal model is demonstrated using a series of experiments.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge