Changpeng Yang
SSL: Sweet Spot Learning for Differentiated Guidance in Agentic Optimization
Jan 30, 2026Abstract:Reinforcement learning with verifiable rewards has emerged as a powerful paradigm for training intelligent agents. However, existing methods typically employ binary rewards that fail to capture quality differences among trajectories achieving identical outcomes, thereby overlooking potential diversity within the solution space. Inspired by the ``sweet spot'' concept in tennis-the racket's core region that produces optimal hitting effects, we introduce \textbf{S}weet \textbf{S}pot \textbf{L}earning (\textbf{SSL}), a novel framework that provides differentiated guidance for agent optimization. SSL follows a simple yet effective principle: progressively amplified, tiered rewards guide policies toward the sweet-spot region of the solution space. This principle naturally adapts across diverse tasks: visual perception tasks leverage distance-tiered modeling to reward proximity, while complex reasoning tasks reward incremental progress toward promising solutions. We theoretically demonstrate that SSL preserves optimal solution ordering and enhances the gradient signal-to-noise ratio, thereby fostering more directed optimization. Extensive experiments across GUI perception, short/long-term planning, and complex reasoning tasks show consistent improvements over strong baselines on 12 benchmarks, achieving up to 2.5X sample efficiency gains and effective cross-task transferability. Our work establishes SSL as a general principle for training capable and robust agents.
Spark: Strategic Policy-Aware Exploration via Dynamic Branching for Long-Horizon Agentic Learning
Jan 28, 2026Abstract:Reinforcement learning has empowered large language models to act as intelligent agents, yet training them for long-horizon tasks remains challenging due to the scarcity of high-quality trajectories, especially under limited resources. Existing methods typically scale up rollout sizes and indiscriminately allocate computational resources among intermediate steps. Such attempts inherently waste substantial computation budget on trivial steps while failing to guarantee sample quality. To address this, we propose \textbf{Spark} (\textbf{S}trategic \textbf{P}olicy-\textbf{A}ware explo\textbf{R}ation via \textbf{K}ey-state dynamic branching), a novel framework that selectively branches at critical decision states for resource-efficient exploration. Our key insight is to activate adaptive branching exploration at critical decision points to probe promising trajectories, thereby achieving precise resource allocation that prioritizes sampling quality over blind coverage. This design leverages the agent's intrinsic decision-making signals to reduce dependence on human priors, enabling the agent to autonomously expand exploration and achieve stronger generalization. Experiments across diverse tasks (e.g., embodied planning), demonstrate that \textsc{Spark} achieves superior success rates with significantly fewer training samples, exhibiting robust generalization even in unseen scenarios.
HyperVL: An Efficient and Dynamic Multimodal Large Language Model for Edge Devices
Dec 16, 2025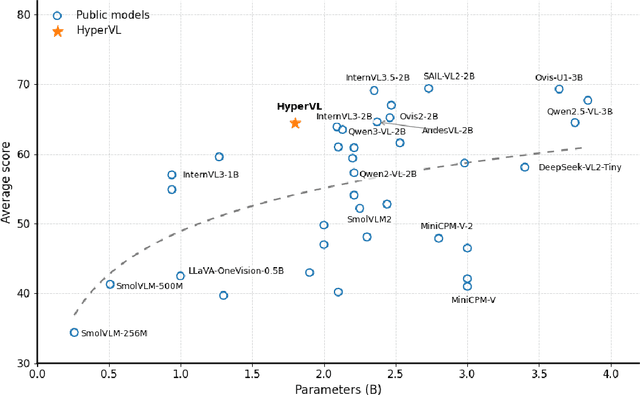

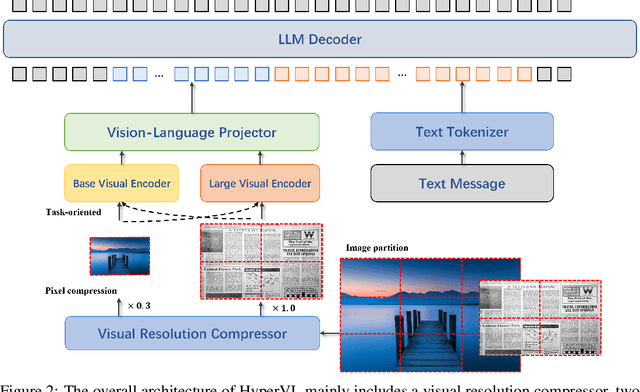
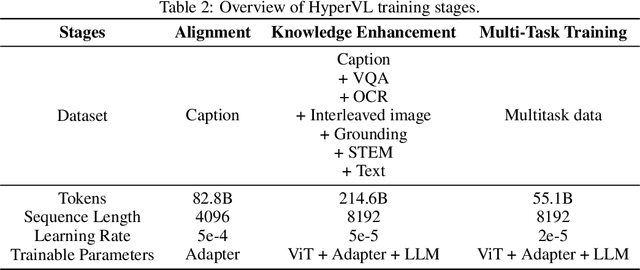
Abstract:Current multimodal large lanauge models possess strong perceptual and reasoning capabilities, however high computational and memory requirements make them difficult to deploy directly on on-device environments. While small-parameter models are progressively endowed with strong general capabilities, standard Vision Transformer (ViT) encoders remain a critical bottleneck, suffering from excessive latency and memory consumption when processing high-resolution inputs.To address these challenges, we introduce HyperVL, an efficient multimodal large language model tailored for on-device inference. HyperVL adopts an image-tiling strategy to cap peak memory usage and incorporates two novel techniques: (1) a Visual Resolution Compressor (VRC) that adaptively predicts optimal encoding resolutions to eliminate redundant computation, and (2) Dual Consistency Learning (DCL), which aligns multi-scale ViT encoders within a unified framework, enabling dynamic switching between visual branches under a shared LLM. Extensive experiments demonstrate that HyperVL achieves state-of-the-art performance among models of comparable size across multiple benchmarks. Furthermore, it significantly significantly reduces latency and power consumption on real mobile devices, demonstrating its practicality for on-device multimodal inference.
Human Motion Video Generation: A Survey
Sep 04, 2025Abstract:Human motion video generation has garnered significant research interest due to its broad applications, enabling innovations such as photorealistic singing heads or dynamic avatars that seamlessly dance to music. However, existing surveys in this field focus on individual methods, lacking a comprehensive overview of the entire generative process. This paper addresses this gap by providing an in-depth survey of human motion video generation, encompassing over ten sub-tasks, and detailing the five key phases of the generation process: input, motion planning, motion video generation, refinement, and output. Notably, this is the first survey that discusses the potential of large language models in enhancing human motion video generation. Our survey reviews the latest developments and technological trends in human motion video generation across three primary modalities: vision, text, and audio. By covering over two hundred papers, we offer a thorough overview of the field and highlight milestone works that have driven significant technological breakthroughs. Our goal for this survey is to unveil the prospects of human motion video generation and serve as a valuable resource for advancing the comprehensive applications of digital humans. A complete list of the models examined in this survey is available in Our Repository https://github.com/Winn1y/Awesome-Human-Motion-Video-Generation.
* Accepted by TPAMI. Github Repo: https://github.com/Winn1y/Awesome-Human-Motion-Video-Generation IEEE Access: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/11106267
Block-wise LoRA: Revisiting Fine-grained LoRA for Effective Personalization and Stylization in Text-to-Image Generation
Mar 12, 2024



Abstract:The objective of personalization and stylization in text-to-image is to instruct a pre-trained diffusion model to analyze new concepts introduced by users and incorporate them into expected styles. Recently, parameter-efficient fine-tuning (PEFT) approaches have been widely adopted to address this task and have greatly propelled the development of this field. Despite their popularity, existing efficient fine-tuning methods still struggle to achieve effective personalization and stylization in T2I generation. To address this issue, we propose block-wise Low-Rank Adaptation (LoRA) to perform fine-grained fine-tuning for different blocks of SD, which can generate images faithful to input prompts and target identity and also with desired style. Extensive experiments demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed method.
DisControlFace: Disentangled Control for Personalized Facial Image Editing
Dec 11, 2023



Abstract:In this work, we focus on exploring explicit fine-grained control of generative facial image editing, all while generating faithful and consistent personalized facial appearances. We identify the key challenge of this task as the exploration of disentangled conditional control in the generation process, and accordingly propose a novel diffusion-based framework, named DisControlFace, comprising two decoupled components. Specifically, we leverage an off-the-shelf diffusion reconstruction model as the backbone and freeze its pre-trained weights, which helps to reduce identity shift and recover editing-unrelated details of the input image. Furthermore, we construct a parallel control network that is compatible with the reconstruction backbone to generate spatial control conditions based on estimated explicit face parameters. Finally, we further reformulate the training pipeline into a masked-autoencoding form to effectively achieve disentangled training of our DisControlFace. Our DisControlNet can perform robust editing on any facial image through training on large-scale 2D in-the-wild portraits and also supports low-cost fine-tuning with few additional images to further learn diverse personalized priors of a specific person. Extensive experiments demonstrate that DisControlFace can generate realistic facial images corresponding to various face control conditions, while significantly improving the preservation of the personalized facial details.
The RoboDepth Challenge: Methods and Advancements Towards Robust Depth Estimation
Jul 27, 2023



Abstract:Accurate depth estimation under out-of-distribution (OoD) scenarios, such as adverse weather conditions, sensor failure, and noise contamination, is desirable for safety-critical applications. Existing depth estimation systems, however, suffer inevitably from real-world corruptions and perturbations and are struggled to provide reliable depth predictions under such cases. In this paper, we summarize the winning solutions from the RoboDepth Challenge -- an academic competition designed to facilitate and advance robust OoD depth estimation. This challenge was developed based on the newly established KITTI-C and NYUDepth2-C benchmarks. We hosted two stand-alone tracks, with an emphasis on robust self-supervised and robust fully-supervised depth estimation, respectively. Out of more than two hundred participants, nine unique and top-performing solutions have appeared, with novel designs ranging from the following aspects: spatial- and frequency-domain augmentations, masked image modeling, image restoration and super-resolution, adversarial training, diffusion-based noise suppression, vision-language pre-training, learned model ensembling, and hierarchical feature enhancement. Extensive experimental analyses along with insightful observations are drawn to better understand the rationale behind each design. We hope this challenge could lay a solid foundation for future research on robust and reliable depth estimation and beyond. The datasets, competition toolkit, workshop recordings, and source code from the winning teams are publicly available on the challenge website.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge