Cheng Yin
Navigating Open Set Scenarios for Skeleton-based Action Recognition
Dec 11, 2023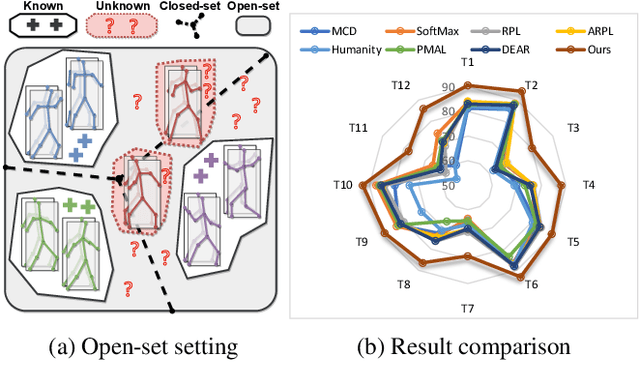
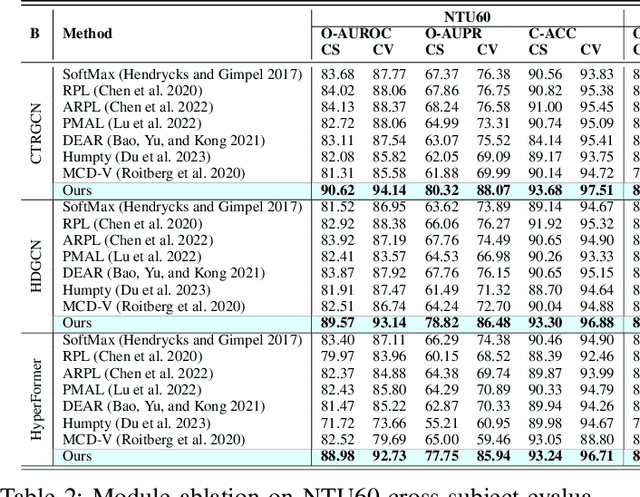
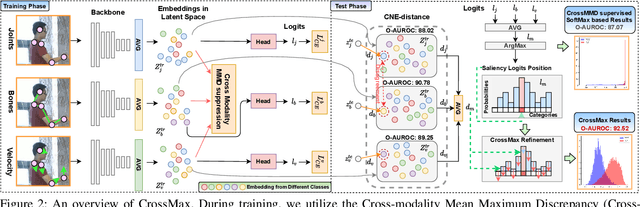
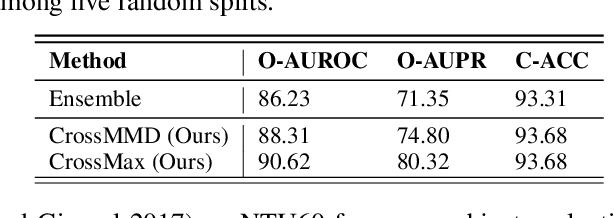
Abstract:In real-world scenarios, human actions often fall outside the distribution of training data, making it crucial for models to recognize known actions and reject unknown ones. However, using pure skeleton data in such open-set conditions poses challenges due to the lack of visual background cues and the distinct sparse structure of body pose sequences. In this paper, we tackle the unexplored Open-Set Skeleton-based Action Recognition (OS-SAR) task and formalize the benchmark on three skeleton-based datasets. We assess the performance of seven established open-set approaches on our task and identify their limits and critical generalization issues when dealing with skeleton information. To address these challenges, we propose a distance-based cross-modality ensemble method that leverages the cross-modal alignment of skeleton joints, bones, and velocities to achieve superior open-set recognition performance. We refer to the key idea as CrossMax - an approach that utilizes a novel cross-modality mean max discrepancy suppression mechanism to align latent spaces during training and a cross-modality distance-based logits refinement method during testing. CrossMax outperforms existing approaches and consistently yields state-of-the-art results across all datasets and backbones. The benchmark, code, and models will be released at https://github.com/KPeng9510/OS-SAR.
A Method to Improve the Performance of Reinforcement Learning Based on the Y Operator for a Class of Stochastic Differential Equation-Based Child-Mother Systems
Nov 07, 2023


Abstract:This paper introduces a novel operator, termed the Y operator, to elevate control performance in Actor-Critic(AC) based reinforcement learning for systems governed by stochastic differential equations(SDEs). The Y operator ingeniously integrates the stochasticity of a class of child-mother system into the Critic network's loss function, yielding substantial advancements in the control performance of RL algorithms.Additionally, the Y operator elegantly reformulates the challenge of solving partial differential equations for the state-value function into a parallel problem for the drift and diffusion functions within the system's SDEs.A rigorous mathematical proof confirms the operator's validity.This transformation enables the Y Operator-based Reinforcement Learning(YORL) framework to efficiently tackle optimal control problems in both model-based and data-driven systems.The superiority of YORL is demonstrated through linear and nonlinear numerical examples showing its enhanced performance over existing methods post convergence.
Deep Reinforcement Learning for Intelligent Reflecting Surface-assisted D2D Communications
Aug 06, 2021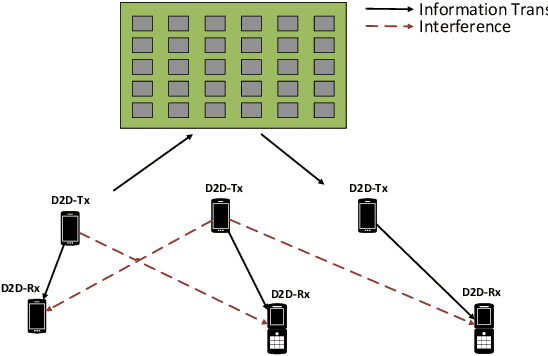

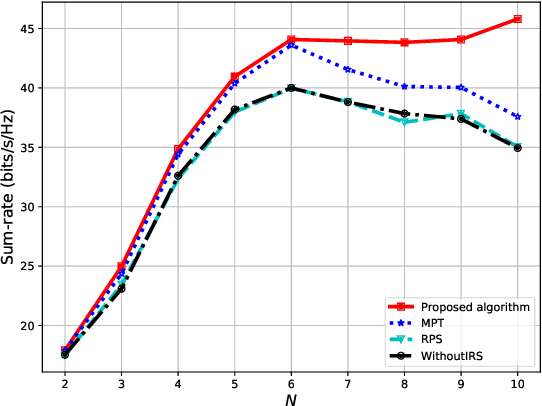
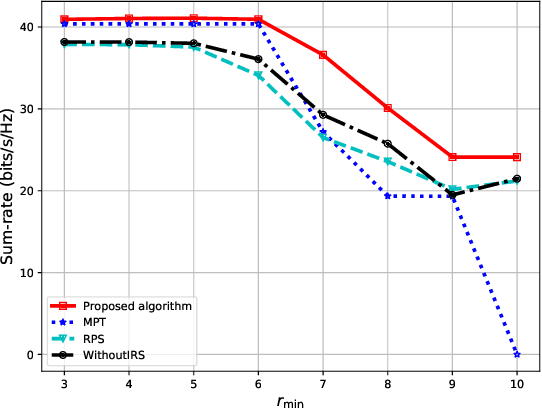
Abstract:In this paper, we propose a deep reinforcement learning (DRL) approach for solving the optimisation problem of the network's sum-rate in device-to-device (D2D) communications supported by an intelligent reflecting surface (IRS). The IRS is deployed to mitigate the interference and enhance the signal between the D2D transmitter and the associated D2D receiver. Our objective is to jointly optimise the transmit power at the D2D transmitter and the phase shift matrix at the IRS to maximise the network sum-rate. We formulate a Markov decision process and then propose the proximal policy optimisation for solving the maximisation game. Simulation results show impressive performance in terms of the achievable rate and processing time.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge