Christian M. Meyer
Empowering Active Learning to Jointly Optimize System and User Demands
May 12, 2020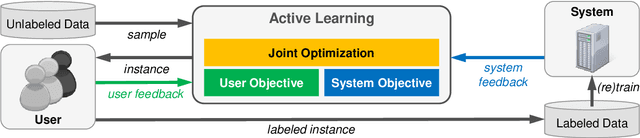
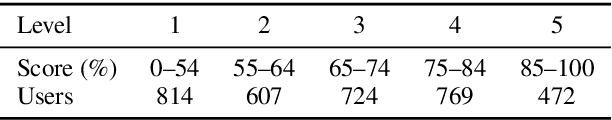
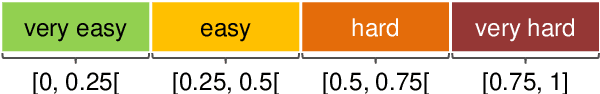
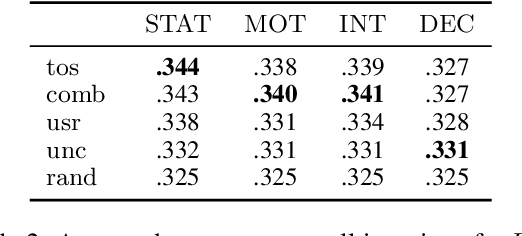
Abstract:Existing approaches to active learning maximize the system performance by sampling unlabeled instances for annotation that yield the most efficient training. However, when active learning is integrated with an end-user application, this can lead to frustration for participating users, as they spend time labeling instances that they would not otherwise be interested in reading. In this paper, we propose a new active learning approach that jointly optimizes the seemingly counteracting objectives of the active learning system (training efficiently) and the user (receiving useful instances). We study our approach in an educational application, which particularly benefits from this technique as the system needs to rapidly learn to predict the appropriateness of an exercise to a particular user, while the users should receive only exercises that match their skills. We evaluate multiple learning strategies and user types with data from real users and find that our joint approach better satisfies both objectives when alternative methods lead to many unsuitable exercises for end users.
When is ACL's Deadline? A Scientific Conversational Agent
Nov 23, 2019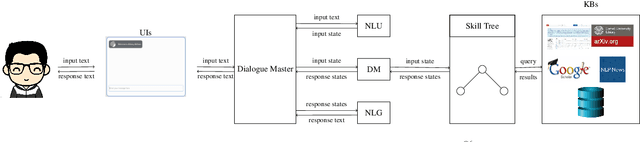

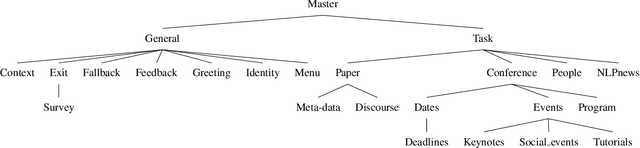
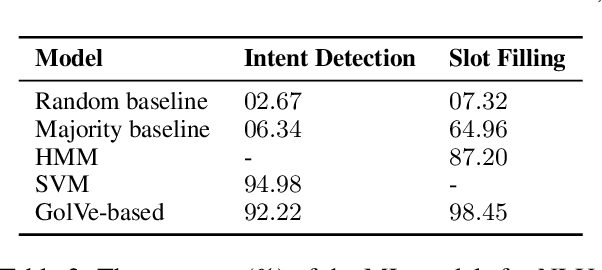
Abstract:Our conversational agent UKP-ATHENA assists NLP researchers in finding and exploring scientific literature, identifying relevant authors, planning or post-processing conference visits, and preparing paper submissions using a unified interface based on natural language inputs and responses. UKP-ATHENA enables new access paths to our swiftly evolving research area with its massive amounts of scientific information and high turnaround times. UKP-ATHENA's responses connect information from multiple heterogeneous sources which researchers currently have to explore manually one after another. Unlike a search engine, UKP-ATHENA maintains the context of a conversation to allow for efficient information access on papers, researchers, and conferences. Our architecture consists of multiple components with reference implementations that can be easily extended by new skills and domains. Our user-based evaluation shows that UKP-ATHENA already responds 45% of different formulations of defined intents with 37% information coverage rate.
MoverScore: Text Generation Evaluating with Contextualized Embeddings and Earth Mover Distance
Sep 26, 2019



Abstract:A robust evaluation metric has a profound impact on the development of text generation systems. A desirable metric compares system output against references based on their semantics rather than surface forms. In this paper we investigate strategies to encode system and reference texts to devise a metric that shows a high correlation with human judgment of text quality. We validate our new metric, namely MoverScore, on a number of text generation tasks including summarization, machine translation, image captioning, and data-to-text generation, where the outputs are produced by a variety of neural and non-neural systems. Our findings suggest that metrics combining contextualized representations with a distance measure perform the best. Such metrics also demonstrate strong generalization capability across tasks. For ease-of-use we make our metrics available as web service.
Better Rewards Yield Better Summaries: Learning to Summarise Without References
Sep 03, 2019



Abstract:Reinforcement Learning (RL) based document summarisation systems yield state-of-the-art performance in terms of ROUGE scores, because they directly use ROUGE as the rewards during training. However, summaries with high ROUGE scores often receive low human judgement. To find a better reward function that can guide RL to generate human-appealing summaries, we learn a reward function from human ratings on 2,500 summaries. Our reward function only takes the document and system summary as input. Hence, once trained, it can be used to train RL-based summarisation systems without using any reference summaries. We show that our learned rewards have significantly higher correlation with human ratings than previous approaches. Human evaluation experiments show that, compared to the state-of-the-art supervised-learning systems and ROUGE-as-rewards RL summarisation systems, the RL systems using our learned rewards during training generate summarieswith higher human ratings. The learned reward function and our source code are available at https://github.com/yg211/summary-reward-no-reference.
FAMULUS: Interactive Annotation and Feedback Generation for Teaching Diagnostic Reasoning
Aug 29, 2019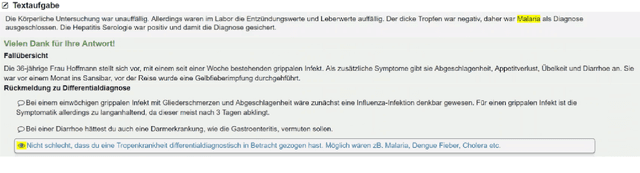

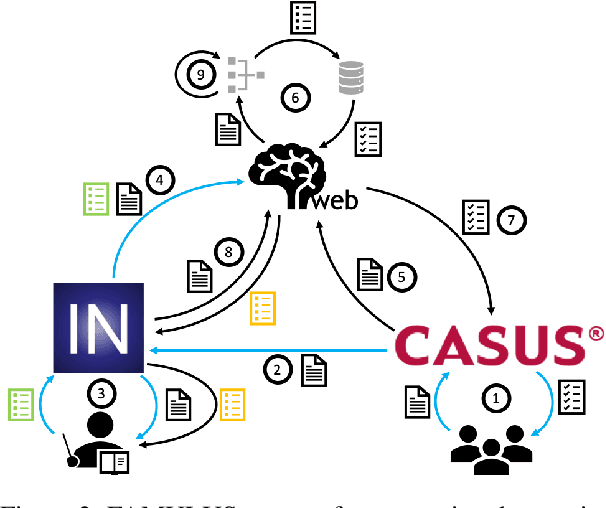
Abstract:Our proposed system FAMULUS helps students learn to diagnose based on automatic feedback in virtual patient simulations, and it supports instructors in labeling training data. Diagnosing is an exceptionally difficult skill to obtain but vital for many different professions (e.g., medical doctors, teachers). Previous case simulation systems are limited to multiple-choice questions and thus cannot give constructive individualized feedback on a student's diagnostic reasoning process. Given initially only limited data, we leverage a (replaceable) NLP model to both support experts in their further data annotation with automatic suggestions, and we provide automatic feedback for students. We argue that because the central model consistently improves, our interactive approach encourages both students and instructors to recurrently use the tool, and thus accelerate the speed of data creation and annotation. We show results from two user studies on diagnostic reasoning in medicine and teacher education and outline how our system can be extended to further use cases.
Reward Learning for Efficient Reinforcement Learning in Extractive Document Summarisation
Jul 30, 2019



Abstract:Document summarisation can be formulated as a sequential decision-making problem, which can be solved by Reinforcement Learning (RL) algorithms. The predominant RL paradigm for summarisation learns a cross-input policy, which requires considerable time, data and parameter tuning due to the huge search spaces and the delayed rewards. Learning input-specific RL policies is a more efficient alternative but so far depends on handcrafted rewards, which are difficult to design and yield poor performance. We propose RELIS, a novel RL paradigm that learns a reward function with Learning-to-Rank (L2R) algorithms at training time and uses this reward function to train an input-specific RL policy at test time. We prove that RELIS guarantees to generate near-optimal summaries with appropriate L2R and RL algorithms. Empirically, we evaluate our approach on extractive multi-document summarisation. We show that RELIS reduces the training time by two orders of magnitude compared to the state-of-the-art models while performing on par with them.
Manipulating the Difficulty of C-Tests
Jul 02, 2019



Abstract:We propose two novel manipulation strategies for increasing and decreasing the difficulty of C-tests automatically. This is a crucial step towards generating learner-adaptive exercises for self-directed language learning and preparing language assessment tests. To reach the desired difficulty level, we manipulate the size and the distribution of gaps based on absolute and relative gap difficulty predictions. We evaluate our approach in corpus-based experiments and in a user study with 60 participants. We find that both strategies are able to generate C-tests with the desired difficulty level.
Preference-based Interactive Multi-Document Summarisation
Jun 07, 2019



Abstract:Interactive NLP is a promising paradigm to close the gap between automatic NLP systems and the human upper bound. Preference-based interactive learning has been successfully applied, but the existing methods require several thousand interaction rounds even in simulations with perfect user feedback. In this paper, we study preference-based interactive summarisation. To reduce the number of interaction rounds, we propose the Active Preference-based ReInforcement Learning (APRIL) framework. APRIL uses Active Learning to query the user, Preference Learning to learn a summary ranking function from the preferences, and neural Reinforcement Learning to efficiently search for the (near-)optimal summary. Our results show that users can easily provide reliable preferences over summaries and that APRIL outperforms the state-of-the-art preference-based interactive method in both simulation and real-user experiments.
Analysis of Automatic Annotation Suggestions for Hard Discourse-Level Tasks in Expert Domains
Jun 06, 2019
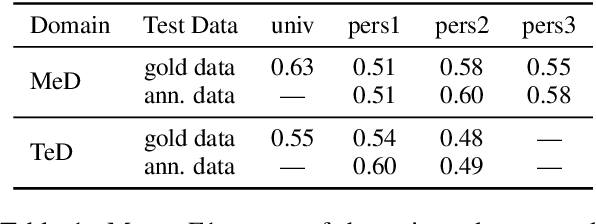
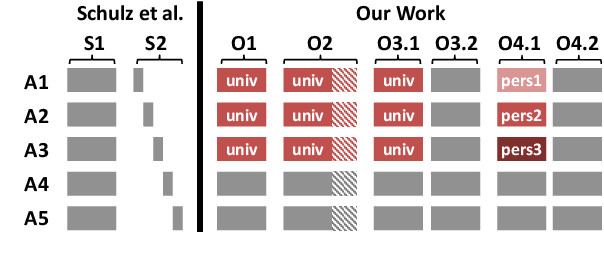
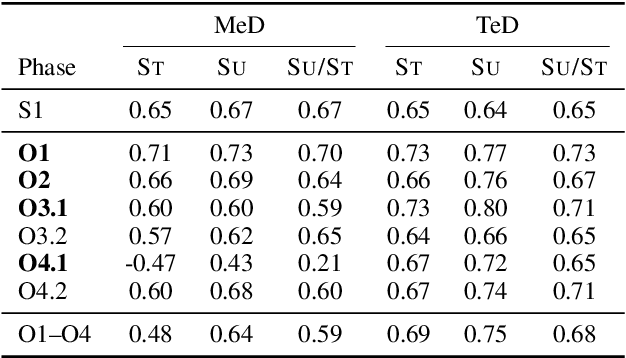
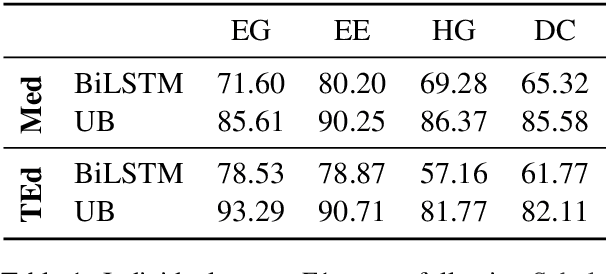
Abstract:Many complex discourse-level tasks can aid domain experts in their work but require costly expert annotations for data creation. To speed up and ease annotations, we investigate the viability of automatically generated annotation suggestions for such tasks. As an example, we choose a task that is particularly hard for both humans and machines: the segmentation and classification of epistemic activities in diagnostic reasoning texts. We create and publish a new dataset covering two domains and carefully analyse the suggested annotations. We find that suggestions have positive effects on annotation speed and performance, while not introducing noteworthy biases. Envisioning suggestion models that improve with newly annotated texts, we contrast methods for continuous model adjustment and suggest the most effective setup for suggestions in future expert tasks.
Challenges in the Automatic Analysis of Students' Diagnostic Reasoning
Nov 26, 2018
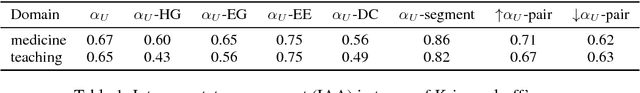

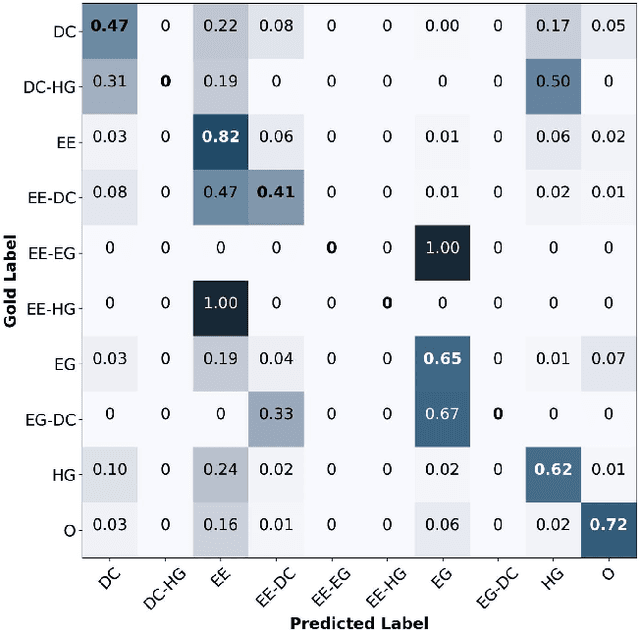
Abstract:Diagnostic reasoning is a key component of many professions. To improve students' diagnostic reasoning skills, educational psychologists analyse and give feedback on epistemic activities used by these students while diagnosing, in particular, hypothesis generation, evidence generation, evidence evaluation, and drawing conclusions. However, this manual analysis is highly time-consuming. We aim to enable the large-scale adoption of diagnostic reasoning analysis and feedback by automating the epistemic activity identification. We create the first corpus for this task, comprising diagnostic reasoning self-explanations of students from two domains annotated with epistemic activities. Based on insights from the corpus creation and the task's characteristics, we discuss three challenges for the automatic identification of epistemic activities using AI methods: the correct identification of epistemic activity spans, the reliable distinction of similar epistemic activities, and the detection of overlapping epistemic activities. We propose a separate performance metric for each challenge and thus provide an evaluation framework for future research. Indeed, our evaluation of various state-of-the-art recurrent neural network architectures reveals that current techniques fail to address some of these challenges.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge