Catherine Lord
End-to-End Joint ASR and Speaker Role Diarization with Child-Adult Interactions
Jan 25, 2026Abstract:Accurate transcription and speaker diarization of child-adult spoken interactions are crucial for developmental and clinical research. However, manual annotation is time-consuming and challenging to scale. Existing automated systems typically rely on cascaded speaker diarization and speech recognition pipelines, which can lead to error propagation. This paper presents a unified end-to-end framework that extends the Whisper encoder-decoder architecture to jointly model ASR and child-adult speaker role diarization. The proposed approach integrates: (i) a serialized output training scheme that emits speaker tags and start/end timestamps, (ii) a lightweight frame-level diarization head that enhances speaker-discriminative encoder representations, (iii) diarization-guided silence suppression for improved temporal precision, and (iv) a state-machine-based forced decoding procedure that guarantees structurally valid outputs. Comprehensive evaluations on two datasets demonstrate consistent and substantial improvements over two cascaded baselines, achieving lower multi-talker word error rates and demonstrating competitive diarization accuracy across both Whisper-small and Whisper-large models. These findings highlight the effectiveness and practical utility of the proposed joint modeling framework for generating reliable, speaker-attributed transcripts of child-adult interactions at scale. The code and model weights are publicly available
Large Language Models based ASR Error Correction for Child Conversations
May 22, 2025Abstract:Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR) has recently shown remarkable progress, but accurately transcribing children's speech remains a significant challenge. Recent developments in Large Language Models (LLMs) have shown promise in improving ASR transcriptions. However, their applications in child speech including conversational scenarios are underexplored. In this study, we explore the use of LLMs in correcting ASR errors for conversational child speech. We demonstrate the promises and challenges of LLMs through experiments on two children's conversational speech datasets with both zero-shot and fine-tuned ASR outputs. We find that while LLMs are helpful in correcting zero-shot ASR outputs and fine-tuned CTC-based ASR outputs, it remains challenging for LLMs to improve ASR performance when incorporating contextual information or when using fine-tuned autoregressive ASR (e.g., Whisper) outputs.
Can Generic LLMs Help Analyze Child-adult Interactions Involving Children with Autism in Clinical Observation?
Nov 16, 2024Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have shown significant potential in understanding human communication and interaction. However, their performance in the domain of child-inclusive interactions, including in clinical settings, remains less explored. In this work, we evaluate generic LLMs' ability to analyze child-adult dyadic interactions in a clinically relevant context involving children with ASD. Specifically, we explore LLMs in performing four tasks: classifying child-adult utterances, predicting engaged activities, recognizing language skills and understanding traits that are clinically relevant. Our evaluation shows that generic LLMs are highly capable of analyzing long and complex conversations in clinical observation sessions, often surpassing the performance of non-expert human evaluators. The results show their potential to segment interactions of interest, assist in language skills evaluation, identify engaged activities, and offer clinical-relevant context for assessments.
Evaluation of state-of-the-art ASR Models in Child-Adult Interactions
Sep 24, 2024



Abstract:The ability to reliably transcribe child-adult conversations in a clinical setting is valuable for diagnosis and understanding of numerous developmental disorders such as Autism Spectrum Disorder. Recent advances in deep learning architectures and availability of large scale transcribed data has led to development of speech foundation models that have shown dramatic improvements in ASR performance. However, the ability of these models to translate well to conversational child-adult interactions is under studied. In this work, we provide a comprehensive evaluation of ASR performance on a dataset containing child-adult interactions from autism diagnostic sessions, using Whisper, Wav2Vec2, HuBERT, and WavLM. We find that speech foundation models show a noticeable performance drop (15-20% absolute WER) for child speech compared to adult speech in the conversational setting. Then, we employ LoRA on the best performing zero shot model (whisper-large) to probe the effectiveness of fine-tuning in a low resource setting, resulting in ~8% absolute WER improvement for child speech and ~13% absolute WER improvement for adult speech.
Data Efficient Child-Adult Speaker Diarization with Simulated Conversations
Sep 13, 2024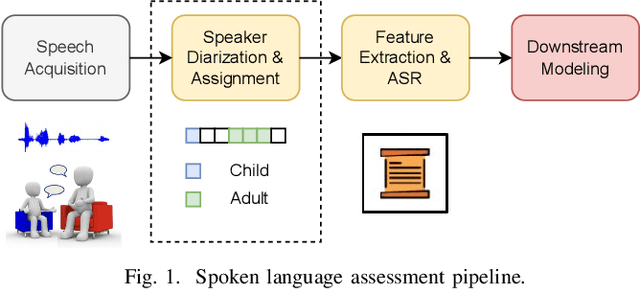
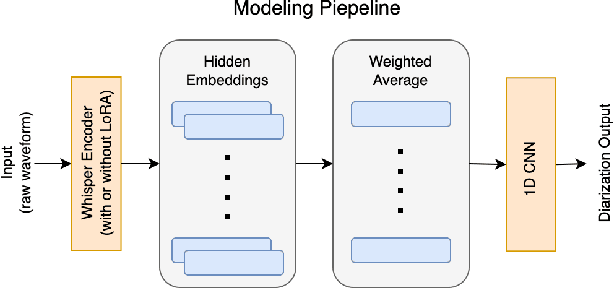

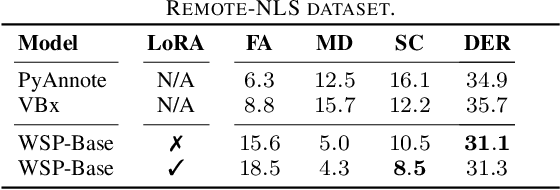
Abstract:Automating child speech analysis is crucial for applications such as neurocognitive assessments. Speaker diarization, which identifies ``who spoke when'', is an essential component of the automated analysis. However, publicly available child-adult speaker diarization solutions are scarce due to privacy concerns and a lack of annotated datasets, while manually annotating data for each scenario is both time-consuming and costly. To overcome these challenges, we propose a data-efficient solution by creating simulated child-adult conversations using AudioSet. We then train a Whisper Encoder-based model, achieving strong zero-shot performance on child-adult speaker diarization using real datasets. The model performance improves substantially when fine-tuned with only 30 minutes of real train data, with LoRA further improving the transfer learning performance. The source code and the child-adult speaker diarization model trained on simulated conversations are publicly available.
Robust Self Supervised Speech Embeddings for Child-Adult Classification in Interactions involving Children with Autism
Jul 31, 2023Abstract:We address the problem of detecting who spoke when in child-inclusive spoken interactions i.e., automatic child-adult speaker classification. Interactions involving children are richly heterogeneous due to developmental differences. The presence of neurodiversity e.g., due to Autism, contributes additional variability. We investigate the impact of additional pre-training with more unlabelled child speech on the child-adult classification performance. We pre-train our model with child-inclusive interactions, following two recent self-supervision algorithms, Wav2vec 2.0 and WavLM, with a contrastive loss objective. We report 9 - 13% relative improvement over the state-of-the-art baseline with regards to classification F1 scores on two clinical interaction datasets involving children with Autism. We also analyze the impact of pre-training under different conditions by evaluating our model on interactions involving different subgroups of children based on various demographic factors.
A Context-Aware Computational Approach for Measuring Vocal Entrainment in Dyadic Conversations
Nov 07, 2022



Abstract:Vocal entrainment is a social adaptation mechanism in human interaction, knowledge of which can offer useful insights to an individual's cognitive-behavioral characteristics. We propose a context-aware approach for measuring vocal entrainment in dyadic conversations. We use conformers(a combination of convolutional network and transformer) for capturing both short-term and long-term conversational context to model entrainment patterns in interactions across different domains. Specifically we use cross-subject attention layers to learn intra- as well as inter-personal signals from dyadic conversations. We first validate the proposed method based on classification experiments to distinguish between real(consistent) and fake(inconsistent/shuffled) conversations. Experimental results on interactions involving individuals with Autism Spectrum Disorder also show evidence of a statistically-significant association between the introduced entrainment measure and clinical scores relevant to symptoms, including across gender and age groups.
Phone Duration Modeling for Speaker Age Estimation in Children
Sep 03, 2021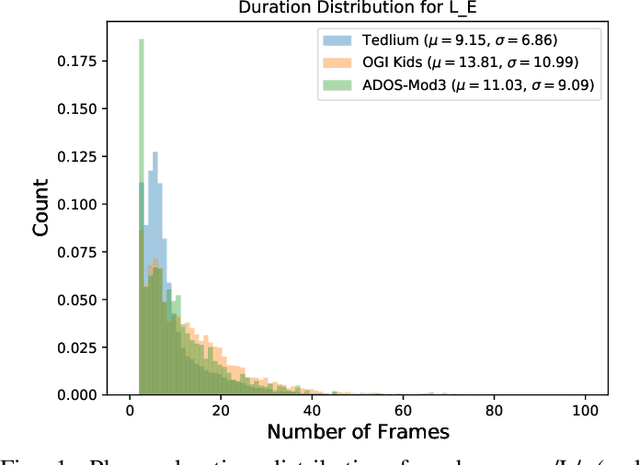
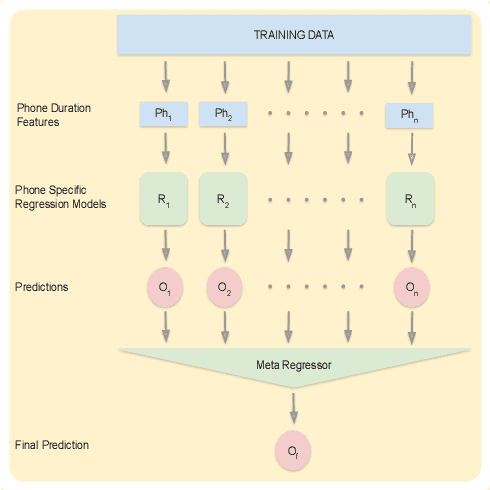
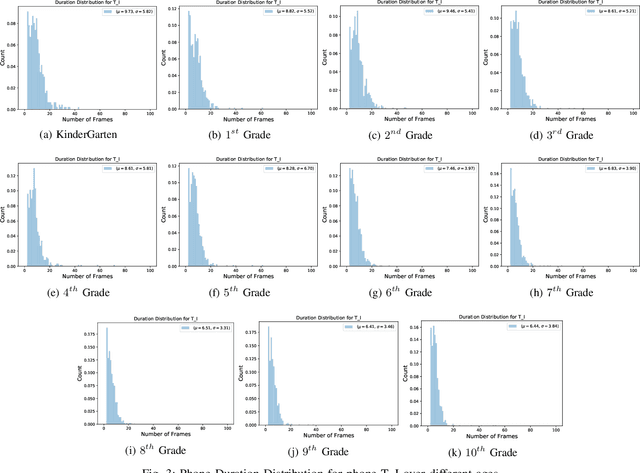
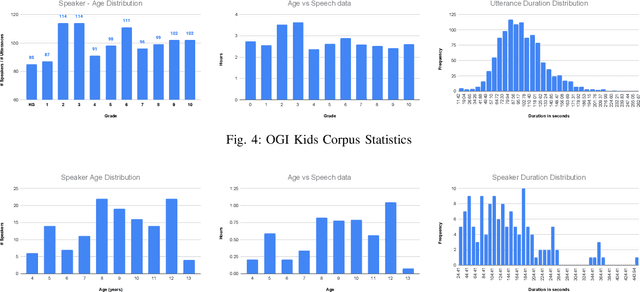
Abstract:Automatic inference of important paralinguistic information such as age from speech is an important area of research with numerous spoken language technology based applications. Speaker age estimation has applications in enabling personalization and age-appropriate curation of information and content. However, research in speaker age estimation in children is especially challenging due to paucity of relevant speech data representing the developmental spectrum, and the high signal variability especially intra age variability that complicates modeling. Most approaches in children speaker age estimation adopt methods directly from research on adult speech processing. In this paper, we propose features specific to children and focus on speaker's phone duration as an important biomarker of children's age. We propose phone duration modeling for predicting age from child's speech. To enable that, children speech is first forced aligned with the corresponding transcription to derive phone duration distributions. Statistical functionals are computed from phone duration distributions for each phoneme which are in turn used to train regression models to predict speaker age. Two children speech datasets are employed to demonstrate the robustness of phone duration features. We perform age regression experiments on age categories ranging from children studying in kindergarten to grade 10. Experimental results suggest phone durations contain important development-related information of children. Phonemes contributing most to estimation of children speaker age are analyzed and presented.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge