Cheng Xiang
EPSegFZ: Efficient Point Cloud Semantic Segmentation for Few- and Zero-Shot Scenarios with Language Guidance
Nov 12, 2025Abstract:Recent approaches for few-shot 3D point cloud semantic segmentation typically require a two-stage learning process, i.e., a pre-training stage followed by a few-shot training stage. While effective, these methods face overreliance on pre-training, which hinders model flexibility and adaptability. Some models tried to avoid pre-training yet failed to capture ample information. In addition, current approaches focus on visual information in the support set and neglect or do not fully exploit other useful data, such as textual annotations. This inadequate utilization of support information impairs the performance of the model and restricts its zero-shot ability. To address these limitations, we present a novel pre-training-free network, named Efficient Point Cloud Semantic Segmentation for Few- and Zero-shot scenarios. Our EPSegFZ incorporates three key components. A Prototype-Enhanced Registers Attention (ProERA) module and a Dual Relative Positional Encoding (DRPE)-based cross-attention mechanism for improved feature extraction and accurate query-prototype correspondence construction without pre-training. A Language-Guided Prototype Embedding (LGPE) module that effectively leverages textual information from the support set to improve few-shot performance and enable zero-shot inference. Extensive experiments show that our method outperforms the state-of-the-art method by 5.68% and 3.82% on the S3DIS and ScanNet benchmarks, respectively.
SingRef6D: Monocular Novel Object Pose Estimation with a Single RGB Reference
Sep 26, 2025Abstract:Recent 6D pose estimation methods demonstrate notable performance but still face some practical limitations. For instance, many of them rely heavily on sensor depth, which may fail with challenging surface conditions, such as transparent or highly reflective materials. In the meantime, RGB-based solutions provide less robust matching performance in low-light and texture-less scenes due to the lack of geometry information. Motivated by these, we propose SingRef6D, a lightweight pipeline requiring only a single RGB image as a reference, eliminating the need for costly depth sensors, multi-view image acquisition, or training view synthesis models and neural fields. This enables SingRef6D to remain robust and capable even under resource-limited settings where depth or dense templates are unavailable. Our framework incorporates two key innovations. First, we propose a token-scaler-based fine-tuning mechanism with a novel optimization loss on top of Depth-Anything v2 to enhance its ability to predict accurate depth, even for challenging surfaces. Our results show a 14.41% improvement (in $\delta_{1.05}$) on REAL275 depth prediction compared to Depth-Anything v2 (with fine-tuned head). Second, benefiting from depth availability, we introduce a depth-aware matching process that effectively integrates spatial relationships within LoFTR, enabling our system to handle matching for challenging materials and lighting conditions. Evaluations of pose estimation on the REAL275, ClearPose, and Toyota-Light datasets show that our approach surpasses state-of-the-art methods, achieving a 6.1% improvement in average recall.
WiFo-CF: Wireless Foundation Model for CSI Feedback
Aug 06, 2025Abstract:Deep learning-based channel state information (CSI) feedback schemes demonstrate strong compression capabilities but are typically constrained to fixed system configurations, limiting their generalization and flexibility. To address this challenge, WiFo-CF, a novel wireless foundation model tailored for CSI feedback, is proposed, uniquely accommodating heterogeneous configurations such as varying channel dimensions, feedback rates, and data distributions within a unified framework through its key innovations: (1) a multi-user, multi-rate self-supervised pre-training strategy; and (2) a Mixture of Shared and Routed Expert (S-R MoE) architecture. Supporting the large-scale pre-training of WiFo-CF is the first heterogeneous channel feedback dataset, whose diverse patterns enable the model to achieve superior performance on both in-distribution and out-of-distribution data across simulated and real-world scenarios. Furthermore, the learned representations effectively facilitate adaptation to downstream tasks such as CSI-based indoor localization, validating WiFo-CF's scalability and deployment potential.
Evolving R2 to R2+: Optimal, Delayed Line-of-sight Vector-based Path Planning
May 08, 2024



Abstract:A vector-based any-angle path planner, R2, is evolved in to R2+ in this paper. By delaying line-of-sight, R2 and R2+ search times are largely unaffected by the distance between the start and goal points, but are exponential in the worst case with respect to the number of collisions during searches. To improve search times, additional discarding conditions in the overlap rule are introduced in R2+. In addition, R2+ resolves interminable chases in R2 by replacing ad hoc points with limited occupied-sector traces from target nodes, and simplifies R2 by employing new abstract structures and ensuring target progression during a trace. R2+ preserves the speed of R2 when paths are expected to detour around few obstacles, and searches significantly faster than R2 in maps with many disjoint obstacles.
Practical Battery Health Monitoring using Uncertainty-Aware Bayesian Neural Network
Apr 20, 2024



Abstract:Battery health monitoring and prediction are critically important in the era of electric mobility with a huge impact on safety, sustainability, and economic aspects. Existing research often focuses on prediction accuracy but tends to neglect practical factors that may hinder the technology's deployment in real-world applications. In this paper, we address these practical considerations and develop models based on the Bayesian neural network for predicting battery end-of-life. Our models use sensor data related to battery health and apply distributions, rather than single-point, for each parameter of the models. This allows the models to capture the inherent randomness and uncertainty of battery health, which leads to not only accurate predictions but also quantifiable uncertainty. We conducted an experimental study and demonstrated the effectiveness of our proposed models, with a prediction error rate averaging 13.9%, and as low as 2.9% for certain tested batteries. Additionally, all predictions include quantifiable certainty, which improved by 66% from the initial to the mid-life stage of the battery. This research has practical values for battery technologies and contributes to accelerating the technology adoption in the industry.
BatSort: Enhanced Battery Classification with Transfer Learning for Battery Sorting and Recycling
Apr 08, 2024



Abstract:Battery recycling is a critical process for minimizing environmental harm and resource waste for used batteries. However, it is challenging, largely because sorting batteries is costly and hardly automated to group batteries based on battery types. In this paper, we introduce a machine learning-based approach for battery-type classification and address the daunting problem of data scarcity for the application. We propose BatSort which applies transfer learning to utilize the existing knowledge optimized with large-scale datasets and customizes ResNet to be specialized for classifying battery types. We collected our in-house battery-type dataset of small-scale to guide the knowledge transfer as a case study and evaluate the system performance. We conducted an experimental study and the results show that BatSort can achieve outstanding accuracy of 92.1% on average and up to 96.2% and the performance is stable for battery-type classification. Our solution helps realize fast and automated battery sorting with minimized cost and can be transferred to related industry applications with insufficient data.
Few-Shot Point Cloud Semantic Segmentation via Contrastive Self-Supervision and Multi-Resolution Attention
Feb 21, 2023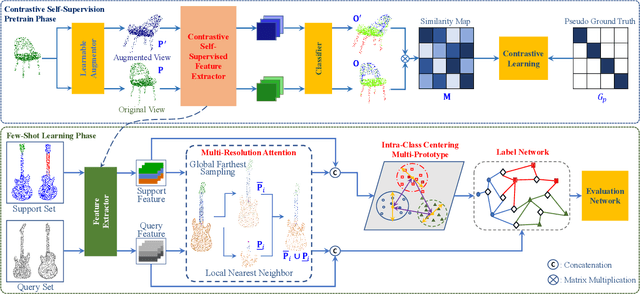
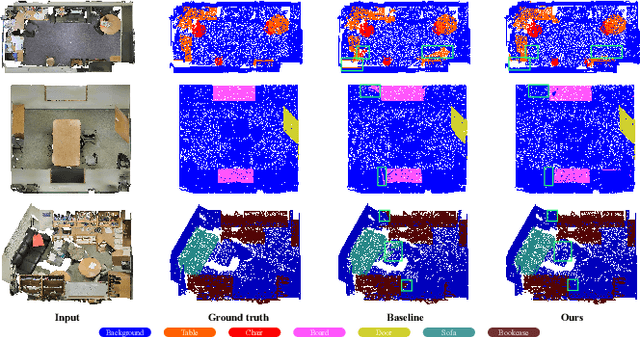
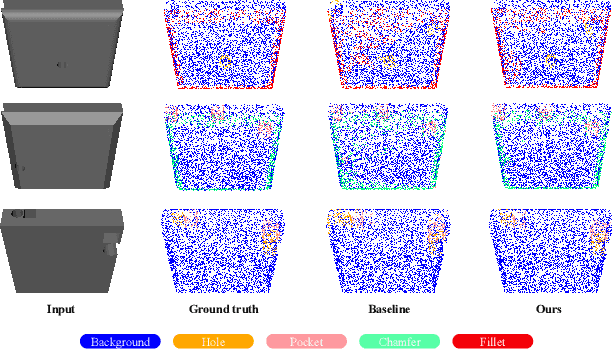
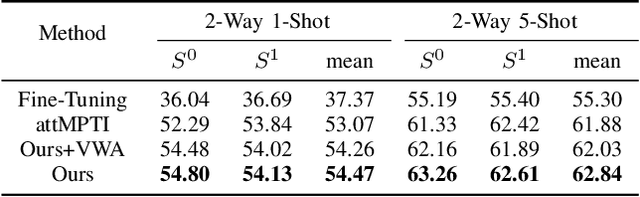
Abstract:This paper presents an effective few-shot point cloud semantic segmentation approach for real-world applications. Existing few-shot segmentation methods on point cloud heavily rely on the fully-supervised pretrain with large annotated datasets, which causes the learned feature extraction bias to those pretrained classes. However, as the purpose of few-shot learning is to handle unknown/unseen classes, such class-specific feature extraction in pretrain is not ideal to generalize into new classes for few-shot learning. Moreover, point cloud datasets hardly have a large number of classes due to the annotation difficulty. To address these issues, we propose a contrastive self-supervision framework for few-shot learning pretrain, which aims to eliminate the feature extraction bias through class-agnostic contrastive supervision. Specifically, we implement a novel contrastive learning approach with a learnable augmentor for a 3D point cloud to achieve point-wise differentiation, so that to enhance the pretrain with managed overfitting through the self-supervision. Furthermore, we develop a multi-resolution attention module using both the nearest and farthest points to extract the local and global point information more effectively, and a center-concentrated multi-prototype is adopted to mitigate the intra-class sparsity. Comprehensive experiments are conducted to evaluate the proposed approach, which shows our approach achieves state-of-the-art performance. Moreover, a case study on practical CAM/CAD segmentation is presented to demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach for real-world applications.
R2: Heuristic Bug-Based Any-angle Path-Planning using Lazy Searches
Jun 28, 2022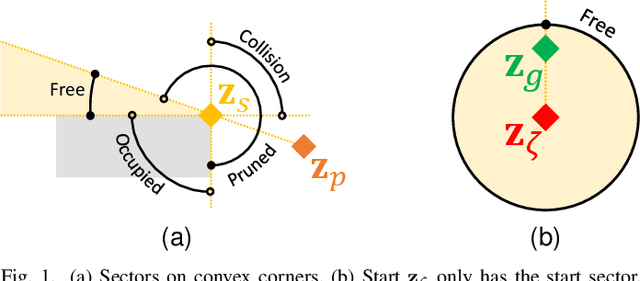
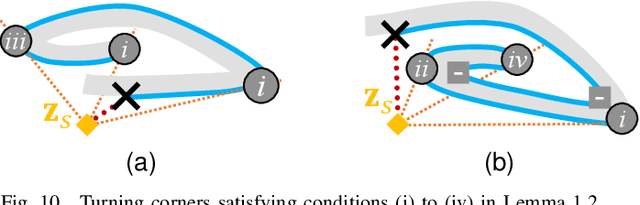
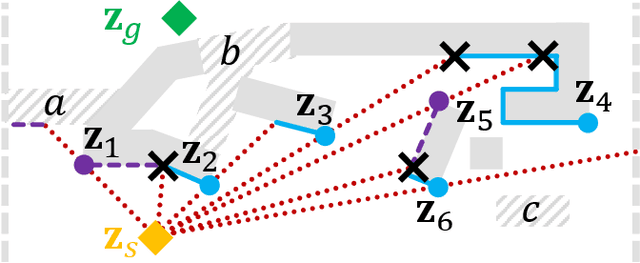
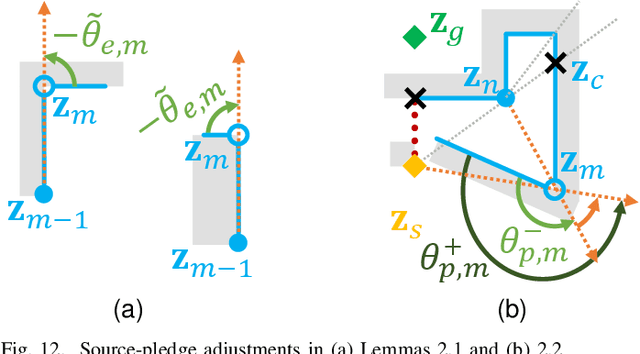
Abstract:R2 is a novel online any-angle path planner that uses heuristic bug-based or ray casting approaches to find optimal paths in 2D maps with non-convex, polygonal obstacles. R2 is competitive to traditional free-space planners, finding paths quickly if queries have direct line-of-sight. On large sparse maps with few obstacle contours, which are likely to occur in practice, R2 outperforms free-space planners, and can be much faster than state-of-the-art free-space expansion planner Anya. On maps with many contours, Anya performs faster than R2. R2 is built on RayScan, introducing lazy-searches and a source-pledge counter to find successors optimistically on contiguous contours. The novel approach bypasses most successors on jagged contours to reduce expensive line-of-sight checks, therefore requiring no pre-processing to be a competitive online any-angle planner.
Incremental Few-Shot Learning via Implanting and Compressing
Apr 07, 2022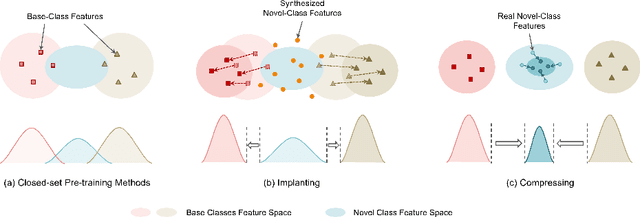
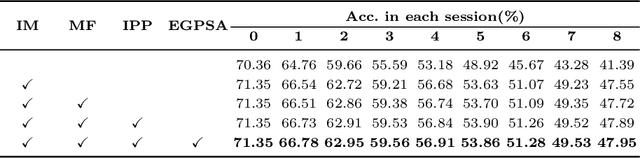
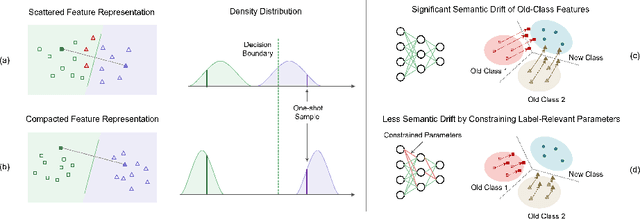
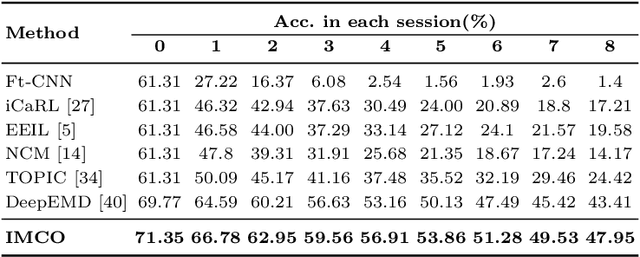
Abstract:This work focuses on tackling the challenging but realistic visual task of Incremental Few-Shot Learning (IFSL), which requires a model to continually learn novel classes from only a few examples while not forgetting the base classes on which it was pre-trained. Our study reveals that the challenges of IFSL lie in both inter-class separation and novel-class representation. Dur to intra-class variation, a novel class may implicitly leverage the knowledge from multiple base classes to construct its feature representation. Hence, simply reusing the pre-trained embedding space could lead to a scattered feature distribution and result in category confusion. To address such issues, we propose a two-step learning strategy referred to as \textbf{Im}planting and \textbf{Co}mpressing (\textbf{IMCO}), which optimizes both feature space partition and novel class reconstruction in a systematic manner. Specifically, in the \textbf{Implanting} step, we propose to mimic the data distribution of novel classes with the assistance of data-abundant base set, so that a model could learn semantically-rich features that are beneficial for discriminating between the base and other unseen classes. In the \textbf{Compressing} step, we adapt the feature extractor to precisely represent each novel class for enhancing intra-class compactness, together with a regularized parameter updating rule for preventing aggressive model updating. Finally, we demonstrate that IMCO outperforms competing baselines with a significant margin, both in image classification task and more challenging object detection task.
Towards Generalized and Incremental Few-Shot Object Detection
Sep 23, 2021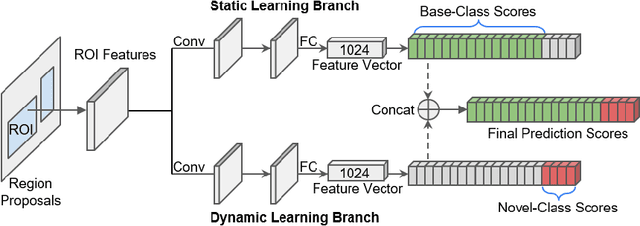
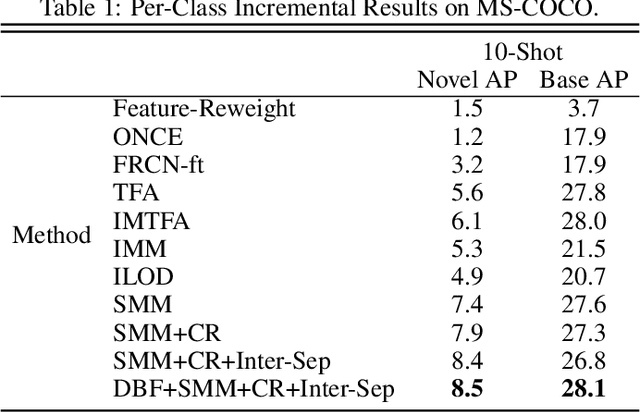
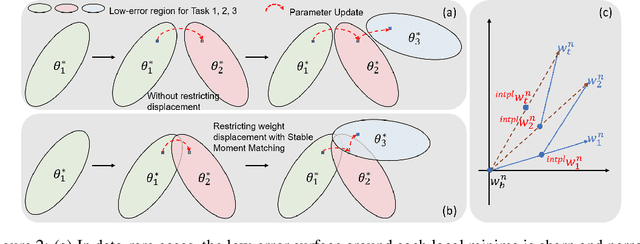
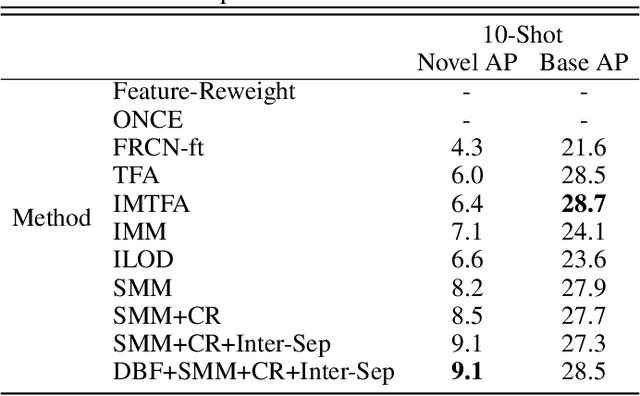
Abstract:Real-world object detection is highly desired to be equipped with the learning expandability that can enlarge its detection classes incrementally. Moreover, such learning from only few annotated training samples further adds the flexibility for the object detector, which is highly expected in many applications such as autonomous driving, robotics, etc. However, such sequential learning scenario with few-shot training samples generally causes catastrophic forgetting and dramatic overfitting. In this paper, to address the above incremental few-shot learning issues, a novel Incremental Few-Shot Object Detection (iFSOD) method is proposed to enable the effective continual learning from few-shot samples. Specifically, a Double-Branch Framework (DBF) is proposed to decouple the feature representation of base and novel (few-shot) class, which facilitates both the old-knowledge retention and new-class adaption simultaneously. Furthermore, a progressive model updating rule is carried out to preserve the long-term memory on old classes effectively when adapt to sequential new classes. Moreover, an inter-task class separation loss is proposed to extend the decision region of new-coming classes for better feature discrimination. We conduct experiments on both Pascal VOC and MS-COCO, which demonstrate that our method can effectively solve the problem of incremental few-shot detection and significantly improve the detection accuracy on both base and novel classes.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge