Camilo Jaimes
USFetal: Tools for Fetal Brain Ultrasound Compounding
Jan 11, 2026Abstract:Ultrasound offers a safe, cost-effective, and widely accessible technology for fetal brain imaging, making it especially suitable for routine clinical use. However, it suffers from view-dependent artifacts, operator variability, and a limited field of view, which make interpretation and quantitative evaluation challenging. Ultrasound compounding aims to overcome these limitations by integrating complementary information from multiple 3D acquisitions into a single, coherent volumetric representation. This work provides four main contributions: (1) We present the first systematic categorization of computational strategies for fetal brain ultrasound compounding, including both classical techniques and modern learning-based frameworks. (2) We implement and compare representative methods across four key categories - multi-scale, transformation-based, variational, and deep learning approaches - emphasizing their core principles and practical advantages. (3) Motivated by the lack of full-view, artifact-free ground truth required for supervised learning, we focus on unsupervised and self-supervised strategies and introduce two new deep learning based approaches: a self-supervised compounding framework and an adaptation of unsupervised deep plug-and-play priors for compounding. (4) We conduct a comprehensive evaluation on ten multi-view fetal brain ultrasound datasets, using both expert radiologist scoring and standard quantitative image-quality metrics. We also release the USFetal Compounding Toolbox, publicly available to support benchmarking and future research. Keywords: Ultrasound compounding, fetal brain, deep learning, self-supervised, unsupervised.
Search Wide, Focus Deep: Automated Fetal Brain Extraction with Sparse Training Data
Oct 29, 2024



Abstract:Automated fetal brain extraction from full-uterus MRI is a challenging task due to variable head sizes, orientations, complex anatomy, and prevalent artifacts. While deep-learning (DL) models trained on synthetic images have been successful in adult brain extraction, adapting these networks for fetal MRI is difficult due to the sparsity of labeled data, leading to increased false-positive predictions. To address this challenge, we propose a test-time strategy that reduces false positives in networks trained on sparse, synthetic labels. The approach uses a breadth-fine search (BFS) to identify a subvolume likely to contain the fetal brain, followed by a deep-focused sliding window (DFS) search to refine the extraction, pooling predictions to minimize false positives. We train models at different window sizes using synthetic images derived from a small number of fetal brain label maps, augmented with random geometric shapes. Each model is trained on diverse head positions and scales, including cases with partial or no brain tissue. Our framework matches state-of-the-art brain extraction methods on clinical HASTE scans of third-trimester fetuses and exceeds them by up to 5\% in terms of Dice in the second trimester as well as EPI scans across both trimesters. Our results demonstrate the utility of a sliding-window approach and combining predictions from several models trained on synthetic images, for improving brain-extraction accuracy by progressively refining regions of interest and minimizing the risk of missing brain mask slices or misidentifying other tissues as brain.
Anatomically Constrained Tractography of the Fetal Brain
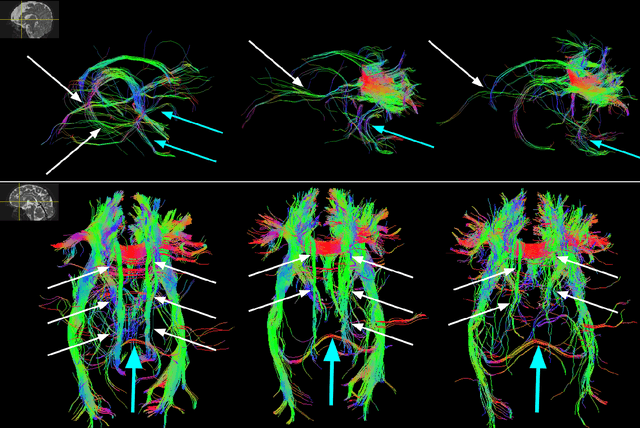
Mar 04, 2024Abstract:Diffusion-weighted Magnetic Resonance Imaging (dMRI) is increasingly used to study the fetal brain in utero. An important computation enabled by dMRI is streamline tractography, which has unique applications such as tract-specific analysis of the brain white matter and structural connectivity assessment. However, due to the low fetal dMRI data quality and the challenging nature of tractography, existing methods tend to produce highly inaccurate results. They generate many false streamlines while failing to reconstruct streamlines that constitute the major white matter tracts. In this paper, we advocate for anatomically constrained tractography based on an accurate segmentation of the fetal brain tissue directly in the dMRI space. We develop a deep learning method to compute the segmentation automatically. Experiments on independent test data show that this method can accurately segment the fetal brain tissue and drastically improve tractography results. It enables the reconstruction of highly curved tracts such as optic radiations. Importantly, our method infers the tissue segmentation and streamline propagation direction from a diffusion tensor fit to the dMRI data, making it applicable to routine fetal dMRI scans. The proposed method can lead to significant improvements in the accuracy and reproducibility of quantitative assessment of the fetal brain with dMRI.
Zero-DeepSub: Zero-Shot Deep Subspace Reconstruction for Rapid Multiparametric Quantitative MRI Using 3D-QALAS
Jul 04, 2023Abstract:Purpose: To develop and evaluate methods for 1) reconstructing 3D-quantification using an interleaved Look-Locker acquisition sequence with T2 preparation pulse (3D-QALAS) time-series images using a low-rank subspace method, which enables accurate and rapid T1 and T2 mapping, and 2) improving the fidelity of subspace QALAS by combining scan-specific deep-learning-based reconstruction and subspace modeling. Methods: A low-rank subspace method for 3D-QALAS (i.e., subspace QALAS) and zero-shot deep-learning subspace method (i.e., Zero-DeepSub) were proposed for rapid and high fidelity T1 and T2 mapping and time-resolved imaging using 3D-QALAS. Using an ISMRM/NIST system phantom, the accuracy of the T1 and T2 maps estimated using the proposed methods was evaluated by comparing them with reference techniques. The reconstruction performance of the proposed subspace QALAS using Zero-DeepSub was evaluated in vivo and compared with conventional QALAS at high reduction factors of up to 9-fold. Results: Phantom experiments showed that subspace QALAS had good linearity with respect to the reference methods while reducing biases compared to conventional QALAS, especially for T2 maps. Moreover, in vivo results demonstrated that subspace QALAS had better g-factor maps and could reduce voxel blurring, noise, and artifacts compared to conventional QALAS and showed robust performance at up to 9-fold acceleration with Zero-DeepSub, which enabled whole-brain T1, T2, and PD mapping at 1 mm isotropic resolution within 2 min of scan time. Conclusion: The proposed subspace QALAS along with Zero-DeepSub enabled high fidelity and rapid whole-brain multiparametric quantification and time-resolved imaging.
A machine learning-based method for estimating the number and orientations of major fascicles in diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging
Jun 19, 2020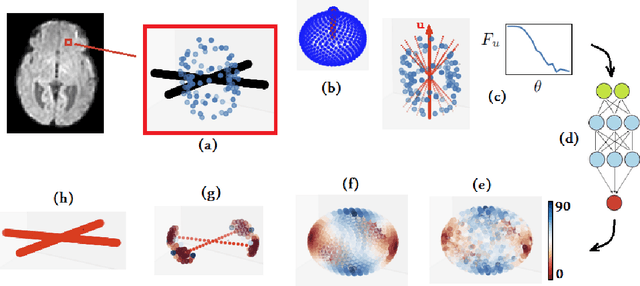
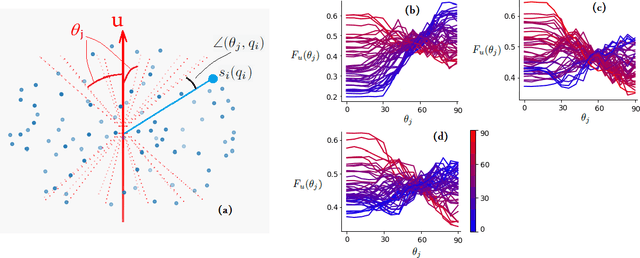

Abstract:Multi-compartment modeling of diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging measurements is necessary for accurate brain connectivity analysis. Existing methods for estimating the number and orientations of fascicles in an imaging voxel either depend on non-convex optimization techniques that are sensitive to initialization and measurement noise, or are prone to predicting spurious fascicles. In this paper, we propose a machine learning-based technique that can accurately estimate the number and orientations of fascicles in a voxel. Our method can be trained with either simulated or real diffusion-weighted imaging data. Our method estimates the angle to the closest fascicle for each direction in a set of discrete directions uniformly spread on the unit sphere. This information is then processed to extract the number and orientations of fascicles in a voxel. On realistic simulated phantom data with known ground truth, our method predicts the number and orientations of crossing fascicles more accurately than several existing methods. It also leads to more accurate tractography. On real data, our method is better than or compares favorably with standard methods in terms of robustness to measurement down-sampling and also in terms of expert quality assessment of tractography results.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge