Long D. Nguyen
MAGPrompt: Message-Adaptive Graph Prompt Tuning for Graph Neural Networks
Feb 05, 2026Abstract:Pre-trained graph neural networks (GNNs) transfer well, but adapting them to downstream tasks remains challenging due to mismatches between pre-training objectives and task requirements. Graph prompt tuning offers a parameter-efficient alternative to fine-tuning, yet most methods only modify inputs or representations and leave message passing unchanged, limiting their ability to adapt neighborhood interactions. We propose message-adaptive graph prompt tuning, which injects learnable prompts into the message passing step to reweight incoming neighbor messages and add task-specific prompt vectors during message aggregation, while keeping the backbone GNN frozen. The approach is compatible with common GNN backbones and pre-training strategies, and applicable across downstream settings. Experiments on diverse node- and graph-level datasets show consistent gains over prior graph prompting methods in few-shot settings, while achieving performance competitive with fine-tuning in full-shot regimes.
Topology-Aware Multiscale Mixture of Experts for Efficient Molecular Property Prediction
Jan 19, 2026Abstract:Many molecular properties depend on 3D geometry, where non-covalent interactions, stereochemical effects, and medium- to long-range forces are determined by spatial distances and angles that cannot be uniquely captured by a 2D bond graph. Yet most 3D molecular graph neural networks still rely on globally fixed neighborhood heuristics, typically defined by distance cutoffs and maximum neighbor limits, to define local message-passing neighborhoods, leading to rigid, data-agnostic interaction budgets. We propose Multiscale Interaction Mixture of Experts (MI-MoE) to adapt interaction modeling across geometric regimes. Our contributions are threefold: (1) we introduce a distance-cutoff expert ensemble that explicitly captures short-, mid-, and long-range interactions without committing to a single cutoff; (2) we design a topological gating encoder that routes inputs to experts using filtration-based descriptors, including persistent homology features, summarizing how connectivity evolves across radii; and (3) we show that MI-MoE is a plug-in module that consistently improves multiple strong 3D molecular backbones across diverse molecular and polymer property prediction benchmark datasets, covering both regression and classification tasks. These results highlight topology-aware multiscale routing as an effective principle for 3D molecular graph learning.
Deep Reinforcement Learning for Intelligent Reflecting Surface-assisted D2D Communications
Aug 06, 2021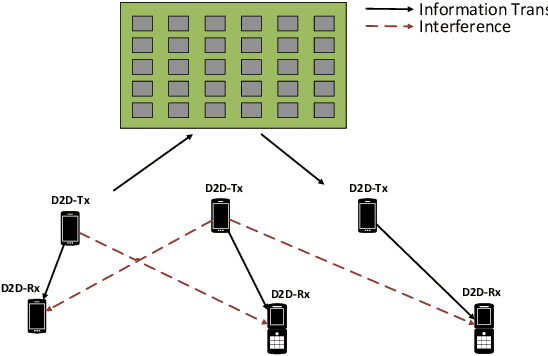

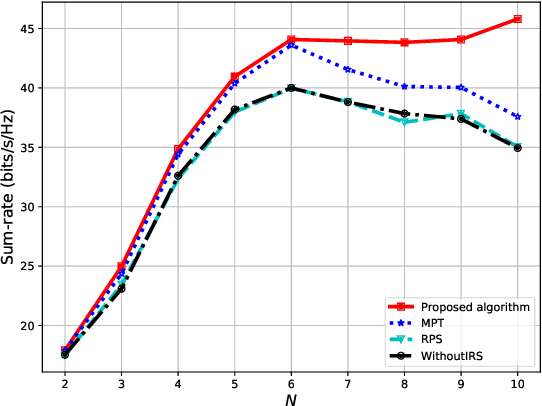
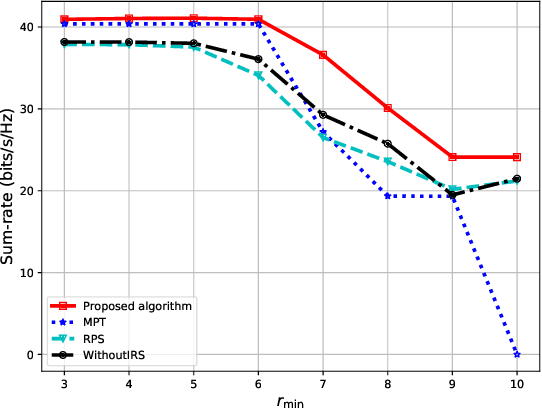
Abstract:In this paper, we propose a deep reinforcement learning (DRL) approach for solving the optimisation problem of the network's sum-rate in device-to-device (D2D) communications supported by an intelligent reflecting surface (IRS). The IRS is deployed to mitigate the interference and enhance the signal between the D2D transmitter and the associated D2D receiver. Our objective is to jointly optimise the transmit power at the D2D transmitter and the phase shift matrix at the IRS to maximise the network sum-rate. We formulate a Markov decision process and then propose the proximal policy optimisation for solving the maximisation game. Simulation results show impressive performance in terms of the achievable rate and processing time.
Intelligent Reconfigurable Surface-assisted Multi-UAV Networks: Efficient Resource Allocation with Deep Reinforcement Learning
May 28, 2021



Abstract:In this paper, we propose intelligent reconfigurable surface (IRS)-assisted unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) networks that can utilise both advantages of agility and reflection for enhancing the network's performance. To aim at maximising the energy efficiency (EE) of the considered networks, we jointly optimise the power allocation of the UAVs and the phaseshift matrix of the IRS. A deep reinforcement learning (DRL) approach is proposed for solving the continuous optimisation problem with time-varying channel gain in a centralised fashion. Moreover, a parallel learning approach is also proposed for reducing the information transmission requirement of the centralised approach. Numerical results show a significant improvement of our proposed schemes compared with the conventional approaches in terms of EE, flexibility, and processing time. Our proposed DRL methods for IRS-assisted UAV networks can be used for real-time applications due to their capability of instant decision-making and handling the time-varying channel with the dynamic environmental setting.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge